Intro
Learn about normal non-fasting blood sugar levels, glucose monitoring, and healthy ranges to manage diabetes and prediabetes, understanding blood glucose, insulin resistance, and glycemic control.
Normal non-fasting blood sugar levels are a crucial aspect of maintaining overall health, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. Blood sugar, also known as glucose, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. When we eat, our body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. The amount of glucose in the blood is measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L). Understanding normal non-fasting blood sugar levels is essential for managing diabetes, preventing complications, and maintaining optimal health.
The importance of monitoring blood sugar levels cannot be overstated. For individuals with diabetes, regular monitoring helps adjust medication, diet, and exercise to maintain blood sugar levels within a target range. Even for those without diabetes, being aware of blood sugar levels can help identify potential health issues early on. Factors such as diet, physical activity, stress, and certain medications can influence blood sugar levels, making it crucial to understand what constitutes normal non-fasting blood sugar levels.
Maintaining normal blood sugar levels is a delicate balance. When blood sugar levels are too high, it can lead to serious health complications, including heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. On the other hand, blood sugar levels that are too low can cause dizziness, confusion, and even loss of consciousness. The body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels is primarily controlled by insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. In individuals with diabetes, the body either does not produce enough insulin or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
Understanding Non-Fasting Blood Sugar
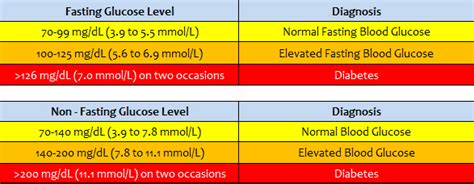
Non-fasting blood sugar refers to the level of glucose in the blood when an individual has not fasted for at least 8 hours. This is in contrast to fasting blood sugar, which is measured after an overnight fast of at least 8 hours. Non-fasting blood sugar levels can fluctuate throughout the day based on various factors, including meals, physical activity, and medications. For individuals with diabetes, monitoring non-fasting blood sugar levels is crucial to adjust treatment plans and prevent complications.
Factors Influencing Non-Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can influence non-fasting blood sugar levels, including:
- Diet: Consuming high-carbohydrate or high-sugar foods can cause blood sugar levels to rise.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise can help lower blood sugar levels by increasing insulin sensitivity.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as steroids and some psychiatric medications, can raise blood sugar levels.
- Stress: Physical or emotional stress can cause the body to release stress hormones, which can increase blood sugar levels.
- Sleep: Poor sleep quality or duration can affect blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity.
Normal Non-Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
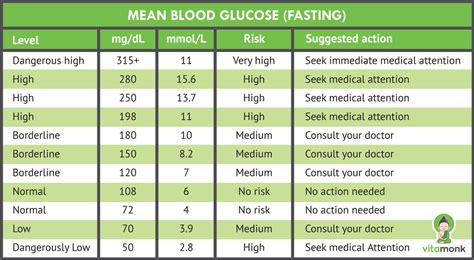
Normal non-fasting blood sugar levels vary slightly depending on the individual and the time of day. Generally, for individuals without diabetes, non-fasting blood sugar levels should be below 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L). For those with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends the following target ranges for non-fasting blood sugar levels:
- Before meals: 70-130 mg/dL (3.9-7.2 mmol/L)
- After meals: Less than 180 mg/dL (10.0 mmol/L)
It's essential to work with a healthcare provider to determine individualized target ranges, as these can vary based on age, health status, and other factors.
Monitoring Non-Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
Monitoring non-fasting blood sugar levels involves using a glucometer, a small device that measures the glucose level in a drop of blood. To get an accurate reading, it's crucial to follow the manufacturer's instructions and ensure the device is calibrated correctly. Individuals with diabetes should work with their healthcare provider to develop a monitoring plan that fits their lifestyle and health needs.
Benefits of Maintaining Normal Non-Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
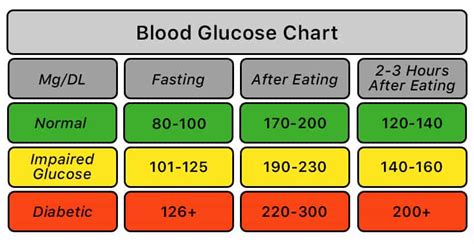
Maintaining normal non-fasting blood sugar levels offers numerous health benefits, including:
- Reduced risk of diabetes complications, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
- Improved energy levels and reduced fatigue.
