Intro
Learn about the Normal A1c Level Range, ideal blood sugar targets, and understand how to maintain healthy glucose levels, preventing diabetes complications with accurate HbA1c tests and effective management strategies.
Maintaining a healthy blood sugar level is crucial for overall well-being, and one of the key indicators of blood sugar control is the hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level. The HbA1c test measures the average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months, providing valuable insights into how well diabetes is being managed. For individuals without diabetes, understanding the normal A1c level range is essential for preventive care and early detection of potential issues.
The importance of monitoring HbA1c levels cannot be overstated, especially for those at risk of developing diabetes or those already living with the condition. Elevated HbA1c levels are associated with an increased risk of diabetes complications, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. Therefore, it is vital to understand what constitutes a normal A1c level range and how to maintain it.
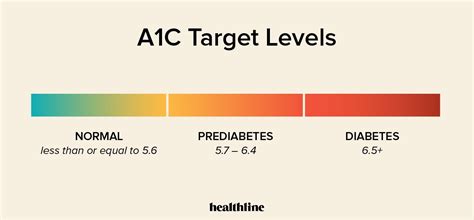
For individuals without diabetes, the normal A1c level range is typically below 5.7%. This value indicates that blood sugar levels are within a healthy range, suggesting a low risk of developing diabetes. However, it is essential to note that even within the normal range, lifestyle factors such as diet, physical activity, and weight management play a significant role in maintaining optimal blood sugar control. Understanding these factors and how they impact HbA1c levels can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health.
Understanding HbA1c Levels
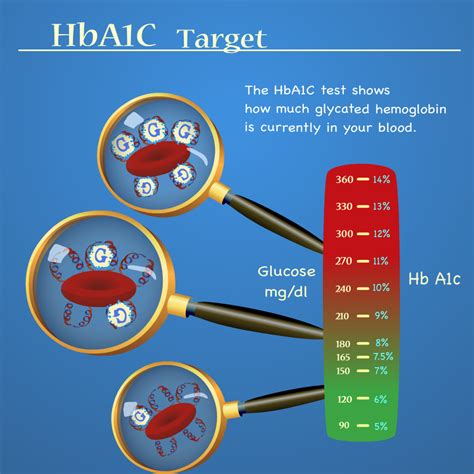
HbA1c levels are measured as a percentage, reflecting the amount of glucose that has bound to hemoglobin in red blood cells. The higher the HbA1c percentage, the higher the average blood glucose levels over the preceding 2-3 months. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) has established the following HbA1c level categories:
- Normal: Below 5.7%
- Prediabetes: 5.7% to 6.4%
- Diabetes: 6.5% or above
Factors Influencing HbA1c Levels
Several factors can influence HbA1c levels, including diet, physical activity, weight, and the presence of certain medical conditions. For example, a diet high in simple carbohydrates and added sugars can lead to elevated blood glucose levels, resulting in higher HbA1c readings. Conversely, regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and maintaining a healthy weight can help keep HbA1c levels within the normal range.Normal A1c Level Range for Different Groups

The normal A1c level range can vary slightly depending on the individual's age, health status, and other factors. For instance:
- Children and Adolescents: For youngsters, the normal HbA1c range is generally considered to be below 5.7%, similar to adults. However, it's crucial for parents and caregivers to work with healthcare providers to interpret these results in the context of the child's overall health and development.
- Pregnant Women: During pregnancy, it's essential to maintain tight blood glucose control to prevent complications for both the mother and the fetus. The target HbA1c level for pregnant women with diabetes is typically below 6.5%.
- Older Adults: For older adults, especially those with limited life expectancy or significant comorbidities, less stringent HbA1c targets may be appropriate, considering the potential risks and benefits of tight glycemic control.
Interpreting HbA1c Results
Interpreting HbA1c results requires considering the individual's overall health context. For example, someone with an HbA1c of 5.8% might be considered to have prediabetes, indicating an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. This result should prompt lifestyle changes and possibly further testing to assess glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity.Strategies for Maintaining Normal A1c Levels
Maintaining normal A1c levels involves a combination of healthy lifestyle choices and, for those with diabetes, adherence to a prescribed treatment plan. Key strategies include:
- Balanced Diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Regular Physical Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can improve insulin sensitivity and help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can raise blood glucose levels; engaging in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help.
Monitoring and Adjusting
For individuals with diabetes or prediabetes, regular monitoring of blood glucose levels, along with periodic HbA1c tests, is crucial. This monitoring allows for the adjustment of treatment plans as needed to maintain HbA1c levels within the target range. Lifestyle changes, medication adjustments, or a combination of both may be necessary to achieve and maintain optimal blood sugar control.Challenges and Considerations

Several challenges and considerations arise when aiming to maintain normal A1c levels. These include:
- Access to Healthcare: Regular check-ups and access to healthcare services are essential for monitoring and managing diabetes.
- Cost of Care: The cost of diabetes care, including medications, supplies, and lifestyle modifications, can be a significant barrier for many individuals.
- Social and Environmental Factors: Social determinants of health, such as socioeconomic status, education level, and environmental factors like food deserts, can significantly impact an individual's ability to maintain healthy lifestyle choices.
Future Directions
Advances in technology, such as continuous glucose monitoring systems and insulin pumps, offer promising solutions for improving blood glucose control and reducing the burden of diabetes management. Additionally, research into new medications and therapeutic approaches aims to provide more effective and personalized treatments for diabetes.Conclusion and Next Steps

Understanding and maintaining normal A1c levels is a critical aspect of diabetes prevention and management. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits, staying informed about the latest research and treatment options, and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals can effectively manage their blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Final Thoughts
The journey to maintaining normal A1c levels is ongoing and requires commitment, patience, and support. By empowering themselves with knowledge and taking proactive steps towards health, individuals can navigate the complexities of blood sugar management and strive towards optimal well-being.What is a normal A1c level for adults?
+A normal A1c level for adults is typically considered to be below 5.7%.
How often should I get my A1c levels checked?
+The frequency of A1c checks depends on your health status and whether you have diabetes. Generally, individuals with diabetes should have their A1c levels checked every 3 months, while those without diabetes may only need it once a year.
Can lifestyle changes alone lower my A1c levels?
+Yes, adopting healthy lifestyle habits such as a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and weight management can help lower A1c levels. However, for some individuals, especially those with diabetes, medication may also be necessary to achieve and maintain target A1c levels.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences regarding maintaining normal A1c levels. How have you managed to keep your blood sugar levels under control? What challenges have you faced, and how did you overcome them? Your insights can provide valuable support and inspiration to others on their own journey to optimal health.
