Intro
Learn the normal diabetes level range and understand blood sugar targets, including fasting glucose, postprandial levels, and HbA1c, to manage diabetes effectively.
Maintaining normal diabetes level ranges is crucial for individuals diagnosed with diabetes, as well as those aiming to prevent the onset of this condition. Diabetes, a chronic health condition characterized by elevated levels of glucose in the blood, can lead to severe complications if not managed properly. The importance of understanding and maintaining normal blood glucose levels cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts the quality of life and long-term health outcomes for individuals with diabetes.
Effective management of diabetes involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, including diet, exercise, and, when necessary, medication. Understanding the target blood glucose levels is fundamental to this management plan. For individuals with diabetes, knowing when their glucose levels are within the normal range helps in assessing the effectiveness of their current treatment plan and making necessary adjustments. Furthermore, for those at risk of developing diabetes, recognizing the signs of abnormal glucose levels and taking preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing the condition.
The quest for maintaining normal diabetes level ranges is not just about personal health; it also has broader implications. Diabetes is a significant public health concern, given its prevalence and the substantial economic burden it imposes on healthcare systems worldwide. By promoting awareness about normal blood glucose levels and the importance of their management, we can work towards reducing the incidence of diabetes-related complications and improving overall population health. This comprehensive approach involves education, early detection, and timely intervention, all of which are critical in the battle against diabetes.
Understanding Blood Glucose Levels
Blood glucose levels refer to the amount of glucose present in the blood at any given time. Glucose, a simple sugar, is the body's primary source of energy. It is derived from the food we eat, particularly from carbohydrates, and is transported to cells throughout the body via the bloodstream. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, plays a critical role in facilitating the entry of glucose into cells. In individuals with diabetes, the body either does not produce enough insulin (Type 1 diabetes) or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces (Type 2 diabetes), leading to elevated blood glucose levels.
Normal Blood Glucose Levels
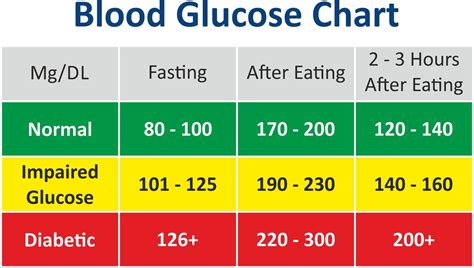
Normal blood glucose levels vary throughout the day, depending on factors such as the time of day, the type and quantity of food consumed, and the individual's level of physical activity. Generally, normal fasting blood glucose levels are between 70 and 99 mg/dL. After eating, blood glucose levels typically rise but should remain below 140 mg/dL two hours after a meal. Understanding these ranges is essential for individuals with diabetes, as they help in making informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication.Importance of Maintaining Normal Diabetes Level Ranges

Maintaining blood glucose levels within the normal range is vital for preventing diabetes-related complications. High blood glucose levels over an extended period can lead to damage to various organs and tissues, including the kidneys, eyes, nerves, and heart. This damage can result in serious health issues, such as kidney failure, blindness, nerve damage, and increased risk of heart disease and stroke. Furthermore, maintaining normal glucose levels reduces the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), both of which can be life-threatening if not promptly treated.
Benefits of Normal Blood Glucose Levels
The benefits of maintaining normal blood glucose levels are numerous and significant. They include: - Reduced risk of diabetes-related complications - Improved quality of life - Enhanced energy levels and mental clarity - Better weight management - Reduced risk of heart disease and stroke - Preservation of kidney and nerve function - Prevention of vision problems, including blindnessStrategies for Maintaining Normal Diabetes Level Ranges

