Intro
Learn normal glucose values and understand blood sugar levels, including fasting glucose, postprandial glucose, and glycated hemoglobin, to manage diabetes and prediabetes effectively.
Maintaining normal glucose values is crucial for overall health and well-being. Glucose, a simple sugar, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. The body regulates glucose levels through a complex process involving the pancreas, liver, and insulin. Understanding normal glucose values is essential for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. In this article, we will delve into the importance of glucose regulation, the factors that influence glucose levels, and the steps individuals can take to maintain normal glucose values.
The importance of glucose regulation cannot be overstated. When glucose levels are within the normal range, the body functions optimally, and the risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage, is minimized. On the other hand, abnormal glucose levels can lead to a range of health problems, including diabetes, which is a major public health concern worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 422 million people worldwide have diabetes, and this number is expected to increase to 578 million by 2030.
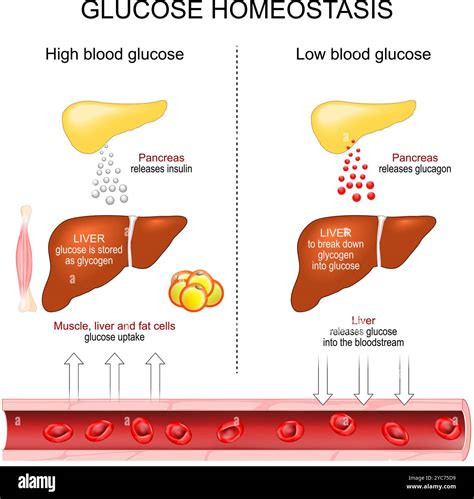
Glucose regulation is a complex process that involves the coordinated effort of multiple organs and hormones. The pancreas plays a central role in glucose regulation by producing insulin, a hormone that helps cells absorb glucose from the bloodstream. When glucose levels rise after a meal, the pancreas releases insulin, which facilitates the uptake of glucose by cells, thereby lowering blood glucose levels. Conversely, when glucose levels fall, the pancreas releases glucagon, a hormone that stimulates the liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream, thereby raising blood glucose levels.
Understanding Normal Glucose Values

Normal glucose values are typically measured using a blood test called a fasting plasma glucose (FPG) test or an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT). The FPG test measures glucose levels after an overnight fast, while the OGTT measures glucose levels after consuming a sugary drink. Normal glucose values vary depending on the test used, but generally, a fasting glucose level of less than 100 mg/dL is considered normal, while a level of 100-125 mg/dL is considered impaired fasting glucose. A level of 126 mg/dL or higher is considered diagnostic of diabetes.
Factors that Influence Glucose Levels
Several factors can influence glucose levels, including diet, physical activity, stress, and certain medications. A diet high in sugary foods and drinks can cause glucose levels to rise, while a diet rich in fiber, fruits, and vegetables can help regulate glucose levels. Regular physical activity, such as walking or jogging, can also help improve insulin sensitivity, which can help lower glucose levels. Stress can cause glucose levels to rise, as the body releases stress hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline, which can raise blood glucose levels.The Importance of Insulin Sensitivity

Insulin sensitivity is a critical factor in glucose regulation. Insulin sensitivity refers to the body's ability to effectively use insulin, allowing glucose to enter cells. When insulin sensitivity is high, glucose levels are more easily regulated, and the risk of chronic diseases is minimized. On the other hand, low insulin sensitivity, also known as insulin resistance, can lead to elevated glucose levels and increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Strategies to Improve Insulin Sensitivity
Several strategies can help improve insulin sensitivity, including regular physical activity, weight loss, and a healthy diet. Aerobic exercises, such as walking or cycling, can improve insulin sensitivity by increasing blood flow and reducing inflammation. Resistance training, such as weightlifting, can also improve insulin sensitivity by increasing muscle mass and reducing body fat. A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can also help improve insulin sensitivity.The Role of Diet in Glucose Regulation
Diet plays a critical role in glucose regulation. A healthy diet can help regulate glucose levels, while an unhealthy diet can lead to elevated glucose levels and increase the risk of chronic diseases. The best diet for glucose regulation is one that is rich in whole, unprocessed foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. These foods are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, which can help regulate glucose levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
Foods that Help Regulate Glucose Levels
Several foods can help regulate glucose levels, including: * Leafy green vegetables, such as spinach and kale * Berries, such as blueberries and strawberries * Nuts and seeds, such as almonds and chia seeds * Fatty fish, such as salmon and tuna * Whole grains, such as brown rice and quinoa * Legumes, such as lentils and chickpeasThe Importance of Monitoring Glucose Levels

Monitoring glucose levels is essential for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. Regular monitoring can help identify trends and patterns in glucose levels, allowing individuals to make informed decisions about their diet, physical activity, and medication. There are several ways to monitor glucose levels, including:
- Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) tests
- Oral glucose tolerance tests (OGTT)
- Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems
- Flash glucose monitoring systems
Benefits of Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems offer several benefits, including: * Real-time glucose data * Trend analysis and pattern recognition * Alerts for high and low glucose levels * Improved insulin dosing and timing * Enhanced glucose control and reduced risk of complicationsManaging Stress and Glucose Levels

Stress can have a significant impact on glucose levels, as the body releases stress hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline, which can raise blood glucose levels. Managing stress is essential for maintaining normal glucose values. Several strategies can help manage stress, including:
- Meditation and mindfulness
- Yoga and tai chi
- Deep breathing exercises
- Progressive muscle relaxation
- Journaling and expressive writing
Benefits of Mindfulness and Glucose Regulation
Mindfulness and meditation offer several benefits for glucose regulation, including: * Reduced stress and anxiety * Improved insulin sensitivity * Enhanced glucose control * Increased feelings of calm and well-being * Improved overall health and quality of lifeConclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, maintaining normal glucose values is crucial for overall health and well-being. By understanding the factors that influence glucose levels, individuals can take steps to regulate their glucose levels and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. This includes adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, and monitoring glucose levels. By taking control of their glucose levels, individuals can improve their overall health and quality of life.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences on maintaining normal glucose values. What strategies have you found to be effective in regulating your glucose levels? What challenges have you faced, and how have you overcome them? Your input and insights can help others who are struggling to manage their glucose levels. Please comment below and share this article with others who may benefit from this information.
What are normal glucose values?
+Normal glucose values are typically less than 100 mg/dL for a fasting plasma glucose test and less than 140 mg/dL for an oral glucose tolerance test.
How can I improve my insulin sensitivity?
+Improving insulin sensitivity can be achieved through regular physical activity, weight loss, and a healthy diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods.
What are the benefits of continuous glucose monitoring?
+Continuous glucose monitoring offers several benefits, including real-time glucose data, trend analysis and pattern recognition, alerts for high and low glucose levels, and improved insulin dosing and timing.
