Intro
Discover how high sedimentation rate impacts health, causing inflammation, infection, and autoimmune issues, affecting erythrocyte sedimentation rate, blood tests, and overall well-being.
Elevated sedimentation rates in the body can have far-reaching consequences on overall health and wellbeing. Sedimentation rate, often measured through blood tests such as the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), is an indicator of inflammation within the body. When this rate is high, it signifies the presence of an inflammatory response, which could be due to various factors including infections, autoimmune diseases, or other medical conditions. Understanding the implications of a high sedimentation rate is crucial for timely intervention and management of underlying health issues.
The human body is incredibly complex, with numerous systems working in harmony to maintain health. However, when one aspect is out of balance, such as an elevated sedimentation rate, it can have a ripple effect on overall health. Inflammation, indicated by a high sedimentation rate, is the body's natural response to injury or infection, but chronic inflammation can lead to severe health complications. It is essential to recognize the signs and understand the effects of high sedimentation rates to take proactive steps towards health management.
Inflammation is a natural bodily response that can sometimes become detrimental if it persists over time. Chronic inflammation has been linked to various diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and even certain types of cancer. The sedimentation rate is a critical marker that helps in identifying the level of inflammation in the body. By understanding the causes and effects of an elevated sedimentation rate, individuals can work towards reducing inflammation and improving their overall health. This knowledge empowers them to make informed decisions about their lifestyle and seek medical attention when necessary.
Introduction to Sedimentation Rate
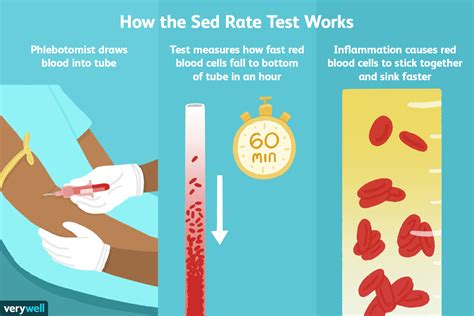
Understanding the Sedimentation Rate Test
The sedimentation rate test is relatively simple and involves taking a blood sample from the patient. The blood is then placed in a tall, thin tube and left to stand for exactly one hour. The rate at which the red blood cells settle is then measured and recorded. Results are typically reported in millimeters per hour (mm/hr). The normal range can vary slightly between laboratories but generally falls within specific values for men and women. It's crucial to understand that a single test result might not provide a complete picture, and healthcare providers often consider the results in the context of the patient's overall health and other diagnostic findings.Causes of High Sedimentation Rate

Treatment Options for Underlying Conditions
Treatment for a high sedimentation rate depends on the underlying cause of the inflammation. For infections, antibiotics or antiviral medications may be prescribed. In the case of autoimmune diseases, treatment often involves the use of anti-inflammatory medications, immunosuppressants, or biologic agents to reduce inflammation and modulate the immune response. For cancer, treatment options such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or targeted therapy may be employed. In some cases, lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes, increased physical activity, and stress management, can help in reducing chronic inflammation.Effects of High Sedimentation Rate on Health
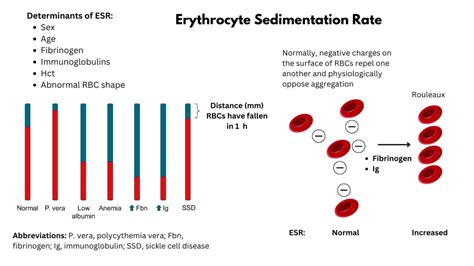
Management and Reduction of Inflammation
Managing and reducing inflammation is crucial to mitigate the effects of a high sedimentation rate on health. This can be achieved through a combination of medical treatment for the underlying condition and lifestyle modifications. Dietary changes, such as adopting an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, can help in reducing inflammation. Regular physical activity, stress reduction techniques like meditation or yoga, and getting adequate sleep are also beneficial. In some cases, supplements like omega-3 fatty acids or turmeric (curcumin) may be recommended for their anti-inflammatory properties, although it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplements.Monitoring and Follow-Up
Importance of Patient Education
Patient education plays a critical role in the management of conditions associated with a high sedimentation rate. By understanding their condition, the importance of treatment adherence, and the role of lifestyle modifications, patients can take an active part in managing their health. This education should cover the signs of worsening inflammation, the importance of follow-up appointments, and how to recognize when to seek immediate medical attention. Empowering patients with knowledge not only improves their health outcomes but also enhances their quality of life.Conclusion and Future Directions

Final Thoughts on Health Management
Ultimately, managing health in the context of a high sedimentation rate requires a holistic approach, combining medical treatment with lifestyle changes. By staying informed, being proactive about health, and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals can effectively manage inflammation and reduce the risk of associated health complications. It's a journey that requires patience, commitment, and a willingness to adapt to new information and treatment strategies as they become available.What is a normal sedimentation rate?
+A normal sedimentation rate can vary slightly between laboratories but generally falls within specific values for men and women. For men, a normal range is typically considered to be 0-15 mm/hr, and for women, it is 0-20 mm/hr.
What are the common causes of a high sedimentation rate?
+Common causes include infections, autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, and certain types of cancer. Other conditions such as kidney disease, liver disease, and heart disease can also lead to an elevated sedimentation rate.
How can I reduce inflammation and lower my sedimentation rate?
+Reducing inflammation involves treating the underlying cause, adopting an anti-inflammatory diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, and getting adequate sleep. In some cases, supplements like omega-3 fatty acids may be recommended, but it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences regarding high sedimentation rates and their impact on health. Your insights can help others understand the importance of managing inflammation and the steps they can take towards a healthier life. Feel free to comment, share this article with others who might benefit, and explore more topics related to health and wellness. Together, we can work towards creating a community that prioritizes health education and supports individuals in their journey towards better health outcomes.
