Intro
Discover Low Blood Pressure Symptoms, including dizziness, fainting, and fatigue. Learn about hypotension causes, treatment, and management to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
Low blood pressure, also known as hypotension, is a condition where the blood pressure in the arteries is lower than normal. This can cause a range of symptoms, from mild to severe, and can be a sign of an underlying health issue. In this article, we will explore the importance of understanding low blood pressure symptoms and how they can impact daily life.
Low blood pressure can be a concern for people of all ages, and it is essential to recognize the symptoms to seek medical attention if necessary. Some people may experience low blood pressure without any symptoms, while others may feel unwell and need to take steps to manage their condition. The good news is that low blood pressure can often be treated with lifestyle changes, medication, or a combination of both.
Understanding low blood pressure symptoms is crucial, as they can be a sign of an underlying health issue. For example, low blood pressure can be a symptom of dehydration, blood loss, or a severe infection. In some cases, low blood pressure can be a side effect of certain medications or a sign of an underlying medical condition, such as diabetes or heart disease. By recognizing the symptoms of low blood pressure, individuals can take steps to manage their condition and prevent complications.
What are the Symptoms of Low Blood Pressure?
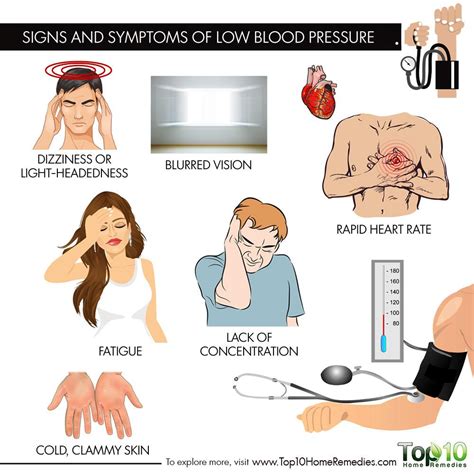
Types of Low Blood Pressure
There are several types of low blood pressure, each with its own set of symptoms and causes. Orthostatic hypotension, for example, is a type of low blood pressure that occurs when standing up from a sitting or lying down position. This can cause dizziness, lightheadedness, and fainting, and is often a concern for older adults. Postprandial hypotension, on the other hand, is a type of low blood pressure that occurs after eating, and can cause symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, and vomiting.Causes of Low Blood Pressure
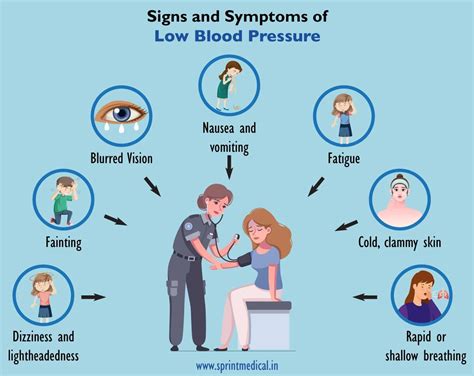
Risk Factors for Low Blood Pressure
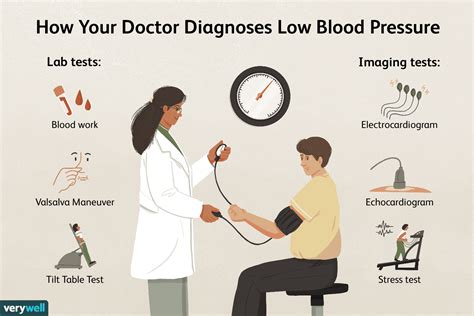
Certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing low blood pressure. These may include age, as older adults are more likely to experience low blood pressure due to age-related changes in the body. Pregnancy, dehydration, and certain medical conditions, such as diabetes and heart disease, can also increase the risk of low blood pressure. Additionally, taking certain medications, such as diuretics and beta blockers, can increase the risk of low blood pressure as a side effect.Diagnosing Low Blood Pressure
Treatment Options for Low Blood Pressure
Treatment options for low blood pressure depend on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms. Lifestyle changes, such as increasing salt intake, drinking more water, and avoiding standing for long periods, can help manage mild cases of low blood pressure. Medications, such as fludrocortisone and midodrine, may be prescribed to increase blood pressure in more severe cases. In some cases, hospitalization may be necessary to treat underlying medical conditions and prevent complications.Managing Low Blood Pressure

Preventing Low Blood Pressure
Preventing low blood pressure requires a healthy lifestyle and regular monitoring. Staying hydrated, eating a balanced diet, and avoiding certain medications can help prevent low blood pressure. Regular exercise, such as walking and yoga, can also help improve circulation and increase blood pressure. Additionally, managing underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes and heart disease, can help prevent low blood pressure.Complications of Low Blood Pressure

Living with Low Blood Pressure
Living with low blood pressure requires a combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and regular monitoring. By understanding the symptoms and causes of low blood pressure, individuals can take steps to manage their condition and prevent complications. Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and avoiding certain medications can help manage low blood pressure and improve overall health.Conclusion and Next Steps

What are the symptoms of low blood pressure?
+The symptoms of low blood pressure can vary from person to person, but common symptoms include dizziness, lightheadedness, and fainting. Other symptoms may include fatigue, weakness, and a lack of energy.
What causes low blood pressure?
+The causes of low blood pressure can be varied, and may include dehydration, blood loss, and severe infections. Certain medications, such as diuretics and beta blockers, can also cause low blood pressure as a side effect.
How is low blood pressure diagnosed?
+Diagnosing low blood pressure typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and blood pressure readings. A healthcare provider may also order additional tests, such as blood tests and electrocardiograms, to rule out underlying medical conditions.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of low blood pressure symptoms, causes, and treatment options. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others. By working together, we can raise awareness and promote education about low blood pressure and its management.
