Intro
Discover a comprehensive Low Roughage Foods List, featuring gentle, easy-to-digest options like lean proteins, low-fiber fruits, and soft vegetables, ideal for sensitive stomachs and digestive issues, including IBS and gastroparesis management.
The importance of dietary fiber, also known as roughage, cannot be overstated. It plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy digestive system, promoting regular bowel movements, and supporting healthy blood sugar levels. However, there are instances where individuals may need to limit their intake of high-fiber foods, such as during certain medical procedures or when managing specific health conditions. In such cases, understanding which foods are low in roughage can be beneficial. This article aims to delve into the world of low roughage foods, exploring their benefits, types, and how they can be incorporated into a balanced diet.
For individuals who require a low-fiber diet, it's essential to know which foods to choose and which to avoid. A low roughage diet is often recommended for people undergoing colonoscopy preparation, those with certain gastrointestinal disorders like inflammatory bowel disease, or after gastrointestinal surgery. The goal is to reduce the amount of undigested food that reaches the colon, minimizing the risk of complications. However, it's crucial to consult with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian to determine the best dietary approach for individual needs.
The concept of low roughage foods might seem restrictive, but there's a wide variety of delicious and nutritious options available. These foods are not only easy to digest but also provide essential vitamins, minerals, and proteins necessary for overall health. Understanding the nutritional value and preparation methods of these foods can help individuals make informed choices, ensuring they maintain a balanced diet even when limiting their fiber intake. From meats and poultry to dairy products and specific types of fruits and vegetables, the list of low roughage foods is extensive and can cater to diverse tastes and dietary preferences.
Introduction to Low Roughage Foods

Low roughage foods are typically characterized by their low fiber content, making them easier to digest. This category includes a range of food groups, from animal products to certain plant-based foods that have been prepared in ways that reduce their fiber content. It's essential to differentiate between foods that are naturally low in fiber and those that have been processed to reduce their fiber content. Naturally low-fiber foods tend to be less processed and can provide a more nutrient-dense diet compared to heavily processed foods.
Benefits of Low Roughage Foods
The benefits of incorporating low roughage foods into one's diet are multifaceted. For individuals with gastrointestinal issues, these foods can help reduce discomfort and minimize the risk of flare-ups. Additionally, during periods of recovery from gastrointestinal surgeries or procedures, a low-fiber diet can be easier on the digestive system, allowing it to heal more efficiently. It's also worth noting that some low roughage foods are rich in proteins, healthy fats, and essential vitamins and minerals, contributing to overall nutritional well-being.Types of Low Roughage Foods

The variety of low roughage foods is quite extensive, catering to different dietary needs and preferences. Here are some examples:
- Meats and Poultry: Chicken, turkey, fish, and lean meats are naturally low in fiber and can be part of a low roughage diet.
- Dairy Products: Milk, cheese, and yogurt are low in fiber and rich in calcium and proteins.
- Eggs: Another excellent source of protein with minimal fiber content.
- Fruits: Bananas, avocados, and canned fruits are lower in fiber compared to other fruits.
- Vegetables: Cooked vegetables like carrots, green beans, and cucumbers are lower in fiber, especially when cooked until tender.
- Grains: Refined grains such as white bread, white rice, and pasta are lower in fiber compared to whole grains.
Preparing Low Roughage Foods
Preparing low roughage foods can be straightforward, with a focus on cooking methods that reduce fiber content. For example, cooking vegetables until they are very tender can break down some of the fiber, making them easier to digest. Similarly, removing seeds and skins from fruits and vegetables can also reduce their fiber content. It's essential to note that while preparing foods in these ways can make them lower in fiber, it's also important to balance this with the need to maintain nutrient intake.Low Roughage Diet and Nutrition
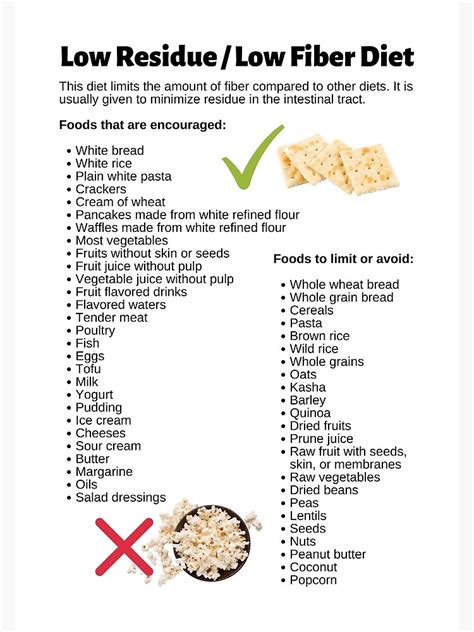
A low roughage diet, when properly planned, can be nutritious and fulfilling. It's crucial to ensure that the diet includes a variety of foods from all food groups to meet nutritional needs. For instance, including lean proteins, healthy fats, and low-fiber fruits and vegetables can provide a balanced mix of nutrients. Additionally, fortified foods and supplements can help fill any nutritional gaps, especially in vitamins and minerals that might be lacking in a low-fiber diet.
