Intro
Discover common Levothyroxine side effects, including thyroid hormone imbalance, weight changes, and medication interactions, to manage hypothyroidism symptoms and minimize adverse reactions.
The importance of understanding levothyroxine side effects cannot be overstated, as this medication is widely prescribed for individuals with hypothyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. Levothyroxine, a synthetic form of thyroxine (T4), works by replacing the missing hormones in the body, thereby regulating metabolism, energy production, and overall thyroid function. However, like all medications, levothyroxine can cause a range of side effects, some of which may be mild and temporary, while others can be more severe and persistent. It is essential for patients to be aware of these potential side effects to ensure they can manage their condition effectively and minimize any adverse reactions.
For individuals taking levothyroxine, it is crucial to monitor their body's response to the medication, as side effects can vary significantly from person to person. Some people may experience no side effects at all, while others may encounter mild symptoms that disappear on their own. However, in some cases, levothyroxine side effects can be more pronounced, requiring medical attention or adjustments to the treatment plan. By understanding the potential side effects of levothyroxine, patients can better navigate their treatment, communicate effectively with their healthcare providers, and maintain optimal thyroid health.
The management of hypothyroidism with levothyroxine is a long-term commitment, and patients must be aware of the potential risks and benefits associated with this medication. While levothyroxine is generally considered safe and effective, its side effects can impact daily life, relationships, and overall well-being. Therefore, it is vital to approach levothyroxine treatment with a comprehensive understanding of its potential effects, both positive and negative. By doing so, individuals with hypothyroidism can work closely with their healthcare providers to find the right balance of medication and lifestyle adjustments, ultimately achieving optimal thyroid function and improving their quality of life.
Introduction to Levothyroxine
How Levothyroxine Works
Levothyroxine is absorbed into the bloodstream after oral administration, where it binds to plasma proteins and is transported to the liver and other tissues. The medication is then converted into T3, which enters the cells and regulates gene expression, protein synthesis, and other cellular processes. The effects of levothyroxine can be seen in various bodily systems, including the cardiovascular, nervous, and muscular systems. By restoring normal thyroid hormone levels, levothyroxine helps alleviate symptoms of hypothyroidism, such as fatigue, weight gain, and dry skin.Common Levothyroxine Side Effects

These side effects are often mild and temporary, resolving on their own within a few weeks of treatment. However, in some cases, they can be more severe or persistent, requiring medical attention or adjustments to the treatment plan.
Less Common Levothyroxine Side Effects
In addition to the common side effects, levothyroxine can also cause less frequent but more serious adverse reactions. These may include: * Allergic reactions, such as hives, itching, or difficulty breathing * Chest pain or irregular heartbeat * Seizures or tremors * Changes in vision or blurred vision * Increased risk of osteoporosis * Menstrual irregularities or fertility problemsIt is essential to seek medical attention immediately if any of these less common side effects occur, as they can be a sign of a more serious underlying condition.
Factors Influencing Levothyroxine Side Effects
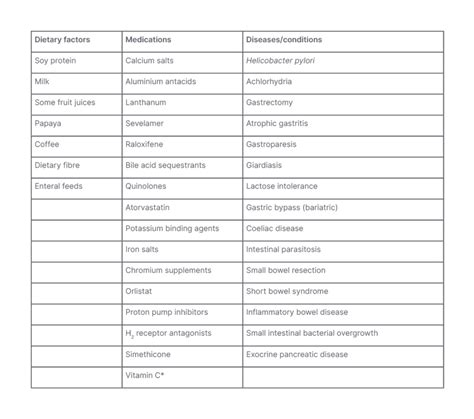
By understanding these factors, healthcare providers can tailor treatment plans to minimize the risk of side effects and optimize the benefits of levothyroxine therapy.
Managing Levothyroxine Side Effects
If side effects occur, there are several strategies that can help manage them. These may include: * Adjusting the dose or timing of levothyroxine administration * Switching to a different formulation or brand of levothyroxine * Implementing lifestyle changes, such as dietary modifications or stress reduction techniques * Adding supplemental medications or therapies to alleviate specific side effects * Regular monitoring of thyroid hormone levels and adjustment of the treatment plan as neededBy working closely with their healthcare providers, individuals taking levothyroxine can minimize the risk of side effects and achieve optimal thyroid health.
Long-Term Effects of Levothyroxine

Regular monitoring of thyroid hormone levels, bone density, and cardiovascular health can help mitigate these long-term effects and ensure the safe and effective use of levothyroxine.
Special Considerations for Levothyroxine Use
Certain individuals may require special consideration when taking levothyroxine, including: * Pregnant or breastfeeding women: Levothyroxine is generally considered safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding, but close monitoring of thyroid hormone levels is essential to ensure the health of both mother and baby. * Older adults: Older adults may be more susceptible to levothyroxine side effects, particularly those with a history of cardiovascular disease or osteoporosis. * Children and adolescents: Levothyroxine is often used to treat hypothyroidism in children and adolescents, but close monitoring of growth and development is essential to ensure the medication is not affecting their physical or cognitive development.By taking these special considerations into account, healthcare providers can tailor treatment plans to meet the unique needs of each individual, minimizing the risk of side effects and optimizing the benefits of levothyroxine therapy.
Conclusion and Future Directions

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with levothyroxine in the comments below. Have you or a loved one taken levothyroxine for hypothyroidism? What side effects have you experienced, and how have you managed them? Your insights and stories can help others navigate their own treatment journeys and inspire further research into the effects of levothyroxine.
What is the most common side effect of levothyroxine?
+The most common side effects of levothyroxine include nausea, headaches, fatigue, and weight loss.
Can levothyroxine cause hair loss?
+Yes, levothyroxine can cause hair loss in some individuals, particularly during the initial treatment phase.
Is levothyroxine safe during pregnancy?
+Levothyroxine is generally considered safe during pregnancy, but close monitoring of thyroid hormone levels is essential to ensure the health of both mother and baby.
