Intro
Discover the ultimate Low Fiber Diet Guide, featuring gentle foods, digestive health tips, and bowel management strategies to ease symptoms and promote gut wellness with a low-fiber meal plan.
A low fiber diet is often recommended for individuals who have certain medical conditions, such as gastrointestinal disorders, or those who are undergoing colonoscopy procedures. The main goal of a low fiber diet is to minimize the amount of undigested food that reaches the colon, reducing the risk of discomfort, pain, and complications. In this article, we will delve into the world of low fiber diets, exploring their benefits, working mechanisms, and providing practical guidance on how to follow one effectively.
The importance of a low fiber diet cannot be overstated, particularly for individuals who suffer from digestive issues. By reducing the amount of fiber in the diet, individuals can help alleviate symptoms such as bloating, gas, and abdominal pain. Additionally, a low fiber diet can be beneficial for those who are preparing for colonoscopy procedures, as it helps to clear the colon of any debris, making it easier for doctors to detect any abnormalities. With the rise of digestive disorders, it is essential to understand the role of fiber in our diets and how to manage it effectively.
A low fiber diet is not just about cutting out fiber-rich foods; it's about making informed choices about the types of foods we eat. By understanding what foods are high in fiber and which ones are low, individuals can make the necessary adjustments to their diets. For instance, foods that are high in fiber include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, while foods that are low in fiber include meat, poultry, fish, and refined carbohydrates. By being mindful of the foods we eat, we can take control of our digestive health and reduce the risk of complications.
Benefits of a Low Fiber Diet
Working Mechanisms of a Low Fiber Diet
A low fiber diet works by reducing the amount of undigested food that reaches the colon, minimizing the risk of discomfort, pain, and complications. By cutting out high-fiber foods, individuals can help reduce the amount of bulk in the stool, making it easier to pass and reducing the risk of straining. Additionally, a low fiber diet can help reduce the amount of gas produced in the colon, alleviating symptoms of bloating and discomfort.Steps to Follow a Low Fiber Diet
Practical Examples of Low Fiber Foods
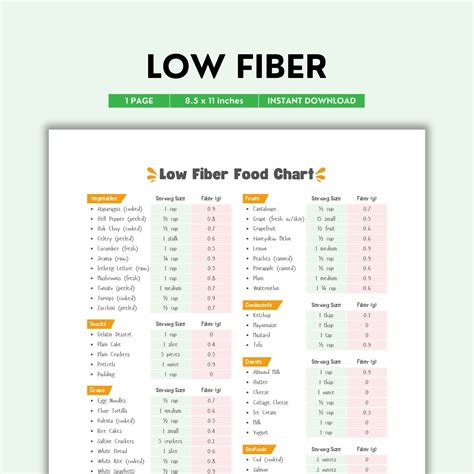
Here are some practical examples of low fiber foods that individuals can include in their diets: * Meat: chicken, beef, pork, lamb * Poultry: chicken, turkey, duck * Fish: cod, salmon, tilapia * Refined carbohydrates: white bread, white rice, pasta * Dairy products: milk, cheese, yogurt * EggsCommon Mistakes to Avoid
Statistical Data and Research
Research has shown that a low fiber diet can be effective in reducing symptoms of digestive disorders and preparing the colon for medical procedures. According to a study published in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology, a low fiber diet was shown to reduce symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) in 75% of participants. Another study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) found that a low fiber diet was effective in reducing the risk of complications during colonoscopy procedures.Conclusion and Next Steps
What is a low fiber diet?
+A low fiber diet is a diet that minimizes the amount of undigested food that reaches the colon, reducing the risk of discomfort, pain, and complications.
What are the benefits of a low fiber diet?
+The benefits of a low fiber diet include reducing symptoms of digestive disorders, preparing the colon for medical procedures, and minimizing the risk of complications.
How do I follow a low fiber diet?
+To follow a low fiber diet, identify high-fiber foods, cut out high-fiber foods, choose low-fiber foods, read food labels, and consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized guidance and support.
