Intro
Discover how low body temperature impacts your health, from fatigue to brain fog, and learn 7 ways it affects you, including metabolism, immune function, and overall well-being, with related symptoms like hypothyroidism and cold intolerance.
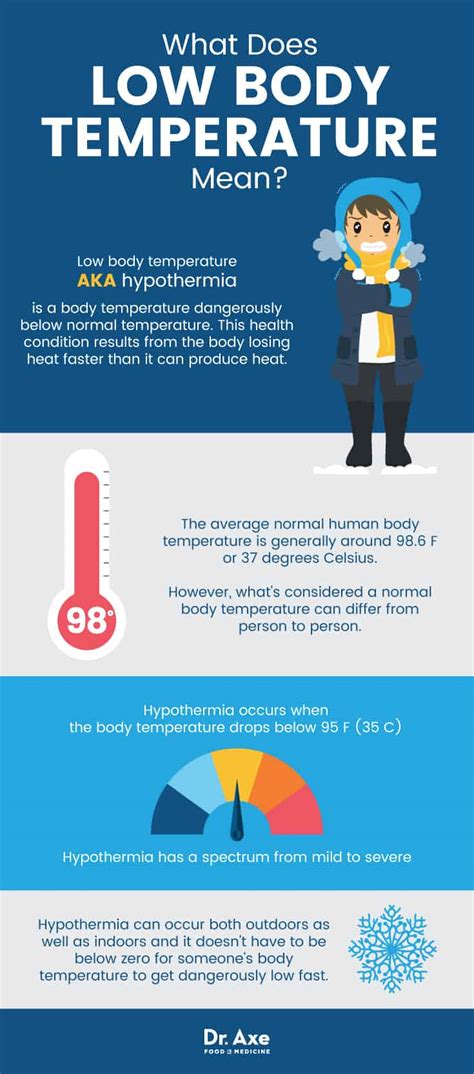
Low body temperature, also known as hypothermia, is a condition where the body loses heat, causing the body temperature to drop below 95°F (35°C). This can be caused by various factors such as exposure to cold environments, certain medical conditions, or the use of certain medications. Having a low body temperature can have significant effects on the body, and it's essential to understand these effects to take necessary precautions and seek medical attention if needed.
The human body is designed to function optimally at a temperature of around 98.6°F (37°C). When the body temperature drops, it can disrupt various bodily functions, leading to a range of symptoms and health issues. From mild symptoms like shivering and confusion to life-threatening conditions like organ failure, the effects of low body temperature can be severe. In this article, we'll explore the various ways low body temperature can affect the body and what can be done to prevent and treat hypothermia.
Low body temperature can affect anyone, regardless of age or health status. However, certain individuals are more susceptible to hypothermia, such as older adults, young children, and people with certain medical conditions. It's crucial to recognize the signs and symptoms of hypothermia and take prompt action to prevent further heat loss and promote warming. With proper understanding and care, it's possible to manage and overcome the effects of low body temperature, ensuring optimal health and well-being.
Introduction to Low Body Temperature
Causes of Low Body Temperature
The causes of low body temperature can be broadly categorized into environmental, medical, and lifestyle-related factors. Environmental factors include exposure to cold temperatures, such as spending time outdoors in cold weather without proper clothing or shelter. Medical conditions like hypothyroidism, diabetes, and certain neurological disorders can also increase the risk of hypothermia. Lifestyle-related factors, such as substance abuse, poor nutrition, and certain medications, can also contribute to low body temperature.Effects of Low Body Temperature on the Body

Physiological Effects of Hypothermia
The physiological effects of hypothermia can be profound, affecting various bodily systems and functions. The cardiovascular system is particularly affected, with slowed heart rate and reduced blood pressure leading to decreased blood flow and oxygen delivery to tissues. The nervous system is also impacted, with impaired cognitive function, confusion, and disorientation. In severe cases, hypothermia can lead to organ failure, including cardiac arrest, respiratory failure, and kidney failure.Treatment and Prevention of Low Body Temperature

Medical Treatment of Hypothermia
Medical treatment of hypothermia depends on the severity of the condition and may involve a range of interventions, including medication, oxygen therapy, and cardiac monitoring. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to provide close monitoring and supportive care. Medications like vasopressors and inotropes may be used to support blood pressure and cardiac function, while oxygen therapy can help increase oxygen delivery to tissues. Cardiac monitoring is essential to detect any cardiac arrhythmias or other complications.Nutritional and Lifestyle Factors in Low Body Temperature

Importance of Nutrition in Hypothermia Prevention
Nutrition plays a critical role in preventing hypothermia, as a balanced diet can help support immune function and overall health. Foods rich in vitamin D, such as fatty fish and fortified dairy products, can help regulate body temperature and prevent hypothermia. Iron-rich foods, such as red meat and leafy greens, can also help support immune function and reduce the risk of infections. Aiming for a balanced diet that includes a variety of whole foods can help promote overall health and reduce the risk of hypothermia.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

Final Thoughts on Low Body Temperature
In final thoughts, low body temperature is a serious medical condition that requires prompt attention and treatment. By understanding the causes, effects, and treatment options for hypothermia, individuals can take steps to prevent and manage this condition. Whether through simple lifestyle changes or medical interventions, promoting optimal body temperature is essential for overall health and well-being. By working together to raise awareness and promote education on hypothermia, we can reduce the risk of this condition and promote a healthier, more resilient community.What is low body temperature?
+Low body temperature, also known as hypothermia, is a medical condition where the body's temperature regulation system is disrupted, causing the body temperature to drop below normal levels.
What are the causes of low body temperature?
+The causes of low body temperature can be broadly categorized into environmental, medical, and lifestyle-related factors, including exposure to cold temperatures, certain medical conditions, and substance abuse.
How can low body temperature be treated and prevented?
+Treatment and prevention of low body temperature involve a range of strategies, from simple measures like warm clothing and shelter to medical interventions like medication and hospitalization. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of hypothermia and seeking prompt medical attention if necessary can help prevent long-term damage and promote recovery.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of low body temperature and its effects on the body. If you have any further questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to reach out. Share this article with friends and family to help raise awareness about the importance of body temperature regulation and the risks of hypothermia. Together, we can promote optimal health and well-being by taking simple precautions and seeking medical attention when necessary.