Nutritional Considerations
When following a low roughage diet, it's essential to be mindful of nutritional deficiencies. Fiber plays a significant role in satiety and can influence blood sugar levels and cholesterol levels. Therefore, managing portion sizes and choosing nutrient-dense foods are critical. Furthermore, staying hydrated is vital, as a low-fiber diet might lead to constipation if not balanced with adequate fluid intake.Managing a Low Roughage Diet
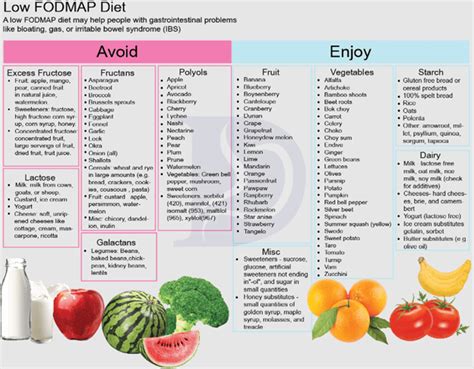
Managing a low roughage diet requires careful planning and attention to nutritional needs. Here are some tips:
- Consult a Professional: Work with a dietitian or healthcare provider to develop a personalized diet plan.
- Keep a Food Diary: Tracking food intake can help identify patterns and ensure that nutritional needs are being met.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water is crucial, especially on a low-fiber diet.
- Gradual Introduction of Foods: When transitioning back to a regular diet, introduce high-fiber foods gradually to allow the digestive system to adjust.
Challenges and Solutions
One of the challenges of a low roughage diet is the potential for nutritional deficiencies and the risk of constipation. To mitigate these risks, it's essential to consume a balanced diet that includes a variety of low-fiber foods and to stay well-hydrated. Additionally, incorporating physical activity can help stimulate bowel movements and improve overall digestive health.Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, a low roughage diet, when necessary and properly managed, can be a valuable tool for individuals with specific health needs. By understanding the types of low roughage foods, their preparation, and how to maintain nutritional balance, individuals can navigate this dietary approach with confidence. As research continues to uncover the complexities of dietary fiber and its impact on health, it's likely that our understanding of low roughage diets will evolve, offering even more tailored advice for those who require them.
Final Thoughts
The journey to understanding and managing a low roughage diet is one that requires patience, dedication, and the right guidance. By embracing the challenges and opportunities presented by this dietary approach, individuals can take significant steps towards improving their health and well-being. Whether as a temporary measure or a long-term dietary adjustment, the knowledge and strategies gained from exploring low roughage foods can contribute to a more informed and healthier relationship with food.What are the primary benefits of a low roughage diet?
+A low roughage diet can help reduce discomfort and minimize the risk of flare-ups in individuals with gastrointestinal issues. It can also be easier on the digestive system during recovery from surgeries or procedures.
How can I ensure I'm getting enough nutrients on a low roughage diet?
+Consulting with a dietitian or healthcare provider can help develop a personalized diet plan that meets nutritional needs. Including a variety of low-fiber foods and considering supplements can also help fill any nutritional gaps.
Are there any risks associated with a long-term low roughage diet?
+Yes, a long-term low roughage diet can lead to nutritional deficiencies, particularly in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. It's essential to work with a healthcare provider to monitor health and adjust the diet as necessary.
We hope this comprehensive guide to low roughage foods has been informative and helpful. Whether you're looking to manage a specific health condition or simply seeking to understand more about dietary fiber and its role in health, the information provided here aims to empower you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about your diet. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with low roughage diets, please don't hesitate to comment below. Your insights can help others navigate their own journeys towards better health and wellness.
