Intro
Learn about normal INR levels range, optimal blood clotting, and warfarin therapy management, ensuring safe international normalized ratio values for cardiovascular health.
Maintaining a healthy blood clotting system is crucial for our overall well-being. One of the key components of this system is the International Normalized Ratio (INR), which measures the time it takes for blood to clot. Normal INR levels range is a topic of great interest, especially for individuals taking anticoagulant medications or those with bleeding disorders. In this article, we will delve into the world of INR, exploring its importance, the normal range, and what it means for our health.
The INR test is a vital tool used by healthcare professionals to assess the effectiveness of anticoagulant therapy, particularly for patients taking warfarin. Warfarin is a blood thinner that helps prevent blood clots from forming, which can reduce the risk of stroke, heart attack, and other cardiovascular events. However, it is essential to monitor the INR levels regularly to ensure that the blood is not too thin or too thick, as this can lead to serious health complications.
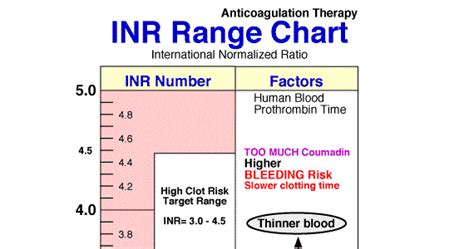
Normal INR levels range from 0.9 to 1.1 for individuals who are not taking anticoagulant medications. This range indicates that the blood is clotting normally, and the risk of bleeding or thrombosis is minimal. However, for patients taking warfarin, the target INR range is typically between 2.0 and 3.0, depending on the individual's condition and the reason for taking the medication. It is crucial to maintain the INR levels within this range to minimize the risk of bleeding or thrombosis.
Understanding INR Levels

Understanding INR levels is essential for individuals taking anticoagulant medications. The INR test measures the time it takes for blood to clot, and the results are compared to a standard sample. The standard sample is assigned an INR value of 1.0, and the patient's sample is then compared to this standard. If the patient's INR value is higher than 1.0, it means that their blood is taking longer to clot, indicating that the anticoagulant medication is working effectively. On the other hand, if the INR value is lower than 1.0, it means that the blood is clotting too quickly, which can increase the risk of thrombosis.
Factors Affecting INR Levels
Several factors can affect INR levels, including diet, lifestyle, and other medications. For example, consuming foods high in vitamin K, such as leafy green vegetables, can decrease INR levels, while taking certain medications, such as antibiotics, can increase INR levels. It is essential to inform healthcare professionals about any changes in diet, lifestyle, or medications to ensure that INR levels are accurately monitored and adjusted as needed.Normal INR Levels Range for Different Conditions

Normal INR levels range can vary depending on the individual's condition and the reason for taking anticoagulant medications. For example, patients with mechanical heart valves may require a higher INR range of 2.5 to 3.5, while patients with atrial fibrillation may require a lower INR range of 2.0 to 3.0. It is crucial to work closely with healthcare professionals to determine the optimal INR range for each individual's condition.
INR Levels and Bleeding Risk
INR levels can also affect the risk of bleeding. If INR levels are too high, the blood may be too thin, increasing the risk of bleeding. On the other hand, if INR levels are too low, the blood may be too thick, increasing the risk of thrombosis. It is essential to maintain INR levels within the target range to minimize the risk of bleeding or thrombosis.Monitoring INR Levels

Monitoring INR levels is crucial for individuals taking anticoagulant medications. Regular INR testing can help healthcare professionals adjust the medication dose to maintain optimal INR levels. Patients can also use point-of-care INR testing devices to monitor their INR levels at home, which can help reduce the risk of bleeding or thrombosis.
Point-of-Care INR Testing
Point-of-care INR testing devices are small, portable devices that can be used to measure INR levels at home. These devices use a small blood sample to measure the INR level, which can help patients monitor their INR levels regularly. Point-of-care INR testing devices can be especially useful for patients who live in remote areas or have limited access to healthcare facilities.Importance of INR Levels in Healthcare
INR levels play a crucial role in healthcare, particularly for individuals taking anticoagulant medications. Maintaining optimal INR levels can help reduce the risk of bleeding or thrombosis, which can improve patient outcomes and quality of life. Healthcare professionals must work closely with patients to monitor INR levels regularly and adjust medication doses as needed to ensure optimal INR levels.
Challenges in Maintaining Optimal INR Levels
Maintaining optimal INR levels can be challenging, particularly for patients taking multiple medications or having complex medical conditions. Healthcare professionals must consider various factors, including diet, lifestyle, and other medications, to ensure that INR levels are accurately monitored and adjusted as needed.Future Directions in INR Testing
Future directions in INR testing include the development of new point-of-care devices and technologies that can improve the accuracy and convenience of INR testing. Additionally, researchers are exploring new anticoagulant medications that may have a more predictable effect on INR levels, reducing the need for frequent monitoring.
Conclusion and Recommendations
In conclusion, normal INR levels range is a critical aspect of healthcare, particularly for individuals taking anticoagulant medications. Maintaining optimal INR levels can help reduce the risk of bleeding or thrombosis, improving patient outcomes and quality of life. Healthcare professionals must work closely with patients to monitor INR levels regularly and adjust medication doses as needed. We recommend that patients take an active role in monitoring their INR levels, inform healthcare professionals about any changes in diet, lifestyle, or medications, and work closely with healthcare professionals to maintain optimal INR levels.What is the normal INR levels range for individuals not taking anticoagulant medications?
+The normal INR levels range for individuals not taking anticoagulant medications is between 0.9 and 1.1.
What is the target INR range for patients taking warfarin?
+The target INR range for patients taking warfarin is typically between 2.0 and 3.0, depending on the individual's condition and the reason for taking the medication.
How often should INR levels be monitored for patients taking anticoagulant medications?
+INR levels should be monitored regularly, typically every 1-4 weeks, depending on the individual's condition and the reason for taking the medication.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with INR testing and anticoagulant medications in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please share it with others who may benefit from this information. Together, we can work towards improving patient outcomes and quality of life by maintaining optimal INR levels.
