Intro
Understand normal PT and INR values with our comprehensive guide, covering prothrombin time, international normalized ratio, blood clotting, and coagulation tests to ensure optimal health and prevent bleeding disorders or thrombosis complications.
Normal PT and INR values are crucial for understanding the blood's clotting mechanism and ensuring that patients are not at risk of excessive bleeding or thrombosis. The Prothrombin Time (PT) and International Normalized Ratio (INR) tests are essential for assessing the blood's coagulation pathway, particularly for patients on anticoagulant therapy, such as warfarin. In this article, we will delve into the significance of these tests, their normal values, and the implications of abnormal results.
The importance of PT and INR tests cannot be overstated, as they provide critical information about the blood's ability to form clots. Clotting is a complex process involving multiple factors, and any disruption in this process can lead to serious health issues. For instance, patients with bleeding disorders, such as hemophilia, may experience prolonged bleeding due to a deficiency in clotting factors. On the other hand, patients with thrombophilia may be at risk of developing blood clots due to an increased tendency for clotting.
The PT test measures the time it takes for blood to clot, while the INR test standardizes the PT result to ensure consistency across different laboratories. Normal PT values typically range from 10 to 14 seconds, although this may vary slightly depending on the laboratory. The INR value is calculated based on the PT result and is usually between 0.9 and 1.1 for individuals not taking anticoagulant medications. These values are essential for diagnosing and managing coagulation disorders, as well as monitoring the effectiveness of anticoagulant therapy.
Understanding PT and INR Tests
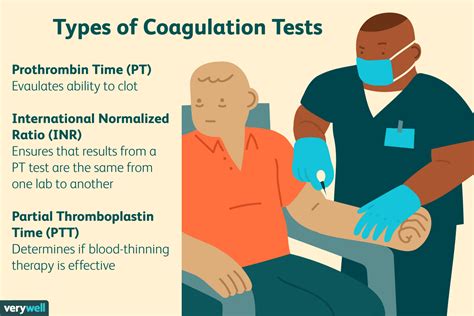
To comprehend the significance of PT and INR tests, it is essential to understand the blood coagulation cascade. The coagulation pathway involves a series of complex reactions that ultimately lead to the formation of a blood clot. The PT test measures the extrinsic and common pathways of coagulation, while the INR test standardizes the PT result to account for variations in laboratory testing. By analyzing PT and INR values, healthcare professionals can identify potential issues with the coagulation pathway and take necessary steps to prevent or treat related disorders.
Benefits of PT and INR Tests
The benefits of PT and INR tests are numerous, including: * Early detection of coagulation disorders * Monitoring of anticoagulant therapy * Identification of patients at risk of bleeding or thrombosis * Guidance for surgical procedures and other medical interventions * Optimization of treatment plans for patients with coagulation disordersNormal PT and INR Values
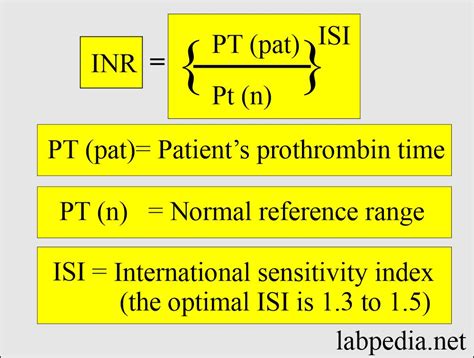
Normal PT values typically range from 10 to 14 seconds, although this may vary slightly depending on the laboratory. The INR value is calculated based on the PT result and is usually between 0.9 and 1.1 for individuals not taking anticoagulant medications. It is essential to note that these values may vary depending on the specific laboratory and testing methods used. Therefore, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the normal PT and INR values for a specific individual.
