Intro
Discover RSV symptoms, causes, and treatments. Learn about respiratory syncytial virus infection, diagnosis, and prevention methods to protect against RSV disease and its complications in infants, toddlers, and adults.
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a common and highly contagious virus that affects people of all ages, but it's most severe in young children and older adults. RSV is the leading cause of lower respiratory infections, such as bronchiolitis and pneumonia, in children under the age of two. Understanding the symptoms of RSV is crucial for early detection and treatment, which can help prevent complications and reduce the risk of severe illness.
RSV infections typically occur during the fall and winter months, with the peak season usually occurring between December and February. The virus spreads quickly through respiratory droplets, such as those produced by coughing and sneezing, as well as through contact with contaminated surfaces. In fact, RSV can survive on surfaces for up to 6 hours, making it easy to spread in areas with high foot traffic, such as schools, daycare centers, and hospitals.
The symptoms of RSV can vary depending on the age and health of the individual. In most cases, RSV infections cause mild, cold-like symptoms that can be treated with rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications. However, in severe cases, RSV can cause life-threatening complications, such as respiratory failure, bronchiolitis, and pneumonia. It's essential to recognize the symptoms of RSV and seek medical attention immediately if you or a loved one is experiencing severe or persistent symptoms.
Understanding RSV Symptoms
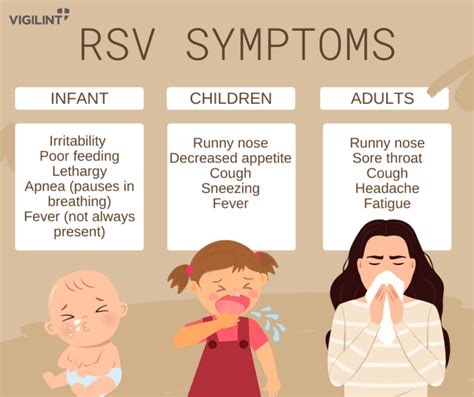
RSV symptoms can be divided into two categories: mild and severe. Mild symptoms are typically seen in healthy adults and children, while severe symptoms are more common in high-risk individuals, such as young children, older adults, and those with underlying health conditions. Common mild symptoms of RSV include runny nose, coughing, sneezing, fever, and loss of appetite. In severe cases, RSV can cause symptoms such as wheezing, difficulty breathing, rapid breathing, chest pain, and cyanosis (a bluish discoloration of the skin).
RSV Symptoms in Children
RSV symptoms in children can be particularly concerning, as they can quickly become severe. In infants, RSV can cause apnea (pauses in breathing), which can be life-threatening if left untreated. Other common symptoms of RSV in children include irritability, lethargy, and loss of interest in feeding. In severe cases, RSV can cause bronchiolitis, which is a inflammation of the small airways in the lungs. Bronchiolitis can cause symptoms such as wheezing, coughing, and difficulty breathing, which can be treated with oxygen therapy and medication.Diagnosing RSV Infections
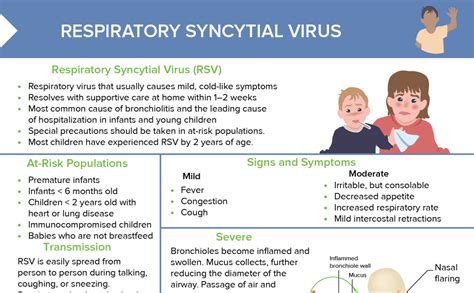
Diagnosing RSV infections can be challenging, as the symptoms are often similar to those of other respiratory viruses. A physical examination and medical history can help healthcare providers suspect RSV, but a definitive diagnosis requires laboratory testing. The most common tests used to diagnose RSV include rapid antigen detection tests, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests, and viral cultures. These tests can detect the presence of RSV in respiratory secretions, such as nasal swabs or throat swabs.
Treatment Options for RSV Infections
Treatment for RSV infections typically focuses on relieving symptoms and supporting the body's natural immune response. In mild cases, treatment may include rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, to reduce fever and relieve pain. In severe cases, treatment may require hospitalization and oxygen therapy to support breathing. In addition, medications such as bronchodilators and corticosteroids may be prescribed to help open up the airways and reduce inflammation.Preventing RSV Infections

Preventing RSV infections requires a combination of good hygiene practices, vaccination, and avoidance of high-risk activities. The most effective way to prevent RSV is through vaccination, which is available for high-risk individuals, such as young children and older adults. The RSV vaccine is typically administered in the fall, before the start of the RSV season. In addition to vaccination, good hygiene practices, such as frequent handwashing, avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick, and avoiding sharing utensils or personal items, can help reduce the risk of transmission.
High-Risk Groups for RSV Infections
Certain groups are at higher risk for developing severe RSV infections, including young children, older adults, and individuals with underlying health conditions. Premature infants, children with heart disease or lung disease, and those with weakened immune systems are particularly vulnerable to severe RSV infections. In addition, older adults, especially those with underlying health conditions, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or heart disease, are also at higher risk for developing severe RSV infections.Complications of RSV Infections

RSV infections can cause a range of complications, from mild to severe. In severe cases, RSV can cause respiratory failure, which requires mechanical ventilation and hospitalization. Other complications of RSV include bronchiolitis, pneumonia, and otitis media (middle ear infection). In addition, RSV infections can exacerbate underlying health conditions, such as asthma or COPD, and increase the risk of developing secondary bacterial infections.
Long-Term Effects of RSV Infections
The long-term effects of RSV infections are not well understood, but research suggests that severe RSV infections in early childhood may be associated with an increased risk of developing asthma and other respiratory diseases later in life. In addition, RSV infections have been linked to an increased risk of developing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and other lung diseases in older adults.Current Research on RSV

Current research on RSV is focused on developing effective treatments and prevention strategies. Several promising treatments, including antiviral medications and immunotherapy, are being investigated in clinical trials. In addition, researchers are working to develop a vaccine that can provide long-term protection against RSV. Other areas of research include the development of point-of-care diagnostic tests and the investigation of the genetic factors that contribute to severe RSV infections.
Future Directions for RSV Research
Future directions for RSV research include the development of more effective treatments and prevention strategies, as well as a better understanding of the genetic and environmental factors that contribute to severe RSV infections. In addition, researchers are exploring the potential for RSV to be used as a model for understanding other respiratory viruses, such as influenza and coronaviruses.What are the symptoms of RSV infection?
+The symptoms of RSV infection can vary depending on the age and health of the individual, but common symptoms include runny nose, coughing, sneezing, fever, and loss of appetite.
How is RSV infection diagnosed?
+RSV infection is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory testing, such as rapid antigen detection tests or PCR tests.
What are the complications of RSV infection?
+RSV infection can cause a range of complications, from mild to severe, including respiratory failure, bronchiolitis, pneumonia, and otitis media.
How can RSV infection be prevented?
+RSV infection can be prevented through a combination of good hygiene practices, vaccination, and avoidance of high-risk activities, such as close contact with individuals who are sick.
What is the treatment for RSV infection?
+Treatment for RSV infection typically focuses on relieving symptoms and supporting the body's natural immune response, and may include rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications, as well as hospitalization and oxygen therapy in severe cases.
In summary, RSV is a common and highly contagious virus that can cause severe respiratory illnesses, particularly in young children and older adults. Understanding the symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of RSV is crucial for reducing the risk of complications and promoting public health. By staying informed and taking proactive steps to prevent RSV, individuals can help protect themselves and their loved ones from the risks associated with this virus. We encourage readers to share their experiences and ask questions in the comments section below, and to explore the resources and references provided for further information on RSV and its prevention.
