Intro
Evaluate liver disease with the Meld Score, a reliable metric for liver function assessment, using related LSI keywords like liver transplant, cirrhosis, and liver failure diagnosis to determine disease severity.
The Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score is a widely used tool for evaluating the severity of liver disease in patients. It is a numerical scale that ranges from 6 to 40, with higher scores indicating more severe disease. The MELD score is calculated based on three laboratory values: bilirubin, creatinine, and international normalized ratio (INR). These values are used to estimate the likelihood of mortality within 90 days, making it a crucial tool for prioritizing liver transplant candidates.
The MELD score has become an essential component of liver disease management, allowing healthcare providers to assess the severity of liver dysfunction and make informed decisions about patient care. For instance, patients with higher MELD scores are more likely to require urgent medical attention, including liver transplantation. In contrast, patients with lower MELD scores may be able to manage their condition with conservative treatment and lifestyle modifications. Understanding the MELD score and its implications is vital for patients, families, and healthcare providers to navigate the complexities of liver disease management.
Liver disease is a significant public health concern, affecting millions of people worldwide. The prevalence of liver disease is increasing due to various factors, including obesity, alcohol consumption, and viral hepatitis. As a result, there is a growing need for effective tools to evaluate the severity of liver disease and prioritize treatment. The MELD score has emerged as a valuable tool in this context, enabling healthcare providers to stratify patients according to their risk of mortality and allocate resources accordingly. By understanding the MELD score and its applications, patients and healthcare providers can work together to develop personalized treatment plans and improve outcomes for individuals with liver disease.
Understanding the MELD Score Calculation
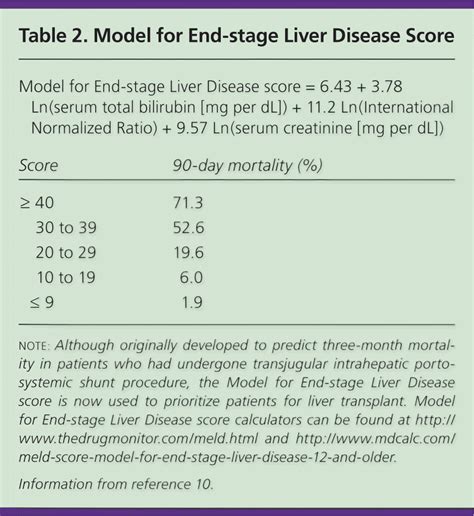
The MELD score is calculated using a complex algorithm that incorporates three laboratory values: bilirubin, creatinine, and INR. These values are used to estimate the likelihood of mortality within 90 days, providing a numerical score that ranges from 6 to 40. The MELD score is calculated as follows: MELD = 10 * (0.957 * ln(creatinine) + 0.378 * ln(bilirubin) + 1.120 * ln(INR)) + 0.643. This formula is used to generate a score that reflects the severity of liver disease, with higher scores indicating more severe disease.
Components of the MELD Score
The MELD score is composed of three laboratory values, each of which provides unique information about liver function. Bilirubin is a measure of liver dysfunction, as elevated levels indicate impaired liver function. Creatinine is a measure of kidney function, as liver disease can lead to kidney damage. INR is a measure of coagulation, as liver disease can impair the production of clotting factors. By combining these values, the MELD score provides a comprehensive assessment of liver function and the risk of mortality.Applications of the MELD Score
The MELD score has several applications in clinical practice, including prioritizing liver transplant candidates, evaluating the severity of liver disease, and monitoring disease progression. By using the MELD score, healthcare providers can identify patients who require urgent medical attention, including liver transplantation. The MELD score is also used to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment and monitor disease progression over time. By tracking changes in the MELD score, healthcare providers can adjust treatment plans and improve outcomes for patients with liver disease.
Limitations of the MELD Score
While the MELD score is a valuable tool for evaluating liver disease, it has several limitations. For example, the MELD score does not account for other factors that can affect liver disease, such as portal hypertension or hepatic encephalopathy. Additionally, the MELD score is not perfect, and some patients may have a low MELD score despite having severe liver disease. To address these limitations, healthcare providers use the MELD score in conjunction with other clinical assessments, such as physical examination and medical history.MELD Score and Liver Transplantation
The MELD score plays a critical role in liver transplantation, as it is used to prioritize candidates for transplantation. Patients with higher MELD scores are more likely to require urgent transplantation, as they are at increased risk of mortality. By using the MELD score, transplant centers can allocate organs to patients who need them most, improving outcomes and reducing mortality. The MELD score is also used to evaluate the effectiveness of liver transplantation, as it can be used to compare outcomes between patients with different MELD scores.
Benefits of the MELD Score in Liver Transplantation
The MELD score has several benefits in liver transplantation, including improved outcomes, reduced mortality, and more efficient allocation of organs. By prioritizing patients with higher MELD scores, transplant centers can reduce the risk of mortality and improve outcomes for patients with severe liver disease. The MELD score also enables transplant centers to allocate organs more efficiently, reducing the risk of organ waste and improving the overall effectiveness of liver transplantation.Future Directions for the MELD Score

The MELD score is a dynamic tool that is continually evolving to meet the needs of patients with liver disease. Future directions for the MELD score include the development of new scoring systems, such as the MELD-Na score, which incorporates serum sodium levels into the calculation. Additionally, there is a growing interest in using the MELD score to evaluate the severity of liver disease in special populations, such as patients with acute liver failure or liver cancer. By continuing to refine and improve the MELD score, healthcare providers can develop more effective treatment plans and improve outcomes for patients with liver disease.
Challenges and Opportunities
The MELD score faces several challenges and opportunities, including the need for ongoing validation and refinement. As liver disease continues to evolve, the MELD score must adapt to meet the changing needs of patients. Additionally, there is a growing need for more effective treatments for liver disease, including new medications and therapies. By addressing these challenges and opportunities, healthcare providers can improve outcomes for patients with liver disease and develop more effective treatment plans.What is the MELD score used for?
+The MELD score is used to evaluate the severity of liver disease and prioritize liver transplant candidates.
How is the MELD score calculated?
+The MELD score is calculated using a complex algorithm that incorporates three laboratory values: bilirubin, creatinine, and INR.
What are the limitations of the MELD score?
+The MELD score has several limitations, including the fact that it does not account for other factors that can affect liver disease, such as portal hypertension or hepatic encephalopathy.
In summary, the MELD score is a valuable tool for evaluating the severity of liver disease and prioritizing liver transplant candidates. By understanding the MELD score and its applications, patients and healthcare providers can work together to develop personalized treatment plans and improve outcomes for individuals with liver disease. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with the MELD score, and to continue the conversation about the importance of liver disease evaluation and management.
