Intro
Discover the normal INR value range and learn about blood clotting, thrombosis, and anticoagulation therapy, including warfarin dosage and PT/INR tests for optimal health management.
The importance of understanding normal INR value ranges cannot be overstated, especially for individuals who are taking anticoagulant medications such as warfarin. INR, or International Normalized Ratio, is a test used to measure the time it takes for blood to clot, and it is crucial for determining the correct dosage of anticoagulant medications. A normal INR value range is typically between 0.9 and 1.1 for individuals who are not taking anticoagulant medications, but this range can vary depending on the laboratory and the specific test used.
For individuals who are taking anticoagulant medications, the target INR range is usually between 2.0 and 3.0, although this can vary depending on the specific condition being treated and the individual's overall health. It is essential to maintain an INR value within the target range to minimize the risk of bleeding complications or thromboembolic events. If the INR value is too high, the individual may be at risk for bleeding, while an INR value that is too low may increase the risk of blood clots.
Understanding the normal INR value range and how to interpret INR test results is critical for individuals who are taking anticoagulant medications. It is also essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to monitor INR values and adjust medication dosages as needed to maintain a safe and effective level of anticoagulation. By doing so, individuals can minimize the risks associated with anticoagulant therapy and maximize the benefits of treatment.
What is INR and How is it Measured?

INR, or International Normalized Ratio, is a test used to measure the time it takes for blood to clot. It is a standardized test that is used to monitor the effectiveness of anticoagulant medications such as warfarin. The INR test measures the ratio of the patient's prothrombin time (PT) to the normal PT, and it is calculated using a formula that takes into account the international sensitivity index (ISI) of the thromboplastin reagent used in the test.
The INR test is typically performed using a blood sample that is drawn from a vein in the arm. The blood sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis, where the PT and INR values are measured using a coagulation analyzer. The results of the INR test are usually available within a few hours, and they are used to determine the correct dosage of anticoagulant medications.
Factors that Can Affect INR Values
There are several factors that can affect INR values, including diet, medications, and underlying medical conditions. For example, certain foods such as leafy green vegetables and cranberry juice can interact with warfarin and affect INR values. Additionally, other medications such as antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications can also interact with warfarin and affect INR values.Underlying medical conditions such as liver disease and kidney disease can also affect INR values. For example, individuals with liver disease may have elevated INR values due to decreased production of clotting factors, while individuals with kidney disease may have decreased INR values due to increased clearance of warfarin.
Normal INR Value Range for Different Conditions
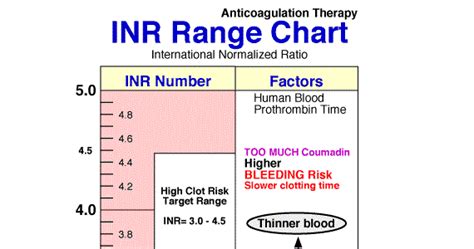
The normal INR value range can vary depending on the specific condition being treated. For example:
- For individuals who are not taking anticoagulant medications, the normal INR value range is typically between 0.9 and 1.1.
- For individuals who are taking warfarin for atrial fibrillation, the target INR range is usually between 2.0 and 3.0.
- For individuals who are taking warfarin for deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism, the target INR range is usually between 2.0 and 3.0.
- For individuals who are taking warfarin for mechanical heart valves, the target INR range is usually between 2.0 and 3.0 for bileaflet valves and between 2.5 and 3.5 for tilting disc valves.
Interpreting INR Test Results
Interpreting INR test results requires careful consideration of several factors, including the individual's medical history, current medications, and laboratory results. The following are some general guidelines for interpreting INR test results:- An INR value below 1.5 indicates that the blood is clotting normally.
- An INR value between 1.5 and 2.0 indicates that the blood is clotting slightly slower than normal.
- An INR value between 2.0 and 3.0 indicates that the blood is clotting at a therapeutic level.
- An INR value above 3.0 indicates that the blood is clotting more slowly than normal, and the individual may be at risk for bleeding complications.
Managing INR Values

Managing INR values requires careful monitoring and adjustment of anticoagulant medications. The following are some general tips for managing INR values:
- Take anticoagulant medications exactly as directed by a healthcare provider.
- Keep track of INR test results and report any changes to a healthcare provider.
- Avoid making significant changes to diet or medications without consulting a healthcare provider.
- Attend regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider to monitor INR values and adjust medications as needed.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
There are several common mistakes that individuals can make when managing INR values, including:- Forgetting to take anticoagulant medications or taking them at the wrong time.
- Making significant changes to diet or medications without consulting a healthcare provider.
- Failing to attend regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider.
- Not reporting changes in INR test results to a healthcare provider.
Benefits of Monitoring INR Values

Monitoring INR values has several benefits, including:
- Reduced risk of bleeding complications or thromboembolic events.
- Improved management of anticoagulant medications.
- Enhanced quality of life for individuals taking anticoagulant medications.
- Reduced risk of hospitalization or emergency department visits due to bleeding complications or thromboembolic events.
Challenges of Monitoring INR Values
Monitoring INR values can be challenging, especially for individuals who are taking multiple medications or have underlying medical conditions. Some common challenges include:- Keeping track of INR test results and reporting changes to a healthcare provider.
- Making significant changes to diet or medications without consulting a healthcare provider.
- Attending regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider.
- Managing the cost of anticoagulant medications and INR testing.
Future Directions for INR Monitoring

The future of INR monitoring is likely to involve the use of new technologies and strategies to improve the management of anticoagulant medications. Some potential future directions include:
- The use of point-of-care INR testing devices that can be used at home.
- The development of new anticoagulant medications that have a more predictable effect on INR values.
- The use of genetic testing to predict an individual's response to anticoagulant medications.
- The development of new strategies for managing INR values in individuals with underlying medical conditions.
Conclusion and Recommendations
In conclusion, monitoring INR values is a critical component of anticoagulant therapy, and it requires careful attention to detail and regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider. By understanding the normal INR value range and how to interpret INR test results, individuals can take a more active role in managing their anticoagulant medications and reducing the risk of bleeding complications or thromboembolic events.We recommend that individuals take the following steps to manage their INR values:
- Take anticoagulant medications exactly as directed by a healthcare provider.
- Keep track of INR test results and report any changes to a healthcare provider.
- Attend regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider to monitor INR values and adjust medications as needed.
- Avoid making significant changes to diet or medications without consulting a healthcare provider.
What is the normal INR value range for individuals who are not taking anticoagulant medications?
+The normal INR value range for individuals who are not taking anticoagulant medications is typically between 0.9 and 1.1.
What is the target INR range for individuals who are taking warfarin for atrial fibrillation?
+The target INR range for individuals who are taking warfarin for atrial fibrillation is usually between 2.0 and 3.0.
How often should INR values be monitored in individuals who are taking anticoagulant medications?
+INR values should be monitored regularly in individuals who are taking anticoagulant medications, typically every 1-4 weeks depending on the individual's condition and response to treatment.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of normal INR value ranges and how to interpret INR test results. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others who may benefit from this information. Additionally, we encourage you to take an active role in managing your anticoagulant medications and reducing the risk of bleeding complications or thromboembolic events.
