Intro
Learn about 5 triglyceride levels, normal ranges, and risks. Understand triglycerides, cholesterol, and heart health with related lipids and fatty acids management.
Triglycerides are a type of fat found in the blood, and having high levels of triglycerides can increase the risk of heart disease. The importance of maintaining healthy triglyceride levels cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in overall cardiovascular health. When triglyceride levels are elevated, it can lead to the development of plaque in the arteries, which can cause them to narrow and harden, ultimately leading to heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular conditions. Therefore, understanding triglycerides and how to manage their levels is essential for maintaining a healthy heart and reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
High triglyceride levels are often associated with other health conditions, such as obesity, diabetes, and high blood pressure. These conditions can increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease, making it essential to manage triglyceride levels through a combination of lifestyle changes and medical treatment. Fortunately, there are many effective ways to lower triglyceride levels, including dietary changes, regular exercise, and medication. By making informed choices about diet and lifestyle, individuals can reduce their triglyceride levels and minimize their risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
The relationship between triglycerides and cardiovascular health is complex, and many factors can influence triglyceride levels. For example, genetics, age, and sex can all play a role in determining an individual's triglyceride levels. Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as hypothyroidism and kidney disease, can also affect triglyceride levels. Understanding these factors and how they impact triglyceride levels can help individuals take a proactive approach to managing their cardiovascular health. By being informed and taking control of their health, individuals can reduce their risk of developing cardiovascular disease and maintain a healthy heart.
Understanding Triglycerides
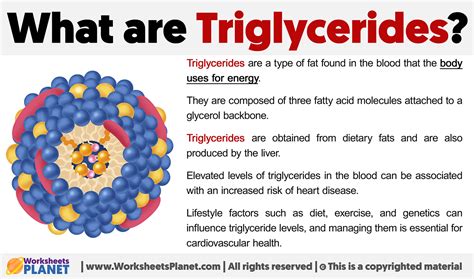
Triglycerides are measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) of blood, and the American Heart Association recommends the following triglyceride levels:
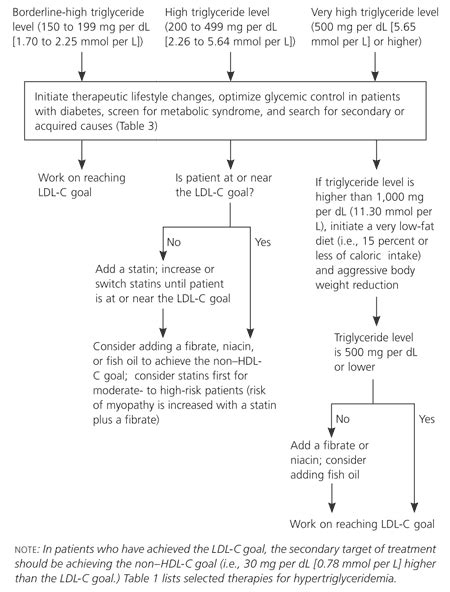
- Normal: Less than 150 mg/dL
- Borderline high: 150-199 mg/dL
- High: 200-499 mg/dL
- Very high: 500 mg/dL or higher Individuals with high triglyceride levels are at increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease, and it is essential to manage their levels through lifestyle changes and medical treatment.
Causes of High Triglyceride Levels
There are several causes of high triglyceride levels, including: * Genetics: Family history can play a role in determining triglyceride levels. * Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase triglyceride levels. * Physical inactivity: Lack of exercise can contribute to high triglyceride levels. * Diet: Consuming a diet high in saturated and trans fats, sugar, and refined carbohydrates can increase triglyceride levels. * Certain medical conditions: Conditions such as hypothyroidism, kidney disease, and liver disease can affect triglyceride levels. * Medications: Certain medications, such as birth control pills and beta-blockers, can increase triglyceride levels.Managing Triglyceride Levels
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Triglyceride Levels
The following lifestyle changes can help manage triglyceride levels: * Eating a healthy diet: Focus on consuming whole, unprocessed foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. * Increasing physical activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week. * Maintaining a healthy weight: Aim for a body mass index (BMI) between 18.5 and 24.9. * Getting enough sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night. * Reducing stress: Engage in stress-reducing activities, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing.Benefits of Lowering Triglyceride Levels

Statistical Data on Triglyceride Levels
According to the American Heart Association,: * More than 30% of adults in the United States have high triglyceride levels. * High triglyceride levels are more common in men than women. * The prevalence of high triglyceride levels increases with age. * Individuals with high triglyceride levels are at increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease.Practical Tips for Managing Triglyceride Levels

Common Mistakes to Avoid When Managing Triglyceride Levels
The following are some common mistakes to avoid when managing triglyceride levels: * Not monitoring triglyceride levels regularly: Failing to regularly monitor triglyceride levels can make it difficult to stay on top of your health. * Not making lifestyle changes: Failing to make lifestyle changes, such as dietary changes and regular exercise, can make it difficult to lower triglyceride levels. * Not seeking medical attention: Failing to seek medical attention if triglyceride levels are high can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. * Not taking medication as prescribed: Failing to take medication as prescribed can reduce its effectiveness in lowering triglyceride levels.Conclusion and Next Steps

We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with managing triglyceride levels in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to reach out. Additionally, if you found this article helpful, please share it with your friends and family to help spread awareness about the importance of managing triglyceride levels.
What are triglycerides?
+Triglycerides are a type of fat found in the blood, and having high levels of triglycerides can increase the risk of heart disease.
What are the causes of high triglyceride levels?
+The causes of high triglyceride levels include genetics, obesity, physical inactivity, diet, certain medical conditions, and medications.
How can I lower my triglyceride levels?
+Lowering triglyceride levels can be achieved through a combination of lifestyle changes, such as dietary changes and regular exercise, and medical treatment.
What are the benefits of lowering triglyceride levels?
+The benefits of lowering triglyceride levels include reduced risk of cardiovascular disease, improved blood flow, improved insulin sensitivity, weight loss, and improved overall health.
How often should I monitor my triglyceride levels?
+It is recommended to monitor triglyceride levels regularly, ideally every 1-2 years, or as recommended by your healthcare provider.
