Intro
Identify Blocked Small Bowel Obstruction Symptoms, including severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting, and learn about intestinal blockage causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for this serious digestive condition.
The small bowel, also known as the small intestine, plays a vital role in the digestive system by breaking down food into nutrients that can be absorbed by the body. However, when the small bowel is blocked, it can lead to a range of symptoms that can be severe and even life-threatening if left untreated. A blocked small bowel obstruction, also known as a small bowel obstruction, occurs when the normal flow of food, fluids, and gas through the small intestine is blocked, preventing the body from absorbing the necessary nutrients.
The symptoms of a blocked small bowel obstruction can vary depending on the severity of the blockage and the individual's overall health. In some cases, the symptoms may develop gradually over time, while in other cases, they may appear suddenly and without warning. Some common symptoms of a blocked small bowel obstruction include severe abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, bloating and gas, constipation or inability to pass gas, and abdominal tenderness. If left untreated, a blocked small bowel obstruction can lead to serious complications, such as dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and even death.
It is essential to seek medical attention immediately if symptoms of a blocked small bowel obstruction occur, as prompt treatment can help prevent serious complications and improve outcomes. In this article, we will delve deeper into the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment of blocked small bowel obstructions, providing readers with a comprehensive understanding of this condition. We will also explore the importance of seeking medical attention promptly and the various treatment options available for managing this condition.
Understanding Small Bowel Obstruction
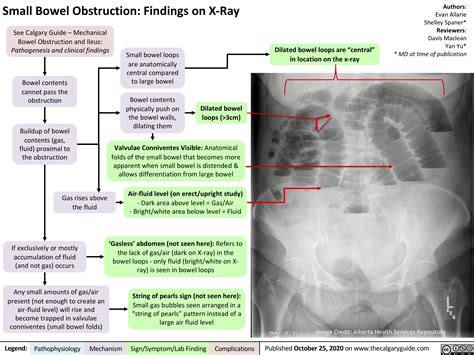
Causes of Small Bowel Obstruction
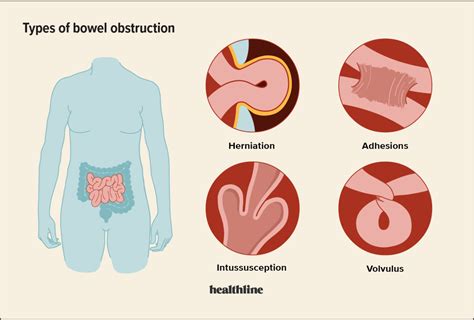
The causes of small bowel obstruction can be divided into two main categories: mechanical and non-mechanical. Mechanical causes include physical blockages, such as adhesions, hernias, and tumors, while non-mechanical causes include conditions that affect the motility of the intestine, such as intestinal pseudo-obstruction. Other causes of small bowel obstruction include volvulus, which is a twisting of the intestine, and intussusception, which is a telescoping of one portion of the intestine into another.Symptoms of Small Bowel Obstruction
In some cases, the symptoms may develop gradually over time, while in other cases, they may appear suddenly and without warning. It is essential to seek medical attention immediately if symptoms of small bowel obstruction occur, as prompt treatment can help prevent serious complications and improve outcomes.
Diagnosis of Small Bowel Obstruction
The diagnosis of small bowel obstruction is typically made using a combination of physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests. The physical examination may reveal abdominal tenderness, distension, and guarding, which is a tightening of the abdominal muscles. Imaging tests, such as X-rays, computed tomography (CT) scans, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, can help confirm the diagnosis and identify the location and cause of the blockage.Treatment of Small Bowel Obstruction
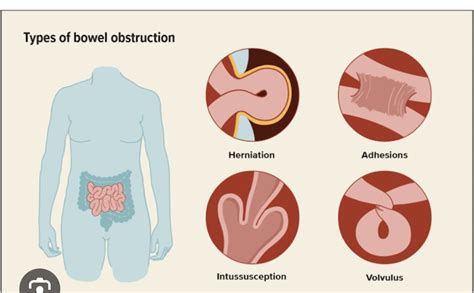
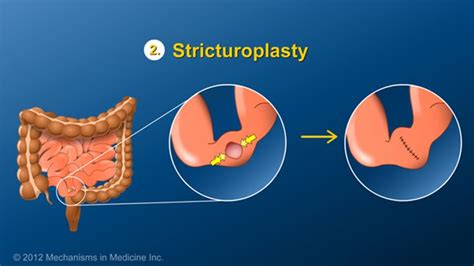
Nonsurgical Treatment
Nonsurgical treatment of small bowel obstruction typically involves bowel rest, fluids, and pain management. Bowel rest involves avoiding solid foods and liquids to allow the bowel to rest and recover. Fluids, such as water and electrolyte solutions, may be given intravenously to help prevent dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. Pain management may involve the use of medications, such as narcotics, to help control abdominal pain.Surgical Treatment
Complications of Small Bowel Obstruction
The complications of small bowel obstruction can be severe and even life-threatening if left untreated. Some possible complications include: * Dehydration and electrolyte imbalances * Bowel ischemia, which is a lack of blood flow to the bowel * Bowel necrosis, which is the death of bowel tissue * Perforation of the bowel, which can lead to peritonitis and sepsis * DeathIt is essential to seek medical attention immediately if symptoms of small bowel obstruction occur, as prompt treatment can help prevent serious complications and improve outcomes.
Prevention of Small Bowel Obstruction
Risk Factors for Small Bowel Obstruction
There are several risk factors for small bowel obstruction, including: * Age: Older adults are at higher risk for small bowel obstruction * Sex: Females are at higher risk for small bowel obstruction * Family history: Individuals with a family history of bowel disorders are at higher risk for small bowel obstruction * Medical history: Individuals with a history of bowel disorders, such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis, are at higher risk for small bowel obstruction * Surgical history: Individuals who have had abdominal surgery are at higher risk for small bowel obstructionWhat are the symptoms of small bowel obstruction?
+The symptoms of small bowel obstruction include severe abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, bloating and gas, constipation or inability to pass gas, and abdominal tenderness.
How is small bowel obstruction diagnosed?
+Small bowel obstruction is typically diagnosed using a combination of physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests, such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans.
What is the treatment for small bowel obstruction?
+The treatment for small bowel obstruction depends on the underlying cause and severity of the blockage, and may involve supportive care, such as bowel rest, fluids, and pain management, or surgery to relieve the blockage and restore normal bowel function.
Can small bowel obstruction be prevented?
+While it may not be possible to prevent all cases of small bowel obstruction, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk, such as avoiding heavy lifting and bending, eating a high-fiber diet, and managing stress.
What are the complications of small bowel obstruction?
+The complications of small bowel obstruction can be severe and even life-threatening if left untreated, and may include dehydration and electrolyte imbalances, bowel ischemia, bowel necrosis, perforation of the bowel, and death.
In conclusion, small bowel obstruction is a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention to prevent serious complications and improve outcomes. By understanding the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment of small bowel obstruction, individuals can take steps to reduce their risk and seek medical attention immediately if symptoms occur. We encourage readers to share this article with others, and to take the necessary steps to prioritize their health and well-being. If you have any questions or concerns about small bowel obstruction, please do not hesitate to reach out to a qualified healthcare professional.
