Intro
Discover key facts about Pantoprazole, a proton pump inhibitor, including its uses, side effects, and interactions, to manage acid reflux and stomach ulcers effectively.
Pantoprazole, a medication known for its effectiveness in treating various gastrointestinal issues, has been a topic of interest for many individuals seeking relief from conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and peptic ulcers. The importance of understanding this drug cannot be overstated, given its widespread use and the potential for significant impact on patients' quality of life. As we delve into the world of pantoprazole, it becomes clear that there is more to this medication than meets the eye, with a complex mechanism of action and a range of benefits and potential side effects that are essential to comprehend.
The use of pantoprazole has become increasingly common, not only due to its efficacy but also because of its relatively favorable safety profile compared to other medications in its class. However, like any drug, it is crucial to approach its use with a thorough understanding of how it works, its potential interactions with other medications, and the precautions that should be taken to minimize adverse effects. This knowledge empowers patients and healthcare providers to make informed decisions about treatment plans, ensuring that the benefits of pantoprazole are maximized while risks are mitigated.
As we explore the realm of pantoprazole, it is evident that there is a wealth of information available, ranging from its chemical composition to patient testimonials about its effectiveness. Navigating this information requires a discerning approach, separating fact from fiction and understanding the nuances of how this medication interacts with the human body. By doing so, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the role that pantoprazole plays in managing gastrointestinal health and make informed choices about their treatment options.
Pantoprazole: An Overview
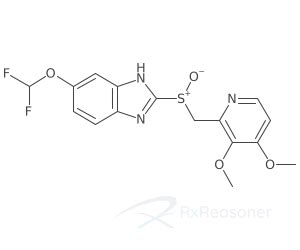
Chemical Structure and Pharmacokinetics
The chemical structure of pantoprazole is characterized by its sulfonyl group and a pyridinylmethyl group, features that contribute to its pharmacological activity. Upon oral administration, pantoprazole is absorbed rapidly, with peak plasma concentrations achieved within approximately one to three hours. It undergoes extensive hepatic metabolism, primarily via the CYP2C19 and CYP3A4 enzymes, resulting in the formation of inactive metabolites that are excreted in the urine and feces.Benefits of Pantoprazole
Treatment of Peptic Ulcers
Pantoprazole is also effective in the treatment of peptic ulcers, including those caused by Helicobacter pylori infection. By reducing gastric acid secretion, it creates an environment conducive to ulcer healing. When used in combination with antibiotics for the eradication of H. pylori, pantoprazole has been shown to increase the success rate of treatment, leading to a higher proportion of patients achieving complete ulcer healing and a reduced risk of ulcer recurrence.Potential Side Effects and Interactions

Drug Interactions
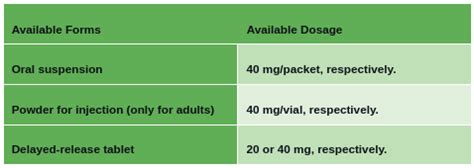
Pantoprazole can interact with other medications, affecting their absorption or metabolism. For example, it can decrease the absorption of drugs like ketoconazole and increase the levels of medications like warfarin and phenytoin by competing for the same metabolic pathways. Therefore, careful consideration of potential drug interactions is necessary when prescribing pantoprazole, especially in patients with complex medication regimens.Dosage and Administration
Patient Education
Patient education plays a vital role in the successful management of gastrointestinal disorders with pantoprazole. Patients should be informed about the proper use of the medication, potential side effects, and the importance of adherence to the prescribed treatment regimen. Additionally, lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes, weight loss, and avoidance of triggers like alcohol and tobacco, can complement the effects of pantoprazole and contribute to improved outcomes.Future Directions and Research

Emerging Trends in Gastrointestinal Health
The landscape of gastrointestinal health is evolving, with emerging trends focusing on personalized medicine, the role of the gut microbiome, and the development of new therapeutic targets. As our understanding of the pathophysiology of gastrointestinal disorders expands, so too will the potential applications of pantoprazole and other PPIs, offering new hope for patients seeking effective and sustainable relief from their symptoms.What is the primary mechanism of action of pantoprazole?
+Pantoprazole works by inhibiting the H+/K+ ATPase (proton pump) in the gastric parietal cells, thereby reducing gastric acid secretion.
What are the common indications for pantoprazole use?
+Pantoprazole is commonly used for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcer disease, and the eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection when used in combination with antibiotics.
Can pantoprazole be used in patients with a history of osteoporosis?
+Patients with a history of osteoporosis should use pantoprazole with caution, as long-term use of proton pump inhibitors has been associated with an increased risk of osteoporosis-related fractures. Regular monitoring of bone health is recommended.
As we conclude our exploration of pantoprazole, it is clear that this medication plays a vital role in the management of gastrointestinal health. By understanding its benefits, potential side effects, and proper use, patients and healthcare providers can work together to maximize its therapeutic potential. We invite readers to share their experiences with pantoprazole, ask questions, and engage in discussions about the latest developments in gastrointestinal health. Your input is invaluable in creating a community that prioritizes informed decision-making and comprehensive care.
