Intro
Maintain healthy blood sugar levels with 5 expert tips. Learn to regulate glucose, prevent spikes, and stabilize normal sugar levels naturally, managing diabetes and prediabetes through diet and lifestyle changes.
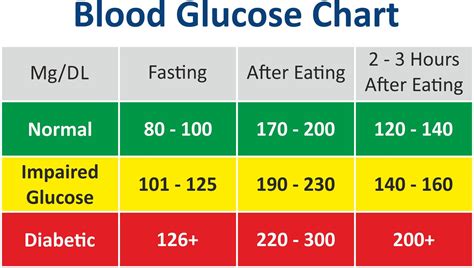
Maintaining normal sugar levels is crucial for overall health and wellbeing. When sugar levels are within a normal range, the body can function properly, and the risk of developing conditions like diabetes and heart disease is reduced. Normal sugar levels are typically between 70 and 140 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) after eating, and below 100 mg/dL when fasting. Achieving and maintaining these levels requires a combination of a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and, in some cases, medication.
Understanding the importance of normal sugar levels is the first step towards making lifestyle changes that can significantly impact health. High sugar levels can lead to a range of health issues, including insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Conversely, low sugar levels, known as hypoglycemia, can cause symptoms like dizziness, confusion, and in severe cases, loss of consciousness. Therefore, managing sugar levels effectively is a key aspect of preventive healthcare.
The management of sugar levels involves a multifaceted approach that includes dietary adjustments, physical activity, stress management, and, for individuals with diabetes, monitoring blood glucose levels and adhering to prescribed treatment plans. By adopting healthy habits and being mindful of the factors that influence sugar levels, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining normal sugar levels and reducing the risk of related health complications. This not only improves quality of life but also contributes to longevity and overall wellbeing.
Understanding Normal Sugar Levels
Factors Influencing Sugar Levels
Several factors can influence sugar levels, including diet, physical activity level, stress, sleep quality, and certain medications. Foods high in simple sugars and refined carbohydrates can cause a rapid spike in blood glucose, while regular physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity, helping to lower and stabilize sugar levels. Stress and poor sleep quality can also impact sugar levels by affecting the body's hormonal balance and metabolic rate.Dietary Approaches to Manage Sugar Levels

Benefits of a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet offers numerous benefits for sugar level management, including: - **Improved Insulin Sensitivity:** Regular consumption of whole foods can enhance the body's response to insulin, reducing the risk of developing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. - **Weight Management:** Eating a diet rich in fiber and lean protein can help with weight management, as these foods tend to be more satiating and support a healthier metabolism. - **Reduced Inflammation:** Whole foods are rich in antioxidants and other nutrients that help reduce inflammation in the body, which is associated with various chronic diseases, including diabetes and cardiovascular disease.Physical Activity and Sugar Levels

Types of Exercise
Different types of exercise offer various benefits for sugar level management: - **Aerobic Exercise:** Activities like walking, jogging, cycling, and swimming improve cardiovascular health and increase insulin sensitivity. - **Resistance Training:** Building muscle through strength training can further improve insulin sensitivity and metabolic health. - **High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT):** This form of exercise has been shown to significantly improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood sugar levels.Stress Management and Sugar Levels
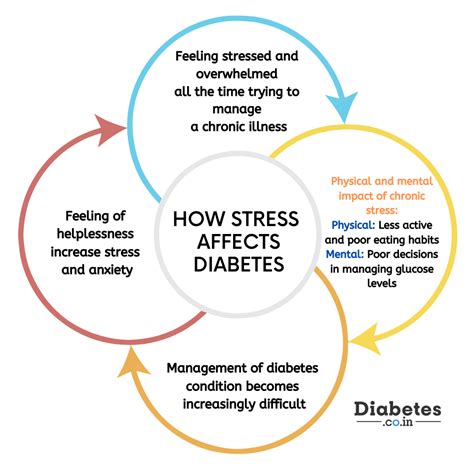
Benefits of Stress Reduction
Reducing stress offers several benefits for overall health and sugar level management, including: - **Improved Hormonal Balance:** Lower stress levels can lead to a more balanced hormonal profile, reducing the negative impact of stress hormones on blood sugar. - **Enhanced Sleep Quality:** Stress reduction techniques can improve sleep quality, which is essential for metabolic health and sugar level regulation. - **Increased Resilience:** Managing stress effectively can increase an individual's resilience to other stressors, promoting overall wellbeing.Monitoring and Maintaining Normal Sugar Levels

Tools for Monitoring
Several tools are available for monitoring blood sugar levels, including: - **Glucose Meters:** These are portable devices that measure the glucose concentration in a blood sample. - **Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs):** CGMs provide real-time glucose readings throughout the day and night, offering insights into glucose trends and patterns. - **Mobile Apps:** Various apps are designed to track glucose levels, diet, exercise, and other health metrics, providing a comprehensive view of an individual's health status.Conclusion and Future Directions

In the pursuit of maintaining normal sugar levels, it is crucial to stay engaged with healthcare providers, monitor health metrics regularly, and be open to adjusting treatment plans as needed. The journey towards optimal sugar level management is ongoing, and by combining the latest scientific knowledge with personalized care, individuals can navigate this path effectively, leading to improved health outcomes and a better quality of life.
What are normal sugar levels?
+Normal sugar levels are typically between 70 and 140 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) after eating, and below 100 mg/dL when fasting.
How can diet affect sugar levels?
+A diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help maintain normal sugar levels by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing inflammation.
What role does physical activity play in managing sugar levels?
+Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, reduces body fat, and helps lower blood sugar levels, making it a crucial component of sugar level management.
We hope this comprehensive guide has provided you with valuable insights into managing normal sugar levels. By applying the principles outlined here, you can take significant steps towards improving your metabolic health and reducing the risk of related diseases. Remember, maintaining normal sugar levels is a journey that requires patience, persistence, and a commitment to healthy lifestyle choices. Share your thoughts, experiences, and questions in the comments below, and let's work together towards achieving better health outcomes for all.
