Intro
Discover normal blood glucose levels and learn how to manage blood sugar, insulin, and diabetes through healthy lifestyle choices and glucose monitoring, ensuring optimal glucose control and overall well-being.
Maintaining normal blood glucose levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Blood glucose, also known as blood sugar, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. When we eat, our body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. The pancreas regulates blood glucose levels by releasing insulin, a hormone that helps cells absorb glucose. In this article, we will delve into the importance of normal blood glucose levels, how they are measured, and what factors can affect them.
Understanding normal blood glucose levels is essential for preventing and managing conditions like diabetes, which affects millions of people worldwide. Diabetes occurs when the body is unable to produce enough insulin or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces, leading to high blood glucose levels. If left unmanaged, high blood glucose levels can cause serious health complications, including heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. Therefore, it is vital to understand what constitutes normal blood glucose levels and how to maintain them.
The importance of normal blood glucose levels cannot be overstated. When blood glucose levels are within a healthy range, the body can function properly, and the risk of developing chronic diseases is reduced. Normal blood glucose levels also help to prevent complications associated with diabetes, such as blindness, amputations, and kidney failure. Furthermore, maintaining normal blood glucose levels can improve overall quality of life, increase energy levels, and enhance mental clarity. In the following sections, we will explore the factors that affect blood glucose levels, how to measure them, and strategies for maintaining normal levels.
What are Normal Blood Glucose Levels?

Factors that Affect Blood Glucose Levels
Several factors can affect blood glucose levels, including diet, physical activity, stress, and certain medications. A diet high in carbohydrates, especially simple sugars, can cause blood glucose levels to rise. On the other hand, regular physical activity can help lower blood glucose levels by increasing insulin sensitivity. Stress can also affect blood glucose levels, as it can cause the body to release stress hormones like cortisol, which can raise blood glucose levels. Certain medications, such as steroids and certain psychiatric medications, can also impact blood glucose levels.How to Measure Blood Glucose Levels
Tips for Maintaining Normal Blood Glucose Levels
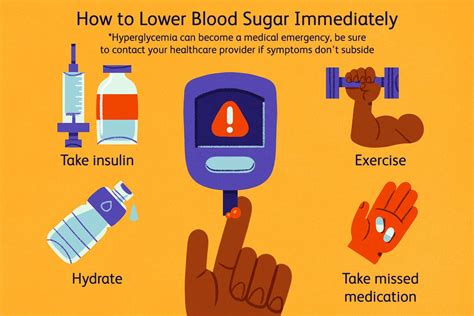
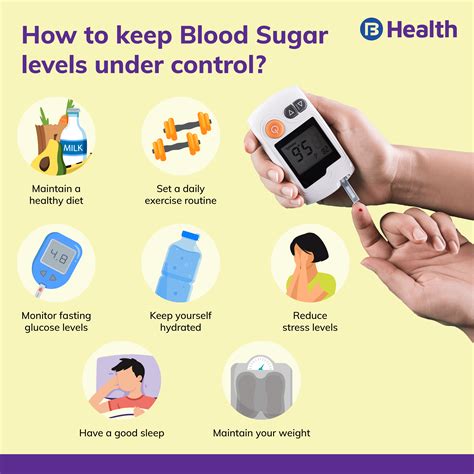
Maintaining normal blood glucose levels requires a combination of healthy lifestyle habits and, if necessary, medication. Here are some tips for maintaining normal blood glucose levels: * Eat a balanced diet that is low in simple sugars and refined carbohydrates * Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming * Get enough sleep each night, aiming for 7-8 hours * Manage stress through techniques like meditation or deep breathing * Monitor blood glucose levels regularly, especially if you have diabetes * Take medication as prescribed by your healthcare providerStrategies for Lowering Blood Glucose Levels
Common Mistakes that Can Raise Blood Glucose Levels
There are several common mistakes that can raise blood glucose levels, including: * Eating too many simple sugars and refined carbohydrates * Not getting enough physical activity * Not monitoring blood glucose levels regularly * Not taking medication as prescribed * Not managing stress effectively * Not getting enough sleepThe Importance of Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels
How to Interpret Blood Glucose Results
Interpreting blood glucose results can be complex, but here are some general guidelines: * If your blood glucose level is below 70 mg/dL, you may be experiencing hypoglycemia * If your blood glucose level is between 70-140 mg/dL, your levels are within a healthy range * If your blood glucose level is above 140 mg/dL, you may be experiencing hyperglycemia * If you have diabetes, your healthcare provider may recommend specific blood glucose targetsConclusion and Next Steps

What are the symptoms of high blood glucose levels?
+The symptoms of high blood glucose levels include increased thirst and urination, blurred vision, fatigue, and slow healing of cuts and wounds.
How often should I monitor my blood glucose levels?
+The frequency of monitoring blood glucose levels depends on the individual and their healthcare provider's recommendations. Generally, people with diabetes should monitor their blood glucose levels at least 4-6 times per day.
What are the risks of not managing high blood glucose levels?
+The risks of not managing high blood glucose levels include heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and blindness. If left unmanaged, high blood glucose levels can also lead to amputations and death.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of normal blood glucose levels and the importance of maintaining them. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with friends and family who may benefit from this information. By working together, we can promote healthy blood glucose levels and prevent complications associated with diabetes.
