Intro
Normal A1C levels are a crucial aspect of diabetes management and overall health. The A1C test, also known as the hemoglobin A1C or HbA1C test, measures the average level of glucose in the blood over the past 2 to 3 months. It's a vital tool for diagnosing and monitoring diabetes, as well as for assessing the risk of developing the condition. In this article, we'll delve into the importance of normal A1C levels, their benefits, and how to achieve and maintain them.
The significance of normal A1C levels cannot be overstated. Elevated A1C levels are a clear indicator of diabetes, and even slightly high levels can increase the risk of developing complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. On the other hand, maintaining normal A1C levels can help prevent or delay the onset of these complications, improving overall health and quality of life. For individuals with diabetes, achieving normal A1C levels can be a challenging but rewarding goal, and it's essential to understand the factors that influence A1C levels and how to manage them effectively.
Understanding normal A1C levels is also crucial for individuals without diabetes, as it can help identify those at risk of developing the condition. By monitoring A1C levels and making lifestyle changes as needed, individuals can reduce their risk of developing diabetes and its associated complications. Furthermore, normal A1C levels can also have a positive impact on overall health, reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease, cognitive decline, and other conditions. With the increasing prevalence of diabetes worldwide, it's essential to prioritize normal A1C levels and take proactive steps to maintain them.
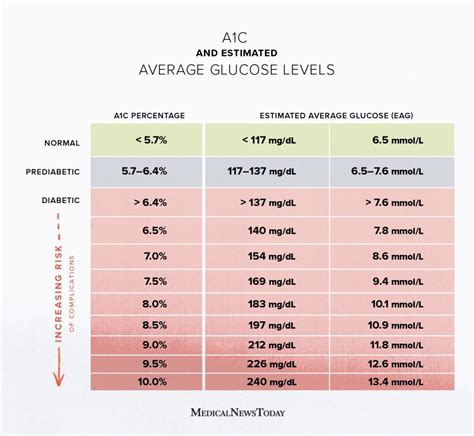
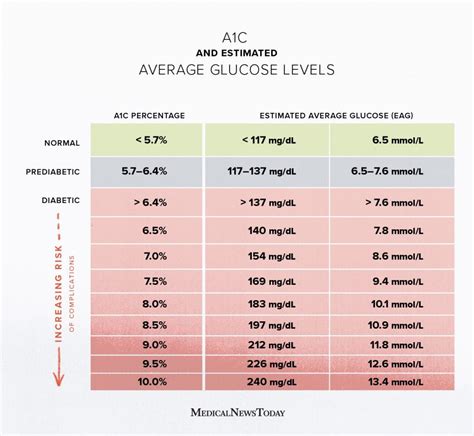
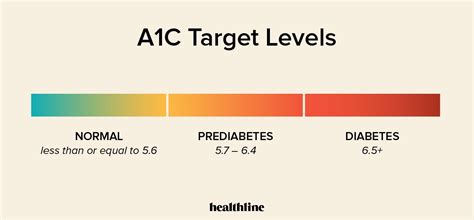
What are Normal A1C Levels?
Benefits of Normal A1C Levels
The benefits of normal A1C levels are numerous and well-documented. Some of the most significant advantages include: * Reduced risk of diabetes complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage * Improved blood sugar control and reduced risk of hypoglycemia * Enhanced overall health and quality of life * Reduced risk of cardiovascular disease, cognitive decline, and other conditions * Improved insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism * Reduced risk of developing type 2 diabetes in individuals with prediabetesHow to Achieve Normal A1C Levels

Factors that Influence A1C Levels
Several factors can influence A1C levels, including: * Diet and nutrition * Physical activity and exercise * Weight and body composition * Sleep and stress levels * Medications and supplements * Underlying medical conditions, such as kidney or liver disease * Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during pregnancy or menopauseMonitoring and Maintaining Normal A1C Levels
Common Challenges and Solutions
Common challenges to achieving and maintaining normal A1C levels include: * Difficulty making lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet or exercise routine * Struggling with medication adherence or side effects * Managing stress and emotional well-being * Dealing with underlying medical conditions or comorbidities * Accessing affordable healthcare and diabetes management resourcesConclusion and Next Steps
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with normal A1C levels in the comments below. What strategies have you found most effective for achieving and maintaining healthy blood sugar levels? What challenges have you faced, and how have you overcome them? By sharing our knowledge and experiences, we can work together to promote healthier lifestyles and reduce the risk of diabetes and its associated complications.
What is a normal A1C level?
+A normal A1C level is typically defined as less than 5.7%. This value indicates that the average level of glucose in the blood over the past 2 to 3 months is within a healthy range.
How often should I get my A1C levels checked?
+The frequency of A1C testing depends on individual factors, such as the presence of diabetes, age, and health status. Typically, A1C levels are checked every 3 to 6 months.
What can I do to lower my A1C levels?
+To lower your A1C levels, focus on making lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, losing weight if necessary, and managing stress levels. Additionally, work with your healthcare provider to adjust your treatment plan as needed.
