Intro
Discover key facts about Metoprolol, a beta blocker medication, including its uses, side effects, and interactions, to better manage hypertension, angina, and heart failure, while minimizing risks and optimizing treatment outcomes.
Metoprolol is a widely prescribed medication for various cardiovascular conditions, including high blood pressure, chest pain, and heart failure. Its effectiveness and relatively low cost make it a staple in many treatment plans. However, like any medication, metoprolol comes with its own set of benefits, risks, and considerations that patients should be aware of. Understanding these aspects can help individuals make informed decisions about their health and ensure they are using metoprolol safely and effectively.
The importance of being informed about metoprolol cannot be overstated, especially given its widespread use. Patients who are knowledgeable about their medications are better equipped to manage their conditions, recognize potential side effects, and communicate effectively with their healthcare providers. This knowledge also empowers individuals to take a more active role in their healthcare, which is crucial for achieving the best possible outcomes. Whether you are considering metoprolol as a treatment option or are already taking it, delving into the specifics of how it works, its benefits, and its potential drawbacks can provide valuable insights into your health management.
For those who are prescribed metoprolol, it is natural to have questions and concerns. How does metoprolol work to alleviate symptoms of cardiovascular diseases? What are the common side effects, and how can they be managed? Are there any lifestyle changes that can enhance the effectiveness of metoprolol or reduce its side effects? Answering these questions not only helps in understanding metoprolol better but also in making the most out of the treatment. It's also important to consider the broader context of cardiovascular health, including diet, exercise, and stress management, as these factors can significantly influence the effectiveness of metoprolol and overall well-being.
Introduction to Metoprolol

How Metoprolol Works
The mechanism of action of metoprolol involves the selective blockade of beta-1 adrenergic receptors in the heart. By blocking these receptors, metoprolol reduces the effects of epinephrine on the heart, leading to a decrease in heart rate, contractility, and the velocity of cardiac contractions. This results in a reduction in cardiac output and a decrease in blood pressure. The selective nature of metoprolol for beta-1 receptors means that it has less effect on airway smooth muscle and peripheral blood vessels compared to non-selective beta-blockers, which can make it a preferable option for patients with certain respiratory conditions, such as asthma.Benefits of Metoprolol
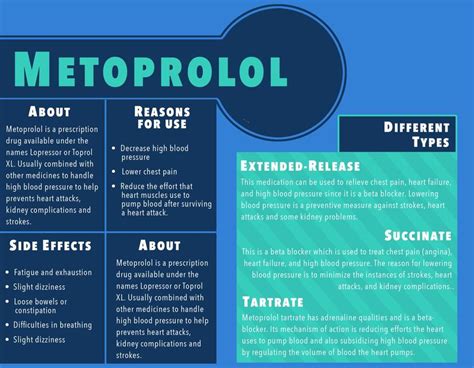
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
While metoprolol is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects in some individuals. Common side effects include: - Fatigue - Dizziness or lightheadedness - Cold hands and feet - Shortness of breath - Nausea or vomiting - Diarrhea or constipation It's also important to note that metoprolol can interact with other medications, including certain antidepressants, antihistamines, and other heart medications, which can lead to adverse effects. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking before starting metoprolol.Metoprolol Dosage and Administration
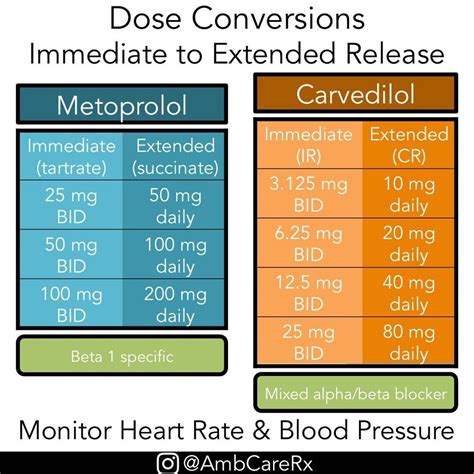
Lifestyle Changes to Enhance Metoprolol Effectiveness
In addition to taking metoprolol as prescribed, making certain lifestyle changes can help enhance its effectiveness and contribute to overall cardiovascular health. These include: - **Diet:** Eating a balanced diet that is low in sodium, saturated fats, and cholesterol can help control blood pressure and cholesterol levels. - **Exercise:** Regular physical activity can help lower blood pressure, improve heart health, and enhance the overall effectiveness of metoprolol. - **Stress Management:** Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, can help manage stress, which is beneficial for heart health. - **Smoking Cessation:** Quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease and improve the effectiveness of metoprolol.Metoprolol and Pregnancy
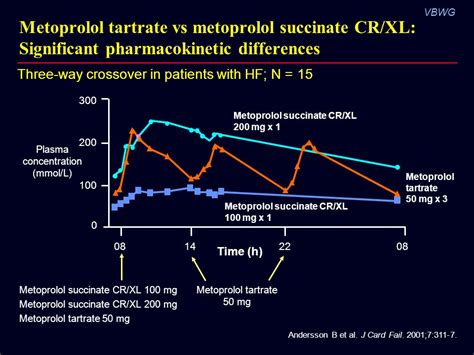
Metoprolol in Breastfeeding
Metoprolol is excreted in breast milk, but the amounts are generally considered to be small and unlikely to cause significant effects in nursing infants. Nevertheless, breastfeeding women should consult their healthcare provider before taking metoprolol, as the decision to use the medication should be based on the individual circumstances and the potential benefits and risks.Conclusion and Future Directions

Final Thoughts
As you continue on your journey to better understand metoprolol and its role in managing cardiovascular health, remember that knowledge is power. Being informed about your medications, lifestyle choices, and the latest in medical research can empower you to take control of your health. Whether you are a patient, a caregiver, or simply someone interested in learning more about metoprolol, we encourage you to share this information with others, ask questions, and seek out additional resources to deepen your understanding.What is metoprolol used for?
+Metoprolol is used to treat high blood pressure, chest pain (angina), and certain heart-related conditions. It belongs to a class of drugs known as beta-blockers, which work by blocking the effects of the hormone epinephrine and by slowing the heart rate and reducing its workload.
Can I stop taking metoprolol without consulting my doctor?
+No, it's not recommended to stop taking metoprolol without consulting your healthcare provider first. Sudden cessation can lead to withdrawal symptoms or worsening of the condition. Your doctor will advise you on how to safely stop taking metoprolol if necessary.
Can metoprolol be used during pregnancy?
+Metoprolol can be used during pregnancy if the benefits to the mother outweigh the risks to the fetus. However, pregnant women should discuss the use of metoprolol with their healthcare provider, as it can affect fetal heart rate and may be associated with growth restriction.
