Intro
Understand normal prothrombin time, a blood clotting test, and its significance in diagnosing coagulation disorders, thrombosis, and bleeding risks with related factors like INR, warfarin, and vitamin K.
Prothrombin time, also known as PT, is a crucial blood test that measures the time it takes for the blood to clot. It is an essential tool for doctors to diagnose and monitor various bleeding and clotting disorders. In this article, we will delve into the world of normal prothrombin time, its importance, and what it reveals about our health.
The prothrombin time test is a widely used diagnostic tool that helps healthcare professionals assess the blood's ability to form clots. Blood clotting is a complex process that involves multiple factors, and PT measures the activity of these factors to determine if they are functioning correctly. A normal prothrombin time indicates that the blood is clotting properly, while an abnormal result may suggest an underlying condition that requires medical attention.
The prothrombin time test is often used in conjunction with other blood tests, such as the partial thromboplastin time (PTT) and the international normalized ratio (INR), to provide a comprehensive picture of a patient's blood clotting profile. By understanding the results of these tests, doctors can diagnose and manage conditions such as bleeding disorders, blood clotting disorders, and monitor patients on anticoagulant therapy.
What is Normal Prothrombin Time?
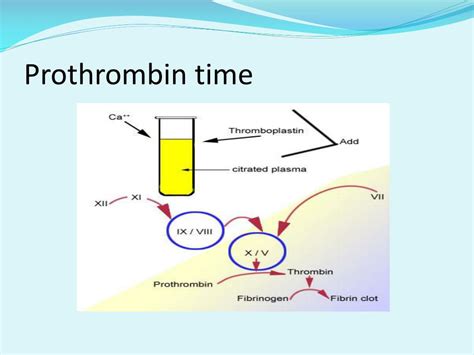
Normal prothrombin time refers to the range of values that indicate a person's blood is clotting normally. The normal range for prothrombin time varies slightly depending on the laboratory and the testing method used. However, in general, a normal prothrombin time is considered to be between 11 and 13.5 seconds. This range may vary slightly depending on the individual and the specific testing conditions.
It is essential to note that prothrombin time is not a standalone test, and the results should be interpreted in conjunction with other clinical findings and laboratory tests. A healthcare professional will consider various factors, including the patient's medical history, symptoms, and other test results, to determine the significance of the prothrombin time result.
Factors that Influence Prothrombin Time
Several factors can influence prothrombin time, including: * Age: Prothrombin time may be slightly longer in older adults due to age-related changes in blood clotting factors. * Sex: Women tend to have slightly shorter prothrombin times than men. * Medications: Certain medications, such as anticoagulants, can affect prothrombin time. * Diet: A diet low in vitamin K can lead to longer prothrombin times. * Liver function: The liver produces many of the clotting factors measured by the prothrombin time test, so liver disease can affect the results.How is Prothrombin Time Measured?

Prothrombin time is measured using a blood sample, typically collected from a vein in the arm. The blood sample is then mixed with a substance called tissue factor, which activates the blood clotting process. The time it takes for the blood to clot is then measured, usually in seconds.
There are several methods for measuring prothrombin time, including:
- Manual methods: These involve adding tissue factor to the blood sample and measuring the time it takes for the blood to clot.
- Automated methods: These use specialized machines to measure prothrombin time.
- Point-of-care methods: These are portable devices that can be used to measure prothrombin time at the bedside or in a clinic.
Interpreting Prothrombin Time Results
Interpreting prothrombin time results requires a thorough understanding of the test and its limitations. A healthcare professional will consider the following factors when interpreting the results: * The normal range for the laboratory and testing method used. * The patient's medical history and symptoms. * The results of other laboratory tests, such as PTT and INR. * The presence of any underlying conditions that may affect blood clotting.Abnormal Prothrombin Time Results
Abnormal prothrombin time results can indicate a range of conditions, including:
- Bleeding disorders: Such as hemophilia or von Willebrand disease.
- Blood clotting disorders: Such as thrombophilia or antiphospholipid syndrome.
- Liver disease: Such as cirrhosis or liver cancer.
- Vitamin K deficiency: Which can be caused by a poor diet or certain medications.
- Anticoagulant therapy: Which can affect prothrombin time in patients taking anticoagulant medications.
Treatment and Management
Treatment and management of abnormal prothrombin time results depend on the underlying condition. In some cases, treatment may involve: * Anticoagulant therapy: To prevent blood clots from forming. * Vitamin K supplements: To correct a deficiency. * Blood transfusions: To replace clotting factors. * Surgery: To treat underlying conditions, such as liver disease.Prothrombin Time and Anticoagulant Therapy

Prothrombin time is an essential tool for monitoring patients on anticoagulant therapy. Anticoagulant medications, such as warfarin, work by inhibiting the production of clotting factors, which can affect prothrombin time. Regular monitoring of prothrombin time is necessary to ensure that the patient is receiving the correct dose of anticoagulant medication.