- Enhanced cognitive function and reduced risk of dementia.
- Better weight management and reduced risk of obesity.
- Improved overall quality of life and life expectancy.
Strategies for Maintaining Normal Non-Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
Several strategies can help maintain normal non-fasting blood sugar levels, including:
- Eating a balanced diet that is low in carbohydrates and added sugars.
- Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or other aerobic exercises.
- Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises.
- Getting adequate sleep each night and establishing a consistent sleep schedule.
- Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
Complications of Abnormal Non-Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
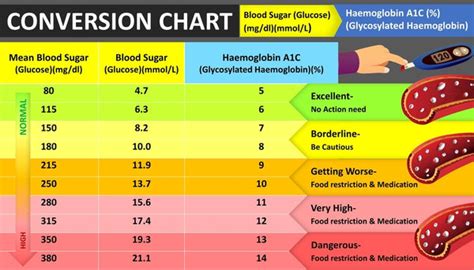
Abnormal non-fasting blood sugar levels can lead to serious health complications, including:
- Heart disease: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and nerves, increasing the risk of heart disease.
- Kidney damage: The kidneys work harder to filter excess glucose from the blood, which can lead to kidney damage and disease.
- Nerve damage: High blood sugar levels can damage nerves, causing numbness, tingling, and pain in the hands and feet.
- Blindness: High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to blindness.
- Amputations: Nerve damage and poor circulation can lead to foot ulcers and amputations.
Preventing Complications
Preventing complications associated with abnormal non-fasting blood sugar levels involves working closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan. This may include medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring of blood sugar levels.
Treatment Options for Abnormal Non-Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
Treatment options for abnormal non-fasting blood sugar levels depend on the individual and the severity of their condition. For individuals with diabetes, treatment may include:
- Medications: Oral medications or insulin therapy to lower blood sugar levels.
- Lifestyle changes: Eating a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress.
- Monitoring: Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels to adjust treatment plans.
For individuals without diabetes, treatment may involve lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet and engaging in regular physical activity.
Emerging Trends in Non-Fasting Blood Sugar Management
Emerging trends in non-fasting blood sugar management include the use of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems, which provide real-time glucose readings throughout the day. Additionally, advances in insulin pump technology and the development of new medications are improving the management of diabetes and reducing the risk of complications.
Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, maintaining normal non-fasting blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health and preventing complications associated with diabetes. By understanding the factors that influence non-fasting blood sugar levels and working with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan, individuals can reduce their risk of complications and improve their quality of life. As research continues to advance, new technologies and treatments will emerge, providing individuals with more effective tools to manage their blood sugar levels and prevent complications.
Final Thoughts
Maintaining normal non-fasting blood sugar levels requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle changes, monitoring, and, when necessary, medication. By taking an active role in managing blood sugar levels, individuals can reduce their risk of complications and improve their overall health. It's essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan that meets individual needs and health goals.
What are normal non-fasting blood sugar levels?
+Normal non-fasting blood sugar levels are typically below 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) for individuals without diabetes. For those with diabetes, target ranges vary but generally include before meals: 70-130 mg/dL (3.9-7.2 mmol/L) and after meals: less than 180 mg/dL (10.0 mmol/L).
How often should I monitor my non-fasting blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of monitoring non-fasting blood sugar levels depends on the individual and their health status. Individuals with diabetes should work with their healthcare provider to develop a monitoring plan that fits their lifestyle and health needs.
What are the complications of abnormal non-fasting blood sugar levels?
+Abnormal non-fasting blood sugar levels can lead to serious health complications, including heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, blindness, and amputations. Maintaining normal blood sugar levels through lifestyle changes, monitoring, and medication can help prevent these complications.
We hope this comprehensive guide to normal non-fasting blood sugar levels has been informative and helpful. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with managing blood sugar levels, please comment below. Sharing knowledge and personal stories can help others better understand and manage their health. Additionally, if you found this article useful, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information. Together, we can work towards a healthier future by promoting awareness and understanding of normal non-fasting blood sugar levels.
