Intro
Discover Low Thyroid Hypothyroidism Symptoms, including fatigue, weight gain, and hair loss, and learn about diagnosis, treatment, and management of underactive thyroid disorders, hypothyroidism diagnosis, and thyroid function.
Hypothyroidism, also known as underactive thyroid, is a condition where the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. These hormones play a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, such as metabolism, growth, and development. When the thyroid gland is underactive, it can lead to a range of symptoms that can affect daily life. In this article, we will delve into the world of hypothyroidism, exploring its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options.
The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck, just below the Adam's apple. It produces two main hormones: triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). These hormones help regulate metabolism, energy production, and growth. When the thyroid gland is underactive, it can lead to a decrease in metabolic rate, energy levels, and overall health. Hypothyroidism is a common condition, affecting millions of people worldwide, and it can affect anyone, regardless of age or sex.
Hypothyroidism can be caused by a range of factors, including autoimmune disorders, thyroid surgery, radiation therapy, and certain medications. In some cases, the exact cause of hypothyroidism may not be known. The symptoms of hypothyroidism can vary from person to person, but common symptoms include fatigue, weight gain, dry skin, hair loss, and cold intolerance. If left untreated, hypothyroidism can lead to more severe complications, such as heart problems, nerve damage, and infertility. Therefore, it is essential to recognize the symptoms of hypothyroidism and seek medical attention if they persist.
Understanding Hypothyroidism

Primary hypothyroidism is the most common type of hypothyroidism, accounting for about 90% of cases. It occurs when the thyroid gland is damaged or diseased, leading to a decrease in thyroid hormone production. Secondary hypothyroidism occurs when the pituitary gland is damaged or diseased, leading to a decrease in thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) production. Tertiary hypothyroidism occurs when the hypothalamus is damaged or diseased, leading to a decrease in thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) production.
Causes of Hypothyroidism

Radiation therapy, such as radioactive iodine therapy, can also lead to hypothyroidism by damaging the thyroid gland. Certain medications, such as lithium and amiodarone, can also cause hypothyroidism as a side effect. In some cases, the exact cause of hypothyroidism may not be known. It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause of hypothyroidism and develop an effective treatment plan.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism

These symptoms can be mild or severe and may develop gradually over time. If left untreated, hypothyroidism can lead to more severe complications, such as heart problems, nerve damage, and infertility. It is essential to recognize the symptoms of hypothyroidism and seek medical attention if they persist.
Diagnosis of Hypothyroidism

Laboratory tests, such as a thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) test and a free thyroxine (FT4) test, may also be ordered to measure thyroid hormone levels. A TSH test measures the level of TSH in the blood, while a FT4 test measures the level of FT4 in the blood. These tests can help determine if the thyroid gland is producing enough thyroid hormones.
Treatment Options for Hypothyroidism
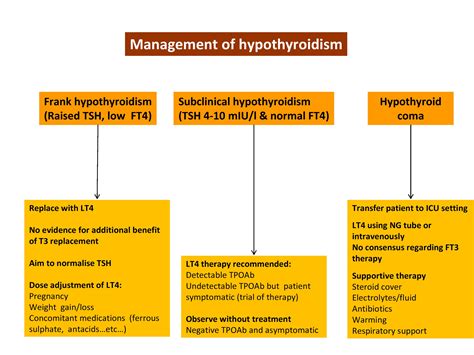
The dosage and type of medication may vary depending on the individual and the severity of hypothyroidism. It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan and to monitor thyroid hormone levels regularly. In addition to medication, lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, can also help manage hypothyroidism and improve overall health.
Managing Hypothyroidism

Stress management techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing, can also help manage stress and anxiety. It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan and to monitor thyroid hormone levels regularly. With the right treatment and lifestyle changes, it is possible to manage hypothyroidism and improve overall health.
Complications of Hypothyroidism
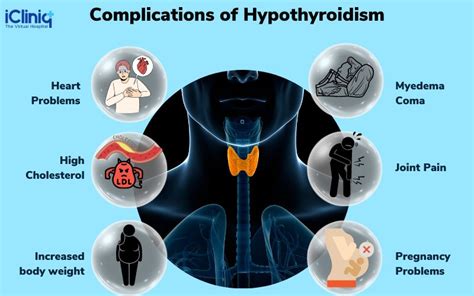
Infertility and miscarriage can also occur in women with untreated hypothyroidism. It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms of hypothyroidism persist, as early treatment can help prevent these complications and improve overall health.
Living with Hypothyroidism
A healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management techniques can also help support thyroid function and overall health. It is also essential to stay informed about hypothyroidism and to connect with others who are living with the condition. With the right support and treatment, it is possible to live a healthy and active life with hypothyroidism.
What are the symptoms of hypothyroidism?
+The symptoms of hypothyroidism can vary from person to person, but common symptoms include fatigue, weight gain, dry skin, hair loss, and cold intolerance.
How is hypothyroidism diagnosed?
+Hypothyroidism is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, such as a thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) test and a free thyroxine (FT4) test.
What are the treatment options for hypothyroidism?
+Treatment for hypothyroidism typically involves thyroid hormone replacement medication, such as levothyroxine (T4), which is converted to triiodothyronine (T3) in the body.
In conclusion, hypothyroidism is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive approach to diagnosis, treatment, and management. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for hypothyroidism, individuals can take control of their health and improve their overall well-being. If you suspect that you or a loved one may be experiencing symptoms of hypothyroidism, it is essential to seek medical attention and work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan. With the right treatment and lifestyle changes, it is possible to manage hypothyroidism and live a healthy and active life. We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with hypothyroidism in the comments below and to reach out to a healthcare provider if you have any questions or concerns.
