Intro
Understand low carbon dioxide blood test results, causes of low CO2 levels, and related symptoms like respiratory alkalosis, metabolic acidosis, and hyperventilation, to manage hypocapnia and maintain healthy bicarbonate levels.
Low carbon dioxide blood test results can be a cause for concern for many individuals. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a vital component of the blood, playing a crucial role in maintaining the body's acid-base balance. The level of CO2 in the blood is an essential indicator of various bodily functions, including respiratory and kidney health. When CO2 levels are lower than normal, it can indicate an underlying health issue that requires attention. In this article, we will delve into the significance of low CO2 blood test results, their potential causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
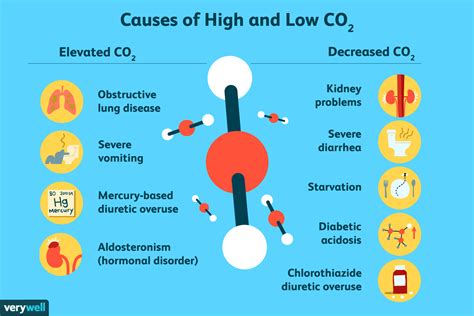
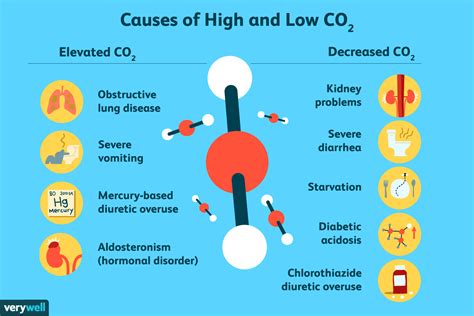
The human body relies on a delicate balance of various substances to function properly. CO2 is one such substance, and its levels in the blood are tightly regulated by the respiratory and renal systems. A low CO2 level, also known as respiratory alkalosis or hypocapnia, can occur when the body loses too much CO2. This can happen due to various reasons, including hyperventilation, where an individual breathes too rapidly or deeply, causing excessive CO2 loss. Other factors, such as certain medications, liver or kidney disease, and salicylate poisoning, can also contribute to low CO2 levels.
Understanding the causes and implications of low CO2 blood test results is essential for developing effective treatment strategies. The symptoms of low CO2 levels can vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include dizziness, lightheadedness, and fainting, as well as numbness or tingling in the hands and feet. In severe cases, low CO2 levels can lead to seizures, coma, or even death. Therefore, it is crucial to seek medical attention if you are experiencing any of these symptoms or have received low CO2 blood test results.
What is a Normal CO2 Level in the Blood?
Causes of Low CO2 Blood Test Results
Symptoms of Low CO2 Levels
The symptoms of low CO2 levels can vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include: * Dizziness or lightheadedness * Fainting or near-fainting * Numbness or tingling in the hands and feet * Muscle cramps or weakness * Seizures or coma (in severe cases)Treatment Options for Low CO2 Blood Test Results
Prevention Strategies
Preventing low CO2 blood test results involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing underlying medical conditions. Some prevention strategies include: * Practicing deep, slow breathing exercises to help regulate CO2 levels * Staying hydrated and maintaining a balanced diet * Managing stress and anxiety through relaxation techniques or therapy * Avoiding excessive aspirin or salicylate-containing medicationsComplications of Low CO2 Blood Test Results
Monitoring and Follow-up
Regular monitoring and follow-up are essential for managing low CO2 blood test results. This may involve: * Regular blood tests to monitor CO2 levels * Adjusting treatment plans as needed * Managing underlying medical conditions * Practicing prevention strategies to prevent future episodesConclusion and Next Steps

What is the normal range for CO2 levels in the blood?
+The normal range for CO2 levels in the blood is typically between 23 and 29 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L).
What are the symptoms of low CO2 levels?
+Common symptoms of low CO2 levels include dizziness, lightheadedness, fainting, numbness or tingling in the hands and feet, and muscle cramps or weakness.
How are low CO2 blood test results treated?
+Treatment for low CO2 blood test results depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition, but may involve breathing exercises, medications, dietary changes, or hospitalization in severe cases.
We hope this article has provided you with valuable insights into low CO2 blood test results. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others who may find it helpful. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and care.
