Intro
Discover key facts about tubal ligation, a permanent birth control method, including its benefits, risks, and reversibility, to make informed decisions about female sterilization and family planning options.
Tubal ligation, also known as having one's "tubes tied," is a surgical procedure for female sterilization and/or permanent birth control. The process involves cutting or blocking the fallopian tubes to prevent pregnancy. This method is chosen by many women for various reasons, including the desire to not have any more children or to prevent pregnancy due to health concerns. Understanding the procedure, its implications, and the facts surrounding it is crucial for anyone considering tubal ligation.
The decision to undergo tubal ligation is significant and should be made with a full understanding of what the procedure entails, its effectiveness, potential risks, and the reversibility of the process. Many factors contribute to a woman's decision, including her age, health status, family situation, and personal preferences regarding birth control and family planning. It's also important to consider the emotional and psychological aspects of choosing a permanent form of birth control.
Tubal ligation is a relatively common procedure, but like any surgical intervention, it comes with its own set of considerations and potential complications. The procedure's success rate, the risks involved, and the recovery process are all important aspects to understand. Moreover, the impact on future fertility and the possibility of reversal, although low, are critical points for discussion. The procedure's permanence means that it's essential for individuals to be certain about their decision, considering both current and future desires regarding childbearing.
What is Tubal Ligation?
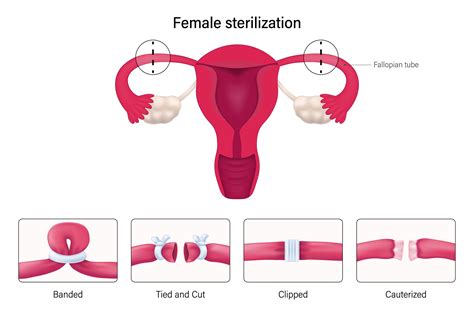
Benefits of Tubal Ligation
The benefits of tubal ligation include its high effectiveness as a form of permanent birth control. Once the procedure is performed, the risk of pregnancy is significantly reduced, offering long-term peace of mind for those who have completed their families or wish to avoid future pregnancies. Additionally, tubal ligation does not interfere with a woman's hormonal balance or menstrual cycle, which can be an advantage over some hormonal forms of birth control. However, it's crucial to weigh these benefits against the potential risks and complications associated with the procedure.Risks and Complications
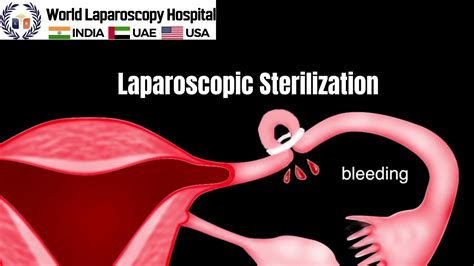
Reversal of Tubal Ligation
For some women, circumstances may change, leading them to desire a reversal of their tubal ligation. The success of reversal procedures, also known as tubal reversal, depends on several factors, including the method used for the initial ligation, the length of the remaining fallopian tube segments, the age of the woman, and the overall health of the reproductive organs. Tubal reversal is generally more successful when the blocked segments are short and when the procedure is performed by an experienced surgeon. However, reversal is not always successful, and the chances of achieving pregnancy after reversal can vary significantly.Alternatives to Tubal Ligation
Decision Making
The decision to undergo tubal ligation should be made carefully, considering all aspects of the procedure, including its permanence, potential risks, and the impact on future fertility. It's essential to have thorough discussions with a healthcare provider, understanding the procedure, the recovery process, and what to expect post-surgery. Additionally, considering alternative forms of birth control and discussing the decision with a partner, if applicable, can provide a comprehensive view of the options available.Post-Procedure Care and Recovery

Emotional and Psychological Considerations
The decision for tubal ligation also involves emotional and psychological considerations. Women may experience a range of emotions, from relief and certainty about their decision to grief or regret. It's essential to have a support system, whether through family, friends, or professional counseling, to navigate these feelings. Discussing these aspects with a healthcare provider can provide valuable insights and help in making an informed decision.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts, questions, or experiences regarding tubal ligation in the comments below. Your input can provide valuable insights and support for others considering this procedure. Additionally, if you found this information helpful, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from a comprehensive understanding of tubal ligation.
What is the success rate of tubal ligation?
+Tubal ligation is highly effective, with a failure rate of less than 1%. However, the exact success rate can depend on the method used and individual factors.
Can tubal ligation be reversed?
+Yes, tubal ligation can be reversed, but the success of the reversal procedure depends on several factors, including the method of the initial ligation and the age of the woman.
What are the alternatives to tubal ligation for permanent birth control?
+Alternatives to tubal ligation include vasectomy for male partners and long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs) such as IUDs and implants for women.