Interpreting PT and INR Results
Interpreting PT and INR results requires a thorough understanding of the coagulation pathway and the factors that influence these tests. A prolonged PT or elevated INR may indicate a bleeding disorder or the presence of anticoagulant medications. On the other hand, a shortened PT or decreased INR may suggest a thrombotic disorder or the presence of clotting factors. By analyzing PT and INR values, healthcare professionals can identify potential issues with the coagulation pathway and take necessary steps to prevent or treat related disorders.Factors Affecting PT and INR Values
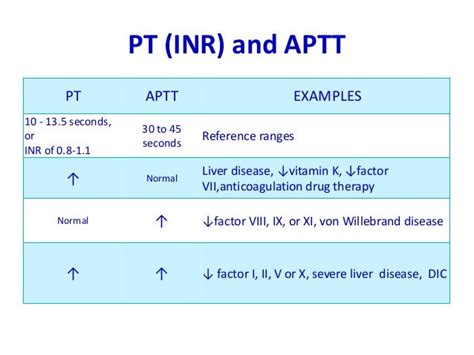
Several factors can affect PT and INR values, including:
- Anticoagulant medications, such as warfarin
- Vitamin K deficiency
- Liver disease
- Kidney disease
- Inherited bleeding disorders, such as hemophilia
- Acquired bleeding disorders, such as disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
Managing Abnormal PT and INR Values
Managing abnormal PT and INR values requires a comprehensive approach that takes into account the underlying cause of the abnormality. This may involve adjusting anticoagulant medications, supplementing with vitamin K, or treating underlying medical conditions. In some cases, patients may require more frequent monitoring of PT and INR values to ensure that their coagulation pathway is functioning properly.PT and INR Values in Clinical Practice
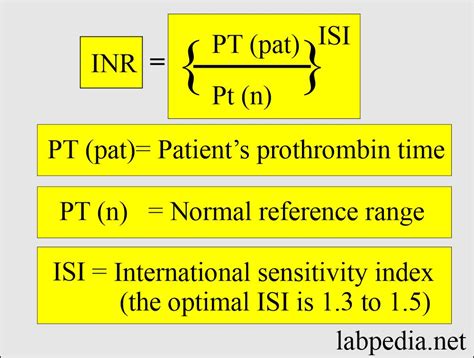
PT and INR values play a critical role in clinical practice, particularly in the management of patients on anticoagulant therapy. By monitoring PT and INR values, healthcare professionals can adjust anticoagulant medications to ensure that patients are receiving the optimal dose. This helps to minimize the risk of bleeding or thrombosis and ensures that patients receive the best possible outcomes.
Case Studies: PT and INR Values in Clinical Practice
Several case studies have demonstrated the importance of PT and INR values in clinical practice. For example, a study published in the Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis found that patients with atrial fibrillation who were treated with warfarin had a significantly reduced risk of stroke and systemic embolism when their INR values were maintained within the therapeutic range. Another study published in the New England Journal of Medicine found that patients with deep vein thrombosis who were treated with anticoagulant medications had a reduced risk of recurrent thrombosis when their PT and INR values were closely monitored.Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, normal PT and INR values are essential for understanding the blood's clotting mechanism and ensuring that patients are not at risk of excessive bleeding or thrombosis. By monitoring PT and INR values, healthcare professionals can identify potential issues with the coagulation pathway and take necessary steps to prevent or treat related disorders. Future directions in the field of coagulation disorders may involve the development of new anticoagulant medications and more precise testing methods for PT and INR values.
Final Thoughts
In final thoughts, PT and INR values are critical components of patient care, particularly for those with coagulation disorders or those taking anticoagulant medications. By understanding the significance of these tests and their normal values, healthcare professionals can provide optimal care for their patients and minimize the risk of bleeding or thrombosis.What is the normal range for PT values?
+Normal PT values typically range from 10 to 14 seconds, although this may vary slightly depending on the laboratory.
What is the normal range for INR values?
+Normal INR values are usually between 0.9 and 1.1 for individuals not taking anticoagulant medications.
What factors can affect PT and INR values?
+Several factors can affect PT and INR values, including anticoagulant medications, vitamin K deficiency, liver disease, kidney disease, inherited bleeding disorders, and acquired bleeding disorders.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of normal PT and INR values and their significance in clinical practice. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with PT and INR tests, please feel free to comment below. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from this information. By working together, we can promote better understanding and management of coagulation disorders and improve patient outcomes.