The international normalized ratio (INR) is a calculation based on prothrombin time that is used to monitor patients on anticoagulant therapy. The INR takes into account the variations in prothrombin time between different laboratories and testing methods, providing a standardized measure of blood clotting.
Importance of Regular Monitoring
Regular monitoring of prothrombin time is crucial for patients on anticoagulant therapy. This helps to: * Ensure that the patient is receiving the correct dose of anticoagulant medication. * Prevent bleeding complications: By detecting any changes in prothrombin time that may indicate an increased risk of bleeding. * Prevent thrombotic complications: By detecting any changes in prothrombin time that may indicate an increased risk of blood clots.Prothrombin Time and Pregnancy
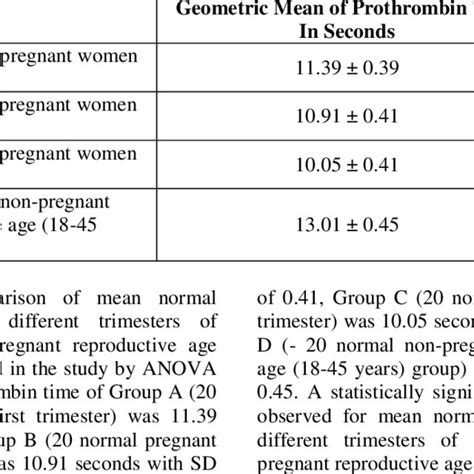
Prothrombin time is an essential test for pregnant women, particularly those with a history of bleeding or clotting disorders. Pregnancy can affect blood clotting, and prothrombin time can help identify any potential complications.
During pregnancy, the blood clotting system is activated to prevent excessive bleeding during childbirth. However, this can also increase the risk of blood clots. Prothrombin time can help healthcare professionals monitor the blood clotting profile of pregnant women and adjust anticoagulant therapy as needed.
Risks and Complications
Pregnant women with abnormal prothrombin time results are at increased risk of: * Bleeding complications: Such as placental abruption or postpartum hemorrhage. * Thrombotic complications: Such as deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism. * Fetal complications: Such as growth restriction or preterm birth.Prothrombin Time and Liver Disease
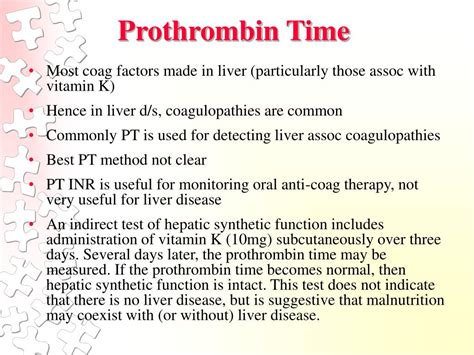
Prothrombin time is an essential test for patients with liver disease. The liver produces many of the clotting factors measured by the prothrombin time test, and liver disease can affect the production of these factors.
Patients with liver disease may have abnormal prothrombin time results, which can indicate:
- Impaired liver function: Such as cirrhosis or liver cancer.
- Coagulopathy: A condition characterized by impaired blood clotting.
- Bleeding complications: Such as gastrointestinal bleeding or easy bruising.
Treatment and Management
Treatment and management of liver disease-related coagulopathy depend on the underlying condition. In some cases, treatment may involve: * Vitamin K supplements: To correct a deficiency. * Blood transfusions: To replace clotting factors. * Anticoagulant therapy: To prevent blood clots from forming. * Liver transplantation: In severe cases of liver disease.What is the normal range for prothrombin time?
+The normal range for prothrombin time is typically between 11 and 13.5 seconds, although this may vary slightly depending on the laboratory and testing method used.
What factors can influence prothrombin time?
+Several factors can influence prothrombin time, including age, sex, medications, diet, and liver function.
What is the significance of prothrombin time in anticoagulant therapy?
+Prothrombin time is an essential tool for monitoring patients on anticoagulant therapy, helping to ensure that the patient is receiving the correct dose of anticoagulant medication and preventing bleeding or thrombotic complications.
Can prothrombin time be used to diagnose liver disease?
+Yes, prothrombin time can be used to diagnose liver disease, as the liver produces many of the clotting factors measured by the prothrombin time test. Abnormal prothrombin time results may indicate impaired liver function or coagulopathy.
What are the risks of abnormal prothrombin time results during pregnancy?
+Abnormal prothrombin time results during pregnancy can increase the risk of bleeding or thrombotic complications, as well as fetal complications such as growth restriction or preterm birth.
In conclusion, prothrombin time is a vital diagnostic tool that provides valuable insights into the blood clotting profile. By understanding the normal range, factors that influence prothrombin time, and the significance of abnormal results, healthcare professionals can diagnose and manage various bleeding and clotting disorders. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with prothrombin time testing in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns about prothrombin time, please do not hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider.
