Intro
Discover the 5 California pay dates and understand California payroll laws, including pay periods, pay stubs, and wage regulations, to ensure compliance and avoid penalties.
The state of California is known for its strong labor laws, which provide numerous protections for employees. One of the key aspects of these laws is the requirement for regular pay dates, ensuring that employees receive their wages in a timely manner. In California, employers are required to pay their employees on a regular basis, with specific rules governing the frequency and timing of paydays.
The importance of regular pay dates cannot be overstated, as it allows employees to budget and plan their finances with certainty. For employers, adhering to these regulations helps maintain a positive and productive work environment, as employees are more likely to be satisfied and motivated when they receive their wages on time. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of California pay dates, exploring the rules and regulations that govern this aspect of employment in the state.
California's labor laws are designed to protect employees and ensure they are treated fairly by their employers. The state's Department of Industrial Relations, through the Division of Labor Standards Enforcement (DLSE), is responsible for enforcing these laws, including those related to pay dates. Employers in California must comply with the state's pay date requirements, which are outlined in the California Labor Code. Understanding these regulations is crucial for both employers and employees, as it helps prevent disputes and ensures a smooth employment relationship.
California Pay Date Requirements

In California, the pay date requirements are based on the type of employee and the frequency of their pay. The California Labor Code specifies that employees must be paid at least twice a month, with no more than 16 days between pay dates for monthly paid employees. For example, if an employee is paid on the 1st and 15th of each month, the employer must ensure that these pay dates are consistent and that the employee receives their wages on or before these dates.
Pay Frequency for Different Types of Employees
The pay frequency for different types of employees in California can vary. For instance: - Executive, administrative, and professional employees who are exempt from overtime requirements may be paid once a month. - Non-exempt employees, who are entitled to overtime pay, must be paid at least twice a month. - Employees who are paid on an hourly or daily basis may be paid weekly, biweekly, or semimonthly.Penalties for Late Payment of Wages

California law imposes penalties on employers who fail to pay their employees on time. If an employer willfully fails to pay an employee's wages, including the failure to pay on the designated pay date, the employee may be entitled to waiting time penalties. These penalties can be substantial, with the employer required to pay the employee's daily rate of pay for each day the wages are late, up to a maximum of 30 days.
Calculating Waiting Time Penalties
Calculating waiting time penalties involves determining the employee's daily rate of pay and then multiplying this by the number of days the wages are late. For example, if an employee's daily rate of pay is $200 and the employer is 10 days late in paying their wages, the waiting time penalty would be $200 * 10 = $2,000.Final Paychecks in California

In California, when an employment relationship ends, the employer is required to provide the employee with their final paycheck immediately, if the employee is terminated or laid off, or within 72 hours if the employee quits. The final paycheck must include all accrued wages, including any unused vacation time, unless the employer has a written policy that forfeits unused vacation time upon termination.
Requirements for Final Paychecks
The requirements for final paychecks in California are strict, with employers required to: - Pay all accrued wages, including unused vacation time, unless a written policy specifies otherwise. - Provide the final paycheck to the employee immediately if they are terminated or laid off. - Provide the final paycheck to the employee within 72 hours if they quit.Pay Stub Requirements in California
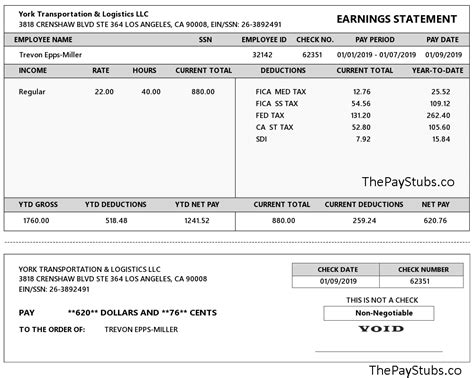
California law requires employers to provide their employees with detailed pay stubs, either in paper form or electronically, with each payment of wages. The pay stub must include specific information, such as the gross wages earned, the total hours worked, the number of piece-rate units earned and any applicable piece rate, all deductions, and the net wages earned.
Information Required on Pay Stubs
The information required on pay stubs in California includes: - Gross wages earned. - Total hours worked. - Number of piece-rate units earned and any applicable piece rate. - All deductions. - Net wages earned.Record Keeping Requirements

Employers in California are required to maintain accurate records of their employees' wages, hours worked, and other employment-related information. These records must be kept for a minimum of three years and must be made available to the employee or their representative upon request.
Types of Records to Maintain
Employers must maintain the following types of records: - Employee identification, including name, address, and social security number. - Job title and description. - Hours worked, including start and end times. - Wages paid, including gross and net amounts. - Deductions and benefits.Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, understanding California pay dates is crucial for both employers and employees. By adhering to the state's pay date requirements, employers can avoid penalties and maintain a positive work environment. Employees, on the other hand, can ensure they receive their wages in a timely manner, allowing them to budget and plan their finances effectively.
As the employment landscape in California continues to evolve, it's essential for employers and employees to stay informed about the latest developments in pay date regulations. This includes understanding the requirements for pay stubs, final paychecks, and record keeping, as well as being aware of the penalties for late payment of wages.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences regarding California pay dates in the comments below. Your insights can help others navigate the complexities of employment law in the state. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with your network to help spread awareness about this important topic.
What are the pay date requirements in California?
+In California, employees must be paid at least twice a month, with no more than 16 days between pay dates for monthly paid employees.
What are the penalties for late payment of wages in California?
+California law imposes waiting time penalties on employers who willfully fail to pay their employees on time, with the employer required to pay the employee's daily rate of pay for each day the wages are late, up to a maximum of 30 days.
What information must be included on pay stubs in California?
+Pay stubs in California must include the gross wages earned, total hours worked, number of piece-rate units earned and any applicable piece rate, all deductions, and the net wages earned.
