Intro
Learn about normal blood sugar fasting levels, glucose targets, and healthy ranges to manage diabetes and prediabetes, understanding blood glucose monitoring and optimal fasting blood sugar levels.
Maintaining normal blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Blood sugar, also known as glucose, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. When we eat, our body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. The body's cells use insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, to absorb glucose from the bloodstream and use it for energy. Normal blood sugar fasting levels are essential to prevent complications associated with diabetes and other health conditions.
The importance of maintaining normal blood sugar levels cannot be overstated. High blood sugar levels can lead to a range of health problems, including diabetes, heart disease, and kidney damage. On the other hand, low blood sugar levels can cause symptoms such as dizziness, confusion, and even loss of consciousness. Therefore, it is essential to understand what normal blood sugar fasting levels are and how to maintain them. In this article, we will delve into the world of blood sugar levels, exploring what is considered normal, how to measure them, and the importance of maintaining healthy levels.
Understanding blood sugar levels is critical for individuals who are at risk of developing diabetes or those who have already been diagnosed with the condition. By knowing what normal blood sugar fasting levels are, individuals can take steps to maintain healthy levels and prevent complications associated with diabetes. Additionally, understanding blood sugar levels can help individuals make informed decisions about their diet and lifestyle, which can have a significant impact on their overall health and well-being.
What are Normal Blood Sugar Fasting Levels?
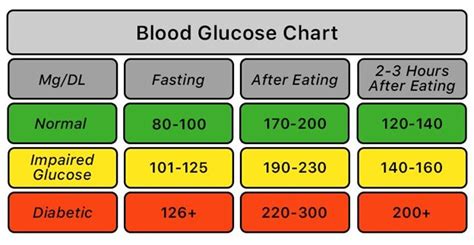
Factors that Affect Blood Sugar Fasting Levels
Several factors can affect blood sugar fasting levels, including diet, physical activity, stress, and certain medications. For example, consuming high-carbohydrate foods or sugary drinks can cause blood sugar levels to rise. On the other hand, regular physical activity, such as walking or jogging, can help lower blood sugar levels. Stress can also affect blood sugar levels, as it can cause the body to release stress hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline, which can raise blood sugar levels.How to Measure Blood Sugar Fasting Levels
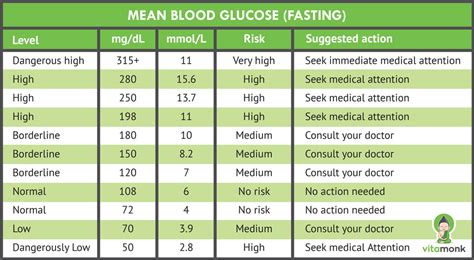
Interpreting Blood Sugar Fasting Levels
Interpreting blood sugar fasting levels is crucial to understanding what the results mean. The following are general guidelines for interpreting blood sugar fasting levels: * Less than 100 mg/dL: Normal * 100-125 mg/dL: Impaired fasting glucose (pre-diabetes) * 126 mg/dL or higher: DiabetesThe Importance of Maintaining Normal Blood Sugar Fasting Levels
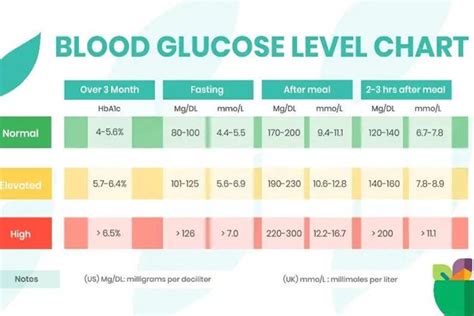
Complications of High Blood Sugar Fasting Levels
High blood sugar fasting levels can lead to a range of complications, including: * Heart disease and stroke * Kidney damage and failure * Nerve damage and neuropathy * Eye damage and blindness * Foot damage and amputationsWays to Maintain Normal Blood Sugar Fasting Levels

Medical Treatment for High Blood Sugar Fasting Levels
Medical treatment for high blood sugar fasting levels may include: * Medications, such as metformin or sulfonylureas * Insulin therapy * Lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise * Regular monitoring of blood sugar levelsConclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with maintaining normal blood sugar fasting levels in the comments section below. Additionally, if you found this article informative and helpful, please share it with your friends and family who may benefit from this information.
What are the symptoms of high blood sugar fasting levels?
+The symptoms of high blood sugar fasting levels may include increased thirst and urination, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts and wounds.
How often should I measure my blood sugar fasting levels?
+The frequency of measuring blood sugar fasting levels depends on individual factors, such as medical history and the presence of other health conditions. Generally, it is recommended to measure blood sugar fasting levels at least once a day, and more often if you have diabetes or are at risk of developing diabetes.
What are the risks of low blood sugar fasting levels?
+The risks of low blood sugar fasting levels may include dizziness, confusion, and even loss of consciousness. Severe low blood sugar levels can be life-threatening and require immediate medical attention.