Maintaining normal blood glucose levels involves a multifaceted approach that includes dietary changes, regular physical activity, monitoring of blood glucose levels, and, when prescribed, adherence to medication regimens. Here are some key strategies:
- Healthy Eating: Focus on consuming a balanced diet that is rich in whole foods, such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit intake of sugary drinks, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week. Additionally, incorporate strength-training activities, high-intensity interval training, and other forms of physical activity to improve insulin sensitivity.
- Monitoring Blood Glucose: Regularly check blood glucose levels to understand how different foods, activities, and medications affect glucose levels. This information is invaluable for making informed decisions about diabetes management.
- Medication Adherence: For individuals requiring medication, adhering to the prescribed regimen is crucial. Medications, including metformin, sulfonylureas, and insulin, help manage blood glucose levels and prevent complications.
Role of Technology in Diabetes Management
Technology plays an increasingly important role in diabetes management, offering tools that can significantly enhance the ability to maintain normal blood glucose levels. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems, insulin pumps, and mobile applications are examples of technological advancements that provide real-time data, facilitate more precise insulin dosing, and offer personalized advice based on an individual's glucose trends and lifestyle.Challenges in Maintaining Normal Diabetes Level Ranges

Despite the importance of maintaining normal blood glucose levels, several challenges exist. These include:
- Lack of Awareness: Limited understanding of diabetes, its management, and the importance of maintaining normal glucose levels can hinder effective control.
- Access to Healthcare: Inequities in access to healthcare services, including diabetes education, monitoring equipment, and medications, can significantly impact an individual's ability to manage their diabetes.
- Psychological Factors: The emotional and psychological burden of living with a chronic condition can affect motivation and adherence to diabetes management plans.
- Socioeconomic Factors: Economic constraints, social support, and cultural beliefs can influence dietary choices, physical activity levels, and overall ability to manage diabetes.
Overcoming Challenges
Overcoming these challenges requires a comprehensive and supportive approach. This includes: - **Education and Awareness:** Enhancing knowledge about diabetes and its management through accessible educational programs. - **Improving Access to Healthcare:** Advocating for equitable access to diabetes care, including medications, monitoring devices, and professional guidance. - **Psychological Support:** Providing resources for emotional and psychological support to help individuals cope with the challenges of living with diabetes. - **Community Engagement:** Fostering community support and social networks to encourage sharing of experiences, advice, and motivation among individuals with diabetes.Future Directions in Diabetes Management
The future of diabetes management holds promise with advancements in technology, medication, and our understanding of the disease. Emerging trends include:
- Personalized Medicine: Tailoring diabetes management plans to the individual's genetic profile, lifestyle, and specific needs.
- Artificial Pancreas: Development of automated insulin delivery systems that mimic the function of a healthy pancreas.
- Stem Cell Research: Exploring the potential of stem cells in regenerating pancreatic cells and restoring natural insulin production.
- Digital Health: Leveraging digital technologies to enhance diabetes education, monitoring, and support, making management more accessible and effective.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Maintaining normal diabetes level ranges is a critical aspect of diabetes management, offering numerous benefits for overall health and quality of life. By understanding the importance of normal blood glucose levels, implementing effective management strategies, and staying informed about the latest advancements in diabetes care, individuals can take proactive steps towards a healthier future. As research and technology continue to evolve, it is essential to remain engaged with healthcare providers, support networks, and educational resources to optimize diabetes management and strive for the best possible outcomes.What are normal blood glucose levels?
+Normal fasting blood glucose levels are between 70 and 99 mg/dL, and after eating, levels should remain below 140 mg/dL two hours after a meal.
Why is it important to maintain normal diabetes level ranges?
+Maintaining normal blood glucose levels is crucial for preventing diabetes-related complications, such as kidney damage, blindness, and heart disease, and for improving overall quality of life.
What strategies can help maintain normal diabetes level ranges?
+Strategies include healthy eating, regular physical activity, monitoring of blood glucose levels, and adherence to medication regimens when prescribed. Additionally, staying informed about the latest in diabetes management and technology can be beneficial.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences on maintaining normal diabetes level ranges. Your insights can help others in their journey towards effective diabetes management. Please comment below, and consider sharing this article with someone who might find it helpful. Together, we can work towards a better understanding of diabetes and its management, ultimately improving the lives of those affected by this condition.
