Intro
Discover normal A1c ranges, understanding blood sugar levels, and diabetes management with our guide on healthy A1c targets, prediabetes, and glycemic control for optimal wellness.
Maintaining a healthy blood sugar level is crucial for overall well-being, especially for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. The A1c test, also known as the hemoglobin A1c or HbA1c test, is a blood test that measures the average level of glucose in the blood over the past 2 to 3 months. It's a vital tool for diagnosing and managing diabetes. Understanding the normal A1c ranges is essential for individuals to take control of their health and make informed decisions about their lifestyle and treatment options.
The importance of A1c tests cannot be overstated, as they provide a clear picture of how well the body is managing blood sugar levels over time. This information is vital for individuals with diabetes, as it helps them adjust their treatment plans, including diet, exercise, and medication, to achieve optimal blood sugar control. Moreover, for those without diabetes, knowing their A1c levels can help identify potential risks and encourage preventive measures to avoid developing the condition. The test is simple, requiring only a blood sample, and the results are typically available quickly.
For individuals looking to understand their A1c results, it's essential to recognize that the test measures the percentage of glucose that has bound to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Normal A1c ranges indicate good blood sugar control, while higher levels suggest the presence of diabetes or prediabetes. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) provides guidelines for interpreting A1c results, categorizing them into different levels of blood sugar control. Understanding these categories and what they mean is the first step towards managing diabetes effectively or preventing its onset.
Understanding A1c Levels
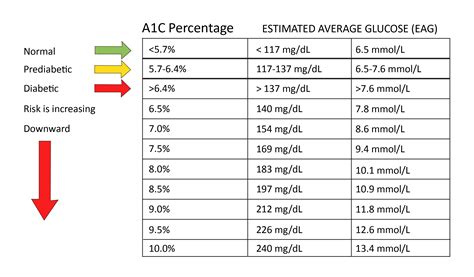
A1c levels are a critical marker for diabetes management and prevention. They reflect average blood glucose levels over the preceding 2 to 3 months, providing a comprehensive view of how well diabetes is being controlled. The ADA recommends the following A1c targets for different groups: for most adults, an A1c level less than 7% is considered a good target, though this may vary depending on the individual's health status, duration of diabetes, life expectancy, resources, and support system. For example, less stringent A1c goals (such as <8%) may be appropriate for patients with limited life expectancy, comorbid conditions, extensive insulin use, or a history of severe hypoglycemia.
A1c Targets for Different Groups
A1c targets can vary significantly among different groups, including children, pregnant women, and older adults. For instance, the target A1c for children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes is typically less than 7.5%, reflecting the need for tight blood sugar control to support growth and development while minimizing the risk of long-term complications. Pregnant women with diabetes aim for even lower targets, usually less than 6.5%, to reduce the risk of complications for both the mother and the baby. Understanding these specific targets is crucial for managing diabetes effectively in diverse populations.Normal A1c Ranges
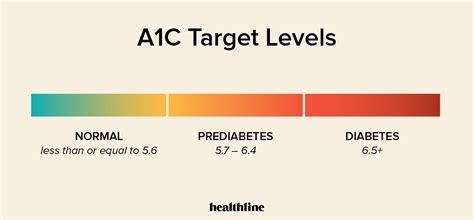
Normal A1c ranges are typically considered to be below 5.7%. This level indicates that the individual has a low risk of developing diabetes and is managing their blood sugar levels effectively. For individuals with diabetes, achieving an A1c level as close to the normal range as possible is a key goal, as it reflects good blood sugar control and reduces the risk of diabetes-related complications. However, it's essential to note that A1c targets may vary based on individual factors, such as age, other health conditions, and the presence of complications.
Interpreting A1c Results
Interpreting A1c results correctly is vital for understanding an individual's risk of diabetes and for managing the condition effectively. An A1c level between 5.7% and 6.4% indicates prediabetes, a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. This range signals an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes and heart disease. An A1c level of 6.5% or higher indicates diabetes. For individuals with diabetes, regular A1c tests help determine how well their treatment plan is working and whether adjustments are needed.Predabetes and Diabetes
Prediabetes and diabetes are conditions characterized by elevated blood sugar levels. Prediabetes is a precursor to type 2 diabetes, where the body's cells become resistant to insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels. If left untreated, prediabetes can progress to type 2 diabetes, a condition that requires lifelong management to prevent serious health complications, including heart disease, kidney failure, and nerve damage. Understanding the difference between prediabetes and diabetes, and knowing the A1c levels that define these conditions, is crucial for early intervention and effective management.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing A1c Levels
For individuals looking to manage their A1c levels, whether to prevent diabetes or to control the condition, several lifestyle changes can be beneficial. These include adopting a healthy diet that is low in sugar and saturated fats, engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming, to improve insulin sensitivity, and maintaining a healthy weight to reduce the risk of insulin resistance. Additionally, quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption can also contribute to better blood sugar control. For those with diabetes, working closely with a healthcare provider to adjust medication and insulin doses as needed is also crucial.Managing Diabetes

Managing diabetes requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular monitoring of blood sugar levels. The goal of diabetes management is to keep blood sugar levels as close to normal as possible to prevent complications. This can involve a combination of diet, exercise, and medication, including insulin therapy for some individuals. Regular A1c tests are a cornerstone of diabetes management, providing valuable feedback on the effectiveness of the current treatment plan and guiding adjustments as needed.
Technologies for Diabetes Management
Advances in technology have significantly improved diabetes management, offering individuals more tools and flexibility in controlling their condition. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems, for example, provide real-time glucose readings, helping individuals make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication. Insulin pumps and smart insulin pens are other technologies that have revolutionized diabetes care, offering precise insulin dosing and reducing the burden of injections. Mobile apps and online platforms also play a crucial role in diabetes management, providing educational resources, tracking tools, and community support.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, understanding normal A1c ranges and their implications for diabetes management is essential for individuals looking to take control of their health. By recognizing the importance of A1c tests, understanding how to interpret results, and making informed lifestyle and treatment decisions, individuals can effectively manage diabetes and prevent its onset. Whether through dietary changes, increased physical activity, or the use of advanced technologies, there are numerous strategies available for achieving and maintaining good blood sugar control.
Call to Action
For readers looking to learn more about managing their A1c levels or seeking support in their diabetes journey, there are many resources available. Consulting with a healthcare provider is the first step towards understanding individual A1c targets and developing a personalized treatment plan. Additionally, engaging with online communities, support groups, and educational websites can provide valuable insights and encouragement. By taking proactive steps towards managing blood sugar levels, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of diabetes-related complications and improve their overall quality of life.What is the normal range for A1c levels?
+Normal A1c levels are typically considered to be below 5.7%. This range indicates a low risk of developing diabetes and effective management of blood sugar levels.
How often should I get an A1c test if I have diabetes?
+Individuals with diabetes should get an A1c test at least twice a year, but the frequency may increase based on the stability of their condition and the effectiveness of their treatment plan.
Can lifestyle changes alone lower A1c levels?
+Yes, lifestyle changes such as adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight can significantly lower A1c levels and improve blood sugar control.
We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, or questions about managing A1c levels and diabetes in the comments below. Your insights can help others on their journey towards better health. Additionally, consider sharing this article with friends and family who might benefit from understanding the importance of A1c tests and diabetes management. Together, we can promote healthier living and support those affected by diabetes.
