Intro
Understand normal blood sugar levels with our chart, featuring target ranges, glucose monitoring, and diabetes management tips, to maintain healthy blood glucose levels and prevent complications.
Maintaining normal blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Blood sugar, also known as glucose, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. When blood sugar levels are too high or too low, it can lead to various health problems, including diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. Understanding normal blood sugar levels and how to manage them is essential for preventing and managing these conditions.
The importance of maintaining normal blood sugar levels cannot be overstated. When blood sugar levels are within a healthy range, the body can function properly, and the risk of developing chronic diseases is reduced. On the other hand, high or low blood sugar levels can cause a range of symptoms, from mild to severe, and can even be life-threatening if left untreated. Therefore, it is essential to understand what constitutes normal blood sugar levels and how to maintain them through a healthy diet, regular exercise, and lifestyle changes.
Normal blood sugar levels vary throughout the day, depending on factors such as food intake, physical activity, and sleep. In general, normal blood sugar levels are between 70 and 140 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) for people without diabetes. However, these levels can fluctuate depending on various factors, including the time of day, meal times, and physical activity levels. Understanding these fluctuations and how to manage them is crucial for maintaining overall health and preventing chronic diseases.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
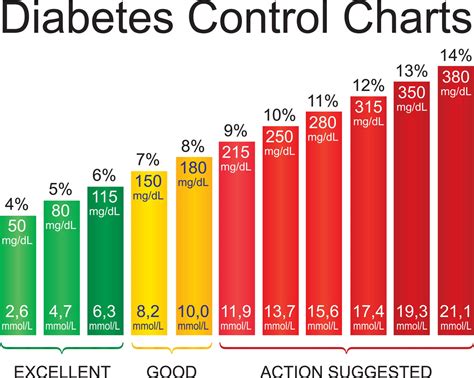
Blood sugar levels are measured using a blood glucose meter or through a lab test. The results are typically reported in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L). Normal blood sugar levels are typically classified into several categories, including:
- Fasting blood sugar: 70-99 mg/dL
- Postprandial blood sugar (after eating): Less than 140 mg/dL
- Random blood sugar: Less than 140 mg/dL
It is essential to note that these values can vary depending on the individual, their diet, and their physical activity levels. Additionally, some people may have different blood sugar level targets, such as pregnant women or people with certain medical conditions.
Factors That Affect Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can affect blood sugar levels, including: * Diet: Eating foods high in sugar, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats can cause blood sugar levels to rise. * Physical activity: Regular exercise can help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. * Sleep: Poor sleep quality and duration can disrupt blood sugar regulation and increase the risk of developing insulin resistance. * Stress: Chronic stress can raise blood sugar levels and worsen insulin resistance.Normal Blood Sugar Levels Chart

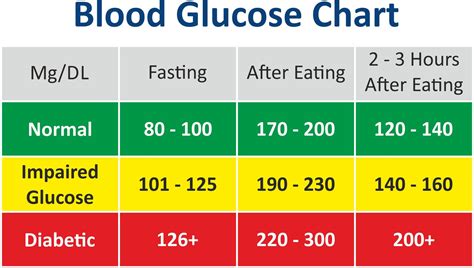
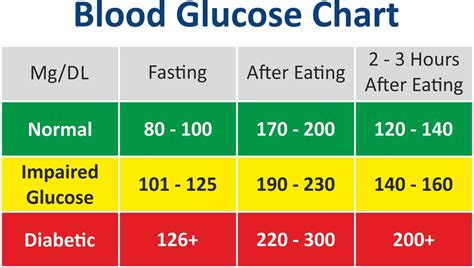
The following chart provides a general guide to normal blood sugar levels:
| Time | Normal Blood Sugar Level (mg/dL) |
|---|---|
| Fasting | 70-99 |
| 1 hour after eating | Less than 140 |
| 2 hours after eating | Less than 120 |
| Before bed | 100-140 |
It is essential to note that these values can vary depending on the individual and their specific circumstances. Additionally, people with diabetes or other medical conditions may have different blood sugar level targets.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Managing blood sugar levels requires a combination of healthy lifestyle habits, including: * Eating a balanced diet that is low in sugar, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats. * Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, jogging, or weightlifting. * Getting enough sleep and practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yoga. * Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly and adjusting diet and lifestyle habits as needed.Blood Sugar Levels and Diabetes
High blood sugar levels can increase the risk of developing diabetes, a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels and insulin resistance. There are two main types of diabetes:
- Type 1 diabetes: An autoimmune disease in which the body attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
- Type 2 diabetes: A metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion.
Both types of diabetes require careful management of blood sugar levels to prevent complications, such as heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage.
Diabetes Diagnosis and Treatment
Diabetes is typically diagnosed using a combination of physical examination, medical history, and lab tests, including: * Fasting blood glucose test * Oral glucose tolerance test * Hemoglobin A1c testTreatment for diabetes typically involves a combination of lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, and medication, such as metformin or insulin therapy.
Maintaining Normal Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining normal blood sugar levels requires a long-term commitment to healthy lifestyle habits, including:
- Eating a balanced diet that is low in sugar, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats.
- Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, jogging, or weightlifting.
- Getting enough sleep and practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yoga.
- Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly and adjusting diet and lifestyle habits as needed.
Additionally, people with diabetes or other medical conditions may need to work with their healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that takes into account their specific needs and circumstances.
Benefits of Maintaining Normal Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining normal blood sugar levels has numerous benefits, including: * Reducing the risk of developing chronic diseases, such as heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage. * Improving energy levels and reducing fatigue. * Enhancing cognitive function and reducing the risk of dementia. * Supporting weight loss and improving overall health and well-being.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, maintaining normal blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. By understanding what constitutes normal blood sugar levels and how to manage them through a healthy diet, regular exercise, and lifestyle changes, individuals can reduce their risk of developing chronic diseases and improve their overall health and well-being.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with maintaining normal blood sugar levels in the comments below. Additionally, if you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to us. We are committed to providing you with the most up-to-date and accurate information on this topic.
What are normal blood sugar levels?
+Normal blood sugar levels are typically between 70 and 140 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) for people without diabetes.
How can I maintain normal blood sugar levels?
+Maintaining normal blood sugar levels requires a combination of healthy lifestyle habits, including eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, getting enough sleep, and practicing stress-reducing techniques.
What are the benefits of maintaining normal blood sugar levels?
+Maintaining normal blood sugar levels has numerous benefits, including reducing the risk of developing chronic diseases, improving energy levels, enhancing cognitive function, and supporting weight loss.
