Intro
Discover Mallory-Weiss tear symptoms, including vomiting, abdominal pain, and bleeding. Learn about this esophageal conditions causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for effective relief.
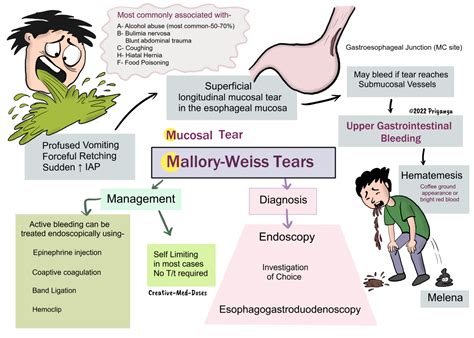
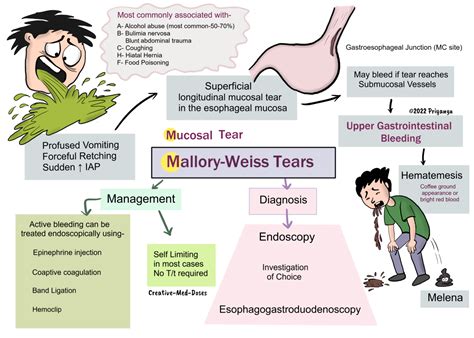
The Mallory-Weiss tear is a significant medical condition that affects many individuals worldwide. It is essential to understand the symptoms, causes, and treatment options available for this condition. The Mallory-Weiss tear is a mucosal or submucosal tear that occurs at the junction of the stomach and esophagus, often due to intense or prolonged vomiting, retching, or coughing. This condition can lead to severe bleeding, which may be life-threatening if left untreated. Recognizing the symptoms of a Mallory-Weiss tear is crucial for prompt medical attention and effective treatment.
The symptoms of a Mallory-Weiss tear can vary from person to person, but common signs include hematemesis, which is vomiting blood or coffee ground-like material, and melena, which is black, tarry stools. Other symptoms may include abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. In some cases, individuals may experience bleeding without any other symptoms, making it challenging to diagnose the condition. It is essential to seek medical attention immediately if any of these symptoms occur, as prompt treatment can significantly improve outcomes.
Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with Mallory-Weiss tears is vital for prevention and management. The condition is often linked to intense or prolonged vomiting, retching, or coughing, which can cause a tear in the mucosa or submucosa of the lower esophagus. Other risk factors include alcohol abuse, eating disorders, and certain medical conditions, such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastritis. Recognizing these risk factors can help individuals take preventive measures and seek medical attention if symptoms occur.
Mallory Weiss Tear Causes
Risk Factors
Several risk factors are associated with Mallory-Weiss tears, including: * Alcohol abuse * Eating disorders, such as bulimia nervosa * Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) * Gastritis * Intense or prolonged vomiting, retching, or coughing * Certain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) * Older age * Poor overall healthMallory Weiss Tear Symptoms and Diagnosis
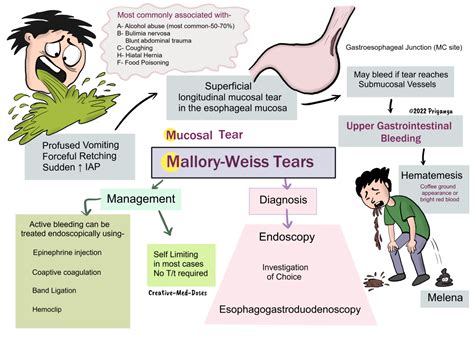
Diagnostic Criteria
The diagnostic criteria for a Mallory-Weiss tear include: * Hematemesis or melena * Abdominal pain or tenderness * Nausea or vomiting * A history of intense or prolonged vomiting, retching, or coughing * Endoscopic evidence of a tear in the mucosa or submucosa of the lower esophagusMallory Weiss Tear Treatment
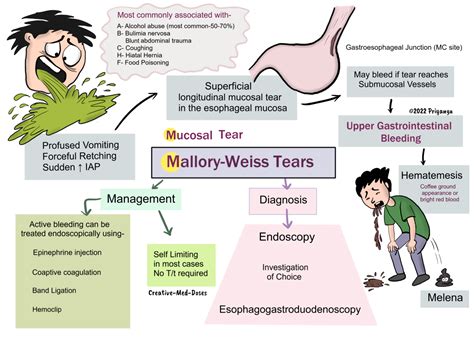
Treatment Options
Treatment options for a Mallory-Weiss tear include: * Supportive care: rest, hydration, and medication to manage symptoms * Endoscopic treatment: cauterization or clipping to control bleeding * Surgery: to repair the tear in severe cases * Blood transfusions: to replace lost blood * Medications: to manage symptoms, such as pain, nausea, and vomitingMallory Weiss Tear Prevention
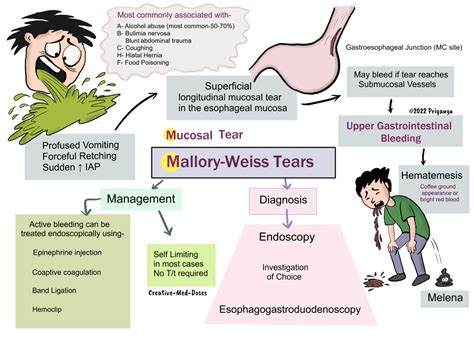
Preventive Measures
Preventive measures for a Mallory-Weiss tear include: * Avoiding triggers, such as intense or prolonged vomiting, retching, or coughing * Managing underlying medical conditions * Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise * Avoiding alcohol abuse and eating disorders * Seeking medical attention if symptoms occurMallory Weiss Tear Complications
Complication Management
Managing complications of a Mallory-Weiss tear requires prompt medical attention and treatment. Individuals should seek immediate medical attention if they experience: * Severe bleeding * Signs of infection, such as fever, chills, or abdominal pain * Difficulty swallowing * Recurrence of symptomsWhat is a Mallory-Weiss tear?
+A Mallory-Weiss tear is a mucosal or submucosal tear that occurs at the junction of the stomach and esophagus, often due to intense or prolonged vomiting, retching, or coughing.
What are the symptoms of a Mallory-Weiss tear?
+The symptoms of a Mallory-Weiss tear include hematemesis, melena, abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
How is a Mallory-Weiss tear diagnosed?
+A Mallory-Weiss tear is diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests, such as endoscopy and upper GI series.
What is the treatment for a Mallory-Weiss tear?
+Treatment for a Mallory-Weiss tear depends on the severity of the condition and may include supportive care, endoscopic treatment, or surgery.
How can a Mallory-Weiss tear be prevented?
+A Mallory-Weiss tear can be prevented by avoiding intense or prolonged vomiting, retching, or coughing, managing underlying medical conditions, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
In conclusion, a Mallory-Weiss tear is a significant medical condition that requires prompt attention and treatment. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options available can help individuals seek medical attention and prevent complications. By taking preventive measures and seeking medical attention if symptoms occur, individuals can reduce their risk of developing a Mallory-Weiss tear and improve their overall health outcomes. We encourage readers to share their experiences and ask questions in the comments below, and to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment.
