Intro
Discover the importance of minerals in food, including essential micronutrients like calcium, iron, and potassium, and learn how they impact nutrition, health, and wellbeing, making informed food choices matter.
The importance of minerals in our diet cannot be overstated. These essential nutrients play a crucial role in maintaining our overall health and wellbeing, from regulating fluid balance and nerve function to supporting healthy bone growth and development. Without adequate mineral intake, our bodies can become deficient, leading to a range of health problems. In this article, we will delve into the world of minerals in food, exploring their benefits, functions, and the best sources to include in our diets.
A well-balanced diet that includes a variety of whole foods can provide all the necessary minerals our bodies need. However, with the rising popularity of processed and convenience foods, many of us are not getting enough minerals from our diets. This can be due to a lack of awareness about the importance of minerals, as well as the challenges of incorporating mineral-rich foods into our busy lives. As we will discuss, minerals are not just important for our physical health, but also for our mental wellbeing and energy levels.
The consequences of mineral deficiency can be severe, ranging from mild symptoms such as fatigue and weakness to more serious health problems like osteoporosis and anemia. Furthermore, mineral deficiencies can also have a significant impact on our mental health, with conditions like depression and anxiety linked to low levels of certain minerals. By understanding the role of minerals in our diets and making informed choices about the foods we eat, we can take a proactive approach to maintaining our health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
Introduction to Minerals

Macrominerals
Macrominerals are the minerals that our bodies need in larger quantities. These include: * Calcium: essential for healthy bone growth and development * Phosphorus: plays a crucial role in many bodily functions, including nerve function and muscle contraction * Magnesium: important for energy production, nerve function, and bone health * Potassium: helps regulate fluid balance and blood pressure * Sodium: essential for maintaining fluid balance and nerve function * Chloride: helps maintain fluid balance and is an essential component of digestive fluidsBenefits of Minerals

Microminerals
Microminerals, on the other hand, are the minerals that our bodies need in smaller quantities. These include: * Iron: essential for healthy red blood cells and preventing anemia * Zinc: important for immune function, wound healing, and protein synthesis * Selenium: acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage * Iodine: essential for healthy thyroid function and preventing iodine deficiency disorders * Copper: plays a crucial role in many bodily functions, including connective tissue health and immune function * Manganese: important for bone health, wound healing, and metabolismFood Sources of Minerals

Mineral Deficiency
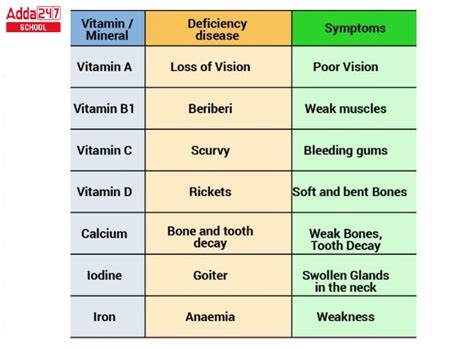
A mineral deficiency occurs when our bodies do not get enough of a particular mineral. This can be due to a lack of mineral-rich foods in our diets, as well as certain medical conditions or medications that interfere with mineral absorption. Some common symptoms of mineral deficiency include: * Fatigue and weakness * Poor appetite and weight loss * Skin problems, such as acne and dry skin * Hair loss and brittle nails * Increased risk of illness and infectionPrevention and Treatment
Mineral Interactions
Minerals can interact with each other and with other nutrients in complex ways. For example, vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption, while iron and zinc can compete with each other for absorption. Understanding these interactions is crucial for maintaining optimal mineral balance and preventing deficiency.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with minerals in the comments section below. Have you experienced any symptoms of mineral deficiency? What strategies have you found helpful in maintaining mineral balance? By sharing our knowledge and experiences, we can support each other in achieving optimal health and wellbeing.
What are the most common symptoms of mineral deficiency?
+The most common symptoms of mineral deficiency include fatigue and weakness, poor appetite and weight loss, skin problems, hair loss, and increased risk of illness and infection.
How can I prevent mineral deficiency?
+You can prevent mineral deficiency by eating a balanced diet that includes a variety of whole foods, taking mineral supplements, avoiding foods that interfere with mineral absorption, managing stress, and getting enough sleep.
What are the best food sources of minerals?
+The best food sources of minerals include leafy green vegetables, nuts and seeds, fatty fish, whole grains, and legumes. These foods are rich in a variety of minerals, including calcium, iron, magnesium, and zinc.
