Intro
Discover the causes of lowered body temperature, including hypothyroidism, anemia, and poor circulation, and learn about symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for hypothermia and related conditions.
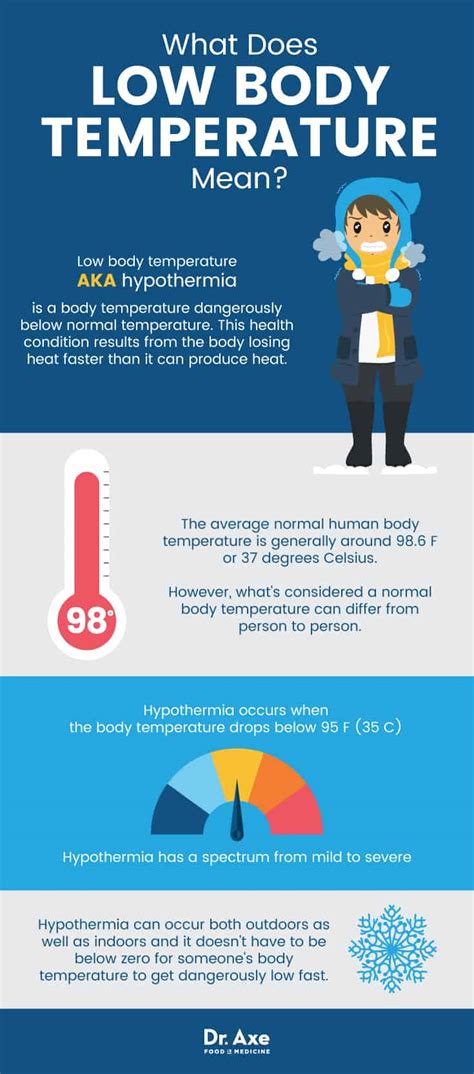
Lowered body temperature, also known as hypothermia, is a medical condition that occurs when the body's core temperature drops below 95°F (35°C). This can happen due to various reasons, including exposure to cold environments, certain medical conditions, or the use of certain medications. Hypothermia can be a life-threatening condition if not treated promptly and properly. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for lowered body temperature.
The human body is designed to maintain a constant internal temperature, regardless of the external environment. However, when the body is exposed to cold temperatures, it can lose heat faster than it can produce it, leading to a drop in core temperature. This can happen in various situations, such as being outside in cold weather without proper clothing, falling into cold water, or being in a cold room without heating. Certain medical conditions, such as hypothyroidism, diabetes, and anemia, can also increase the risk of developing hypothermia.
In addition to these factors, certain medications, such as sedatives and antidepressants, can also contribute to lowered body temperature. These medications can interfere with the body's ability to regulate its temperature, making it more susceptible to hypothermia. Furthermore, older adults and young children are more vulnerable to hypothermia due to their reduced ability to regulate their body temperature.
Causes of Lowered Body Temperature

Environmental Causes
Environmental causes of lowered body temperature include: * Exposure to cold temperatures: Being outside in cold weather without proper clothing or being in a cold room without heating can cause the body to lose heat rapidly. * Cold water: Falling into cold water or being submerged in cold water for an extended period can cause hypothermia. * Cold air: Being in a cold environment with cold air can cause the body to lose heat rapidly.Medical Causes of Lowered Body Temperature
Symptoms of Lowered Body Temperature
The symptoms of lowered body temperature can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Mild hypothermia may cause symptoms such as: * Shivering * Confusion * Dizziness * Fatigue * Nausea and vomitingSevere hypothermia can cause more serious symptoms, including:
- Loss of consciousness
- Slow breathing
- Slow heart rate
- Pale or blue-tinged skin
- Dilated pupils
Treatment Options for Lowered Body Temperature

Severe hypothermia requires immediate medical attention. Treatment options may include:
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) if the person is unresponsive
- Oxygen therapy to help increase oxygen levels in the blood
- IV fluids to help warm the body
- Medications to help increase blood flow and warm the body
- Hospitalization to monitor the person's condition and provide ongoing treatment
Prevention Strategies
Prevention is key when it comes to lowered body temperature. To prevent hypothermia, it's essential to: * Dress warmly in cold weather * Stay dry and avoid getting wet * Avoid drinking alcohol or using certain medications that can increase the risk of hypothermia * Stay active and move around to keep the blood flowing * Use warm bedding and blankets to stay warm at nightComplications of Lowered Body Temperature

Risk Factors
Certain individuals are more vulnerable to lowered body temperature, including: * Older adults * Young children * People with certain medical conditions, such as hypothyroidism or diabetes * People who take certain medications, such as sedatives or antidepressants * People who are exposed to cold temperatures or cold waterDiagnosis and Treatment
Treatment for lowered body temperature typically involves:
- Warming the person up gradually
- Providing oxygen therapy
- Administering IV fluids
- Using medications to help increase blood flow and warm the body
- Hospitalization to monitor the person's condition and provide ongoing treatment
Recovery and Prognosis
The recovery and prognosis for lowered body temperature depend on the severity of the condition and how quickly treatment is received. With prompt and proper treatment, most people can make a full recovery. However, if left untreated, hypothermia can be fatal.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of lowered body temperature, it's essential to seek medical attention immediately. With prompt and proper treatment, most people can make a full recovery. Remember to stay warm, stay safe, and seek medical attention if necessary.
What is the normal body temperature range?
+The normal body temperature range is between 97.7°F (36.5°C) and 99.5°F (37.5°C).
What are the symptoms of mild hypothermia?
+The symptoms of mild hypothermia include shivering, confusion, dizziness, fatigue, and nausea and vomiting.
How can I prevent hypothermia?
+You can prevent hypothermia by dressing warmly in cold weather, staying dry, avoiding drinking alcohol or using certain medications, staying active, and using warm bedding and blankets to stay warm at night.
We hope this article has provided you with valuable information about lowered body temperature. If you have any further questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to reach out. Share this article with your friends and family to help spread awareness about the importance of staying warm and safe in cold environments.
