Intro
Chest pain causes concern, learn about symptoms, sharp chest pain, tightness, and discomfort, exploring heart-related, respiratory, and musculoskeletal reasons, to identify underlying issues.
Chest pain is a common symptom that can be caused by a variety of factors, ranging from mild to severe. It's essential to understand the potential causes and symptoms of chest pain to seek proper medical attention when needed. Chest pain can be a sign of an underlying condition that requires immediate attention, such as a heart attack or pulmonary embolism. On the other hand, it can also be caused by less severe conditions like indigestion or muscle strain.
The importance of understanding chest pain lies in its potential to be a warning sign for a life-threatening condition. According to the American Heart Association, chest pain is one of the most common symptoms of a heart attack, which is a leading cause of death worldwide. Furthermore, chest pain can also be a symptom of other serious conditions, such as pneumonia, lung cancer, or a pulmonary embolism. Therefore, it's crucial to be aware of the potential causes and symptoms of chest pain to seek medical attention promptly.
Chest pain can manifest in different ways, depending on the underlying cause. It can be a sharp, stabbing pain or a dull, aching sensation. It can be constant or intermittent, and it can radiate to other areas of the body, such as the arms, back, or jaw. Understanding the different types of chest pain and their potential causes can help individuals seek proper medical attention and receive timely treatment. In this article, we will delve into the various causes and symptoms of chest pain, as well as provide guidance on when to seek medical attention.
Chest Pain Causes
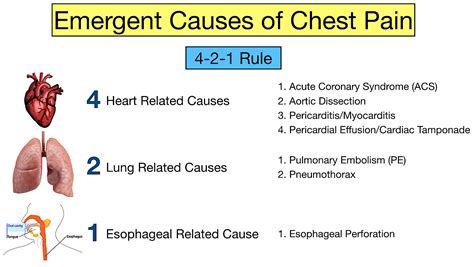
Cardiac Causes of Chest Pain
Cardiac causes of chest pain are often the most concerning, as they can be life-threatening. Coronary artery disease, for example, occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked, reducing blood flow to the heart. This can cause chest pain, known as angina, which can be a warning sign of a heart attack. Heart attacks, also known as myocardial infarctions, occur when the blood flow to the heart is blocked, causing damage to the heart muscle. Arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation, can also cause chest pain due to abnormal heart rhythms.Chest Pain Symptoms

Types of Chest Pain
There are several types of chest pain, each with distinct characteristics. Stable angina, for example, is a type of chest pain that occurs when the heart muscle does not receive enough oxygen-rich blood. Unstable angina, on the other hand, is a type of chest pain that occurs when the blood flow to the heart is suddenly reduced. Variant angina, also known as Prinzmetal's angina, is a type of chest pain that occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart spasm.Diagnosing Chest Pain
Diagnostic Tests for Chest Pain
Diagnostic tests for chest pain can help determine the underlying cause of the symptoms. Electrocardiograms (ECGs), for example, measure the electrical activity of the heart to detect abnormal heart rhythms or signs of a heart attack. Chest X-rays can help diagnose respiratory conditions, such as pneumonia or lung cancer. Blood tests, such as troponin tests, can help diagnose heart attacks or other cardiac conditions.Treating Chest Pain
Medications for Chest Pain
Medications for chest pain can help alleviate symptoms and treat the underlying condition. Beta blockers, for example, can help reduce blood pressure and improve blood flow to the heart. Nitrates, such as nitroglycerin, can help relax the blood vessels and improve blood flow to the heart. Antacids and proton pump inhibitors can help reduce stomach acid production and alleviate symptoms of GERD.Preventing Chest Pain

Lifestyle Changes for Preventing Chest Pain
Lifestyle changes can help prevent chest pain by reducing the risk of underlying medical conditions. A healthy diet, for example, can help lower cholesterol levels and reduce blood pressure. Regular exercise, such as walking or jogging, can help improve cardiovascular health and reduce stress. Stress management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can also help reduce stress and anxiety.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with chest pain in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to ask. Additionally, if you found this article helpful, please share it with others who may benefit from the information.
What are the most common causes of chest pain?
+Chest pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including cardiac, respiratory, gastrointestinal, and musculoskeletal conditions. The most common causes of chest pain include coronary artery disease, heart attacks, pneumonia, bronchitis, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
How can I distinguish between cardiac and non-cardiac chest pain?
+Cardiac chest pain is often described as a sharp, stabbing pain or a dull, aching sensation in the chest, arms, back, or jaw. Non-cardiac chest pain, on the other hand, can be caused by a variety of factors, such as muscle strain, indigestion, or respiratory conditions. If you are experiencing chest pain, it's essential to seek medical attention promptly to determine the underlying cause.
What are the risk factors for chest pain?
+Risk factors for chest pain include a family history of heart disease, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, obesity, and physical inactivity. Additionally, individuals with underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes or lung disease, may be at higher risk for chest pain.
