Intro
Learn how the new flu virus spreads through human contact, airborne transmission, and contaminated surfaces, with 5 key methods of infection, including mutation, reassortment, and animal hosts, to understand flu prevention and mitigation strategies.
The flu, also known as influenza, is a highly contagious respiratory illness that affects millions of people worldwide each year. The rapid spread of new flu viruses has become a significant concern for global health authorities, as it can lead to widespread outbreaks and even pandemics. Understanding how new flu viruses spread is crucial in developing effective prevention and control strategies. In this article, we will delve into the ways new flu viruses spread and explore the factors that contribute to their transmission.
The spread of new flu viruses is a complex process that involves various factors, including human behavior, environmental conditions, and the characteristics of the virus itself. As new flu viruses emerge, it is essential to stay informed about the latest developments and take proactive measures to protect ourselves and our communities. By understanding the ways new flu viruses spread, we can better prepare for and respond to outbreaks, ultimately reducing the risk of infection and mitigating the impact of the flu on public health.
The importance of understanding how new flu viruses spread cannot be overstated. The flu is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, and new flu viruses can spread quickly and unpredictably. The 2009 H1N1 pandemic, for example, highlighted the need for rapid response and effective communication in controlling the spread of new flu viruses. By staying informed and taking proactive measures, we can reduce the risk of infection and protect ourselves and our loved ones from the flu.
Introduction to New Flu Virus Transmission
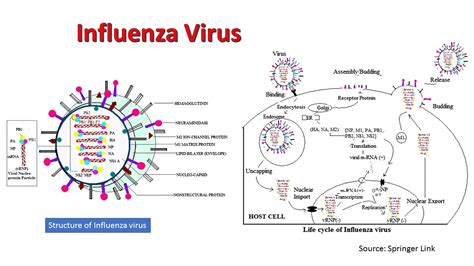
Factors Contributing to New Flu Virus Transmission
Several factors contribute to the transmission of new flu viruses, including: * Human behavior, such as poor hygiene practices and lack of vaccination * Environmental conditions, such as crowded living and working conditions * Characteristics of the virus, such as its virulence and transmissibility * Global connectivity, which facilitates the rapid spread of the virus across bordersRespiratory Droplet Transmission
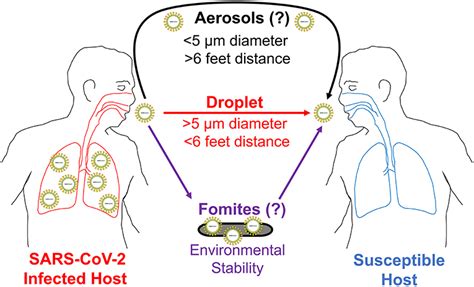
Prevention Strategies for Respiratory Droplet Transmission
To prevent respiratory droplet transmission, the following strategies can be employed: * Practice good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing and covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing * Wear masks in crowded areas or when in close contact with infected individuals * Maintain a safe distance from infected individuals * Avoid touching the eyes, nose, and mouthContact Transmission

Prevention Strategies for Contact Transmission
To prevent contact transmission, the following strategies can be employed: * Practice good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing and cleaning of contaminated surfaces * Avoid touching contaminated surfaces * Avoid sharing personal items * Use disposable utensils, towels, and beddingAirborne Transmission
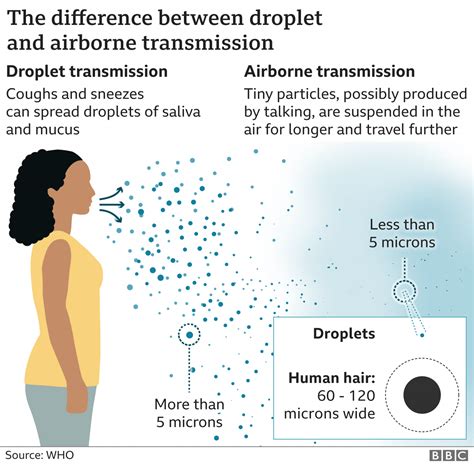
Prevention Strategies for Airborne Transmission
To prevent airborne transmission, the following strategies can be employed: * Practice good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing and wearing masks * Avoid close contact with infected individuals * Use air purifiers and ventilation systems to reduce airborne particles * Stay in well-ventilated areasVector-Borne Transmission
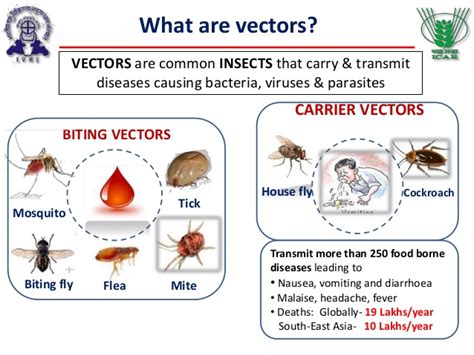
Prevention Strategies for Vector-Borne Transmission
To prevent vector-borne transmission, the following strategies can be employed: * Practice good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing and wearing protective clothing * Avoid areas with high vector activity * Use insect repellents and insecticides to reduce vector populations * Avoid contact with contaminated animal productsConclusion and Future Directions

As we look to the future, it is essential to continue researching and developing new strategies for preventing and controlling the spread of new flu viruses. This includes investing in vaccine development, improving diagnostic capabilities, and enhancing global surveillance and communication. By working together, we can reduce the impact of the flu on public health and create a safer, healthier world for everyone.
What are the most common modes of transmission for new flu viruses?
+The most common modes of transmission for new flu viruses are respiratory droplet transmission, contact transmission, and airborne transmission.
How can I protect myself from getting infected with a new flu virus?
+To protect yourself from getting infected with a new flu virus, practice good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing and covering your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing. Avoid close contact with infected individuals, and use preventive measures, such as masks and air purifiers.
What are the symptoms of a new flu virus infection?
+The symptoms of a new flu virus infection can vary, but common symptoms include fever, cough, sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, muscle or body aches, headaches, fatigue, and diarrhea or vomiting.
How long does it take for symptoms of a new flu virus infection to appear?
+The symptoms of a new flu virus infection can appear anywhere from 1 to 4 days after exposure to the virus.
Can new flu viruses be treated with antibiotics?
+No, new flu viruses cannot be treated with antibiotics. Antibiotics are effective against bacterial infections, not viral infections. Treatment for new flu virus infections typically involves antiviral medications, rest, and hydration.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the ways new flu viruses spread and the strategies for preventing and controlling their transmission. If you have any further questions or would like to share your thoughts on this topic, please don't hesitate to comment below. Additionally, if you found this article informative and helpful, please consider sharing it with your friends and family to help spread awareness about the importance of flu prevention and control.
