Intro
Discover key facts about Metoprolol ER Succinate, a beta-blocker medication, including its uses, side effects, and interactions, to manage hypertension, angina, and heart failure effectively.
Metoprolol ER succinate is a medication that has been widely used for the treatment of various cardiovascular conditions, including high blood pressure, angina, and heart failure. Understanding the mechanism, benefits, and potential side effects of this drug is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of metoprolol ER succinate, exploring its uses, how it works, and what patients can expect when taking this medication.
The importance of managing cardiovascular health cannot be overstated. Conditions such as hypertension and heart failure can significantly impact an individual's quality of life and, if left untreated, can lead to severe complications, including heart attack, stroke, and even death. Metoprolol ER succinate plays a critical role in the management of these conditions by helping to reduce the heart's workload and improve its efficiency. This, in turn, can lead to better overall health outcomes for patients.
As we discuss metoprolol ER succinate, it's essential to consider the broader context of cardiovascular health. The management of heart conditions often involves a multifaceted approach, including lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and medication. Metoprolol ER succinate is just one tool in this arsenal, but it is a significant one. By understanding how this medication works and its potential benefits and risks, patients and healthcare providers can make informed decisions about its use.
Introduction to Metoprolol ER Succinate

Metoprolol ER succinate is a beta-blocker, a class of drugs that reduce the workload on the heart and open blood vessels, causing the heart to beat slower and with less force. This medication is specifically formulated as an extended-release tablet, designed to release the active ingredient metoprolol slowly over time, providing a steady and consistent effect throughout the day. The "ER" in its name stands for extended release, highlighting its unique formulation compared to immediate-release versions of metoprolol.
How Metoprolol ER Succinate Works
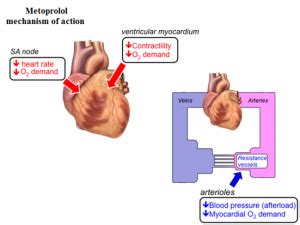
Metoprolol ER succinate works by selectively blocking beta-1 receptors in the heart, which are responsible for the heart's rate and contraction force. By blocking these receptors, metoprolol reduces the heart rate and the force of contraction, lowering blood pressure and reducing the heart's oxygen demand. This action is particularly beneficial for patients with conditions like angina, where the heart muscle does not receive enough oxygen, leading to chest pain.
Benefits of Metoprolol ER Succinate
The benefits of metoprolol ER succinate are multifaceted:
- Reduces Blood Pressure: By decreasing the heart's workload, metoprolol ER succinate helps to lower blood pressure, reducing the risk of heart attack, stroke, and kidney damage.
- Improves Survival After Heart Attack: For patients who have suffered a heart attack, metoprolol ER succinate can improve survival rates by reducing the risk of another heart attack.
- Reduces Angina Symptoms: By decreasing the heart's demand for oxygen, metoprolol ER succinate can reduce the frequency and severity of angina episodes.
- Manages Heart Failure: Metoprolol ER succinate can help improve the heart's pumping efficiency and reduce symptoms of heart failure, such as shortness of breath and fatigue.
Side Effects and Precautions
Like all medications, metoprolol ER succinate can cause side effects. Common side effects include:
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Shortness of breath
- Bradycardia (slow heart rate)
- Cold hands and feet
- Hair loss
It's essential for patients to discuss any concerns or side effects with their healthcare provider. In some cases, the benefits of metoprolol ER succinate may outweigh the risks, but monitoring and adjustments to the treatment plan may be necessary.
Precautions and Interactions
Metoprolol ER succinate can interact with other medications, and certain precautions should be taken:
- Medication Interactions: Metoprolol ER succinate can interact with other heart medications, as well as certain antidepressants and antihistamines. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Metoprolol ER succinate should be used with caution in pregnant women and those who are breastfeeding, as it can affect the fetus or baby.
- Diabetes: Metoprolol ER succinate can mask symptoms of low blood sugar and affect blood sugar levels. Patients with diabetes should monitor their blood sugar levels closely.
Administration and Dosage
The dosage of metoprolol ER succinate varies depending on the condition being treated and the patient's response to the medication. It is typically taken once daily, with or without food. Patients should not stop taking metoprolol ER succinate without consulting their healthcare provider, as sudden withdrawal can lead to worsening of angina or other heart conditions.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are crucial for patients taking metoprolol ER succinate. This includes:
- Blood Pressure Checks: Regular blood pressure checks to ensure the medication is effectively lowering blood pressure.
- Heart Rate Monitoring: Monitoring heart rate to avoid bradycardia.
- Symptom Management: Adjusting the dosage or adding other medications as needed to manage symptoms of angina, heart failure, or other conditions.
Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, metoprolol ER succinate is a valuable medication in the management of various cardiovascular conditions. Its ability to reduce the heart's workload, lower blood pressure, and improve survival rates makes it a critical component of treatment plans for many patients. As research continues to evolve, understanding the role of metoprolol ER succinate and its potential benefits and risks will remain essential for optimizing patient outcomes.
We invite readers to share their experiences or ask questions about metoprolol ER succinate in the comments below. This open dialogue can help foster a better understanding of the medication and its implications for cardiovascular health.
What is metoprolol ER succinate used for?
+Metoprolol ER succinate is used to treat high blood pressure, angina, and heart failure. It works by reducing the heart's workload and improving its efficiency.
How does metoprolol ER succinate work?
+Metoprolol ER succinate works by blocking beta-1 receptors in the heart, reducing the heart rate and the force of contraction, which lowers blood pressure and reduces the heart's oxygen demand.
What are the common side effects of metoprolol ER succinate?
+Common side effects include fatigue, dizziness, shortness of breath, bradycardia, cold hands and feet, and hair loss. Patients should discuss any concerns or side effects with their healthcare provider.
