Intro
Discover the 5 causes of high WBC, including infections, inflammation, and immune disorders, and learn how to manage elevated white blood cell counts with medical treatments and lifestyle changes.
The human body is a complex and fascinating system, and one of its most crucial components is the immune system. The immune system is responsible for protecting the body against infections, diseases, and other foreign substances. One of the key indicators of the immune system's health is the white blood cell (WBC) count. A high WBC count can be a sign of an underlying infection or disease, and it's essential to understand the causes of an elevated WBC count. In this article, we'll delve into the world of WBCs, exploring what they are, their functions, and the 5 causes of high WBC counts.
A high WBC count can be a cause for concern, and it's natural to feel anxious or worried when confronted with abnormal test results. However, it's essential to remember that an elevated WBC count is not always a sign of a severe disease. In many cases, it can be a temporary response to a minor infection or inflammation. Nevertheless, it's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause of a high WBC count.
The immune system is a remarkable defense mechanism that protects the body against a vast array of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and other foreign substances. WBCs, also known as leukocytes, play a vital role in the immune system, helping to fight off infections and diseases. There are several types of WBCs, each with distinct functions and characteristics. The most common types of WBCs include neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils. Each type of WBC has a unique role in the immune response, and an imbalance in any of these cell types can lead to an elevated WBC count.
Introduction to High WBC Counts
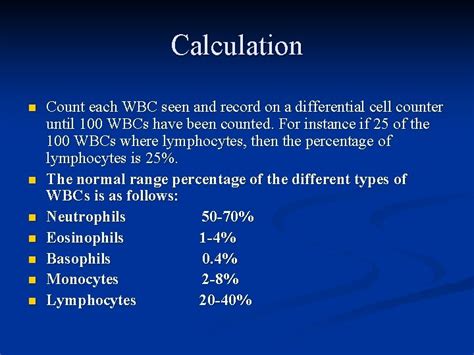
A high WBC count, also known as leukocytosis, occurs when the body produces an excessive number of WBCs. This can be a response to a variety of stimuli, including infections, inflammation, and diseases. A high WBC count can be detected through a blood test, and it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause of the elevation. In some cases, a high WBC count can be a sign of a severe disease, such as leukemia or lymphoma. However, in many cases, it can be a temporary response to a minor infection or inflammation.
Cause 1: Infections
Infections are one of the most common causes of high WBC counts. When the body detects the presence of a pathogen, it responds by producing more WBCs to fight off the infection. This can lead to an elevated WBC count, which can be detected through a blood test. Infections that can cause a high WBC count include bacterial infections, such as pneumonia or tuberculosis, and viral infections, such as influenza or HIV. Fungal infections, such as candidiasis or aspergillosis, can also cause an elevated WBC count.
Types of Infections that Can Cause High WBC Counts
Some of the most common types of infections that can cause high WBC counts include: * Bacterial infections, such as pneumonia or tuberculosis * Viral infections, such as influenza or HIV * Fungal infections, such as candidiasis or aspergillosis * Parasitic infections, such as malaria or toxoplasmosisCause 2: Inflammation
Inflammation is another common cause of high WBC counts. When the body detects tissue damage or injury, it responds by producing more WBCs to repair the damaged tissue. This can lead to an elevated WBC count, which can be detected through a blood test. Inflammation can be caused by a variety of factors, including injuries, infections, and autoimmune diseases. Conditions such as arthritis, lupus, or rheumatoid arthritis can cause chronic inflammation, leading to an elevated WBC count.
Types of Inflammation that Can Cause High WBC Counts
Some of the most common types of inflammation that can cause high WBC counts include: * Acute inflammation, such as injuries or infections * Chronic inflammation, such as arthritis or lupus * Autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis or multiple sclerosisCause 3: Allergic Reactions
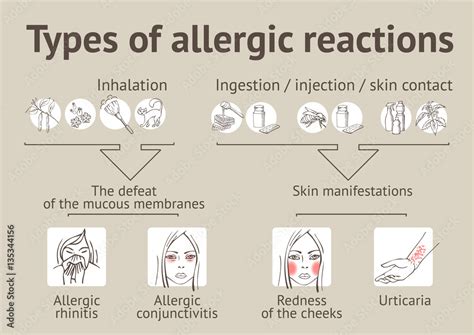
Allergic reactions are another common cause of high WBC counts. When the body detects the presence of an allergen, it responds by producing more WBCs to fight off the perceived threat. This can lead to an elevated WBC count, which can be detected through a blood test. Allergic reactions can be caused by a variety of factors, including foods, medications, or environmental substances. Conditions such as asthma or atopic dermatitis can cause chronic allergic reactions, leading to an elevated WBC count.
Types of Allergic Reactions that Can Cause High WBC Counts
Some of the most common types of allergic reactions that can cause high WBC counts include: * Food allergies, such as peanut or shellfish allergies * Medication allergies, such as penicillin or sulfa allergies * Environmental allergies, such as dust or pollen allergiesCause 4: Stress

Stress is another common cause of high WBC counts. When the body experiences stress, it responds by producing more WBCs to fight off the perceived threat. This can lead to an elevated WBC count, which can be detected through a blood test. Stress can be caused by a variety of factors, including emotional, physical, or psychological stress. Conditions such as anxiety or depression can cause chronic stress, leading to an elevated WBC count.
Types of Stress that Can Cause High WBC Counts
Some of the most common types of stress that can cause high WBC counts include: * Emotional stress, such as anxiety or depression * Physical stress, such as injury or illness * Psychological stress, such as trauma or burnoutCause 5: Medications

Medications are another common cause of high WBC counts. Certain medications, such as steroids or immunosuppressants, can affect the production of WBCs, leading to an elevated count. This can be a side effect of the medication, and it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause of the elevation. Conditions such as cancer or autoimmune diseases can require medications that affect WBC production, leading to an elevated WBC count.
Types of Medications that Can Cause High WBC Counts
Some of the most common types of medications that can cause high WBC counts include: * Steroids, such as prednisone or dexamethasone * Immunosuppressants, such as cyclosporine or tacrolimus * Chemotherapy medications, such as methotrexate or doxorubicinWhat is a high WBC count?
+A high WBC count, also known as leukocytosis, occurs when the body produces an excessive number of WBCs. This can be a response to a variety of stimuli, including infections, inflammation, and diseases.
What are the symptoms of a high WBC count?
+The symptoms of a high WBC count can vary depending on the underlying cause. Common symptoms include fever, fatigue, and weakness. In some cases, a high WBC count can be asymptomatic, and the only indication of an elevated count is through a blood test.
How is a high WBC count diagnosed?
+A high WBC count is typically diagnosed through a blood test. The test measures the number of WBCs in the blood, and an elevated count can indicate an underlying infection, inflammation, or disease.
In conclusion, a high WBC count can be a sign of an underlying infection, inflammation, or disease. It's essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause of an elevated WBC count. By understanding the 5 causes of high WBC counts, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their health and prevent complications. We encourage readers to share their experiences and ask questions in the comments below. Let's work together to promote health and wellness, and to provide support and resources for those affected by high WBC counts.
