Intro
Discover effective medication for prediabetes treatment, including metformin and lifestyle changes, to manage blood sugar levels and prevent type 2 diabetes complications.
Prediabetes is a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. It is a warning sign that an individual is at risk of developing type 2 diabetes, and it is essential to take preventive measures to avoid this condition. Medication for prediabetes treatment is often prescribed to help manage blood sugar levels and prevent the progression to type 2 diabetes. In this article, we will explore the importance of treating prediabetes, the different types of medications available, and the benefits and risks associated with each.
The importance of treating prediabetes cannot be overstated. If left untreated, prediabetes can lead to type 2 diabetes, which is a serious condition that can cause a range of health problems, including heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), over 88 million adults in the United States have prediabetes, and without treatment, up to 70% of these individuals will develop type 2 diabetes within 5 years. Therefore, it is crucial to take proactive steps to manage blood sugar levels and prevent the progression to type 2 diabetes.
Treating prediabetes is not just about managing blood sugar levels; it is also about adopting a healthy lifestyle. This includes eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight. However, for some individuals, lifestyle changes alone may not be enough to manage blood sugar levels, and medication may be necessary. There are several types of medications available for prediabetes treatment, including metformin, thiazolidinediones, and alpha-glucosidase inhibitors. Each of these medications works in a different way to manage blood sugar levels, and the choice of medication will depend on the individual's specific needs and health status.
Understanding Prediabetes
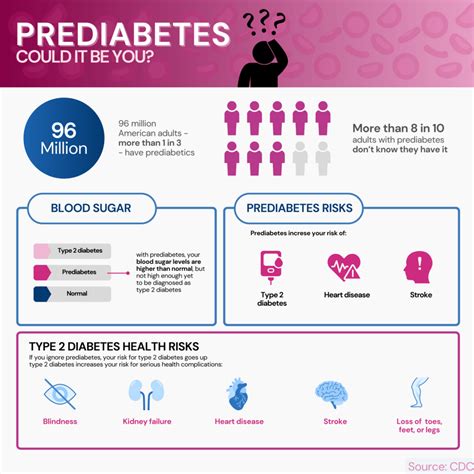
Risk Factors for Prediabetes
The risk factors for prediabetes are similar to those for type 2 diabetes and include: * Obesity * Physical inactivity * Family history of diabetes * Age (45 or older) * Certain ethnicities (African American, Hispanic/Latino, American Indian) * History of gestational diabetes or delivering a baby over 4 kg * Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) * Sleep apnea * Certain medications (steroids, certain psychiatric medications)Medications for Prediabetes Treatment
Benefits and Risks of Medications
Each of these medications has its benefits and risks, and the choice of medication will depend on the individual's specific needs and health status. For example: * Metformin is generally well-tolerated, but it can cause gastrointestinal side effects such as diarrhea and nausea. * Thiazolidinediones can cause weight gain and increased risk of heart failure. * Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors can cause gastrointestinal side effects such as bloating and gas. * GLP-1 receptor agonists can cause nausea and vomiting, and increased risk of pancreatitis. * SGLT2 inhibitors can cause increased risk of urinary tract infections and kidney damage.Lifestyle Changes for Prediabetes Treatment

Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Monitoring blood sugar levels is essential for prediabetes treatment. This can be done using a blood glucose meter or a continuous glucose monitor. The goal is to keep blood sugar levels within a target range, which will depend on the individual's specific needs and health status.Preventing the Progression to Type 2 Diabetes

Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, prediabetes is a serious condition that requires prompt attention and treatment. By understanding the risks and benefits of medication, making lifestyle changes, and monitoring blood sugar levels, individuals can reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes. If you have been diagnosed with prediabetes, it is essential to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan. With the right treatment and lifestyle changes, it is possible to prevent the progression to type 2 diabetes and maintain good health.What is prediabetes?
+Prediabetes is a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to be classified as diabetes.
What are the symptoms of prediabetes?
+The symptoms of prediabetes are often mild and may not be noticeable, but they can include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, and blurred vision.
How is prediabetes treated?
+Prediabetes is treated with a combination of lifestyle changes and medication. Lifestyle changes include eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight. Medications such as metformin, thiazolidinediones, and alpha-glucosidase inhibitors may also be prescribed to help manage blood sugar levels.
Can prediabetes be prevented?
+Yes, prediabetes can be prevented by maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight.
What are the risks of untreated prediabetes?
+Untreated prediabetes can lead to type 2 diabetes, which is a serious condition that can cause a range of health problems, including heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
