Intro
Manage diabetes with 5 blood sugar tips, including glucose monitoring, healthy eating, and insulin management, to maintain stable blood glucose levels and prevent complications like hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
Managing diabetes requires a deep understanding of how to control blood sugar levels. It's a condition that affects millions of people worldwide, and its impact on daily life can be significant. From dietary changes to regular monitoring, there are several strategies that can help individuals with diabetes lead healthier, more balanced lives. The importance of managing diabetes cannot be overstated, as uncontrolled blood sugar levels can lead to a variety of serious health complications, including heart disease, kidney damage, and vision problems. By adopting a few simple yet effective tips, individuals with diabetes can better manage their condition and improve their overall quality of life.
Effective management of diabetes involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments and medical interventions. For many people, this means making significant changes to their diet, increasing their physical activity levels, and monitoring their blood sugar levels regularly. It also involves working closely with healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan that takes into account the individual's specific needs and health status. By taking a proactive and informed approach to managing their diabetes, individuals can reduce their risk of developing complications and enjoy a longer, healthier life.
The journey to managing diabetes successfully begins with education and awareness. Understanding how different factors such as diet, exercise, and stress affect blood sugar levels is crucial. It's also important to be aware of the symptoms of high and low blood sugar, as recognizing these can help individuals take prompt action to prevent serious health issues. Furthermore, staying up-to-date with the latest research and advancements in diabetes care can provide individuals with the tools and knowledge they need to make informed decisions about their health. Whether it's through online resources, support groups, or healthcare providers, there are many ways for individuals with diabetes to access the information and support they need to thrive.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
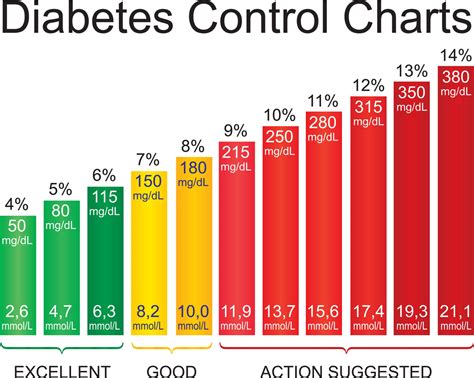
Importance of Regular Monitoring
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes. It provides valuable insights into how the body is responding to different foods, physical activities, and medications. By tracking blood sugar levels over time, individuals can identify patterns and trends that help them make adjustments to their diabetes management plan. This might involve changing the timing or dosage of medications, adjusting the diet to include more blood sugar-friendly foods, or increasing physical activity levels. Regular monitoring also helps individuals recognize the early signs of high or low blood sugar, enabling them to take prompt action to prevent serious complications.Dietary Changes for Managing Diabetes

Key Foods for Diabetes Management
Certain foods are particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes. These include: - Leafy green vegetables like spinach and kale, which are rich in fiber and antioxidants. - Berries such as blueberries and strawberries, which are high in fiber and antioxidants but low in carbohydrates. - Fatty fish like salmon, which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids that can help reduce inflammation. - Whole grains like brown rice and quinoa, which are high in fiber and can help regulate blood sugar levels. - Legumes such as lentils and chickpeas, which are rich in protein, fiber, and complex carbohydrates.Exercise and Physical Activity

Getting Started with Exercise
Getting started with an exercise program can be challenging, especially for individuals who are new to physical activity. Here are some tips to help get started: - Consult with a healthcare provider before beginning any new exercise program. - Start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of workouts. - Find activities that are enjoyable and that fit into the lifestyle, such as walking, swimming, or cycling. - Consider working with a personal trainer or fitness coach who has experience with diabetes management. - Monitor blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise to understand how physical activity affects blood sugar levels.Stress Management and Diabetes

Practical Stress Management Techniques
Here are some practical stress management techniques that can help individuals with diabetes: - Practice mindfulness and meditation to reduce stress and improve mood. - Engage in physical activity, such as walking or yoga, to help manage stress and improve blood sugar control. - Connect with friends and family, or join a support group, to build a strong social support network. - Get enough sleep each night, aiming for 7-8 hours, to help regulate stress hormones and blood sugar levels. - Consider seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor who has experience with diabetes management.Medications and Diabetes Management
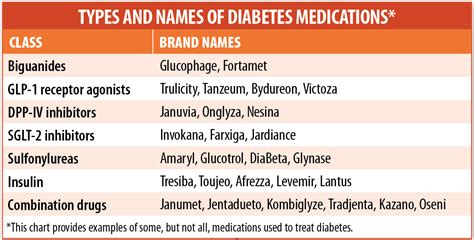
Common Diabetes Medications
Here are some common diabetes medications: - Metformin, which helps the body use insulin more efficiently and can also help with weight management. - Sulfonylureas, which stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin. - Meglitinides, which also stimulate insulin production but have a faster onset of action. - Thiazolidinediones, which help the body use insulin more effectively and can also improve cholesterol levels. - GLP-1 receptor agonists, which help the body produce more insulin and can also slow gastric emptying.What are the symptoms of high blood sugar?
+The symptoms of high blood sugar include increased thirst and urination, blurred vision, headaches, and fatigue. If left untreated, high blood sugar can lead to serious health complications.
How often should I monitor my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of blood sugar monitoring depends on the type of diabetes and the individual's treatment plan. Generally, individuals with type 1 diabetes need to monitor their blood sugar levels more frequently than those with type 2 diabetes.
Can I manage my diabetes through diet and exercise alone?
+For some individuals with type 2 diabetes, it may be possible to manage the condition through diet and exercise alone, especially if the condition is caught early. However, this approach should always be done under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
As we conclude our exploration of diabetes management, it's clear that controlling blood sugar levels is a multifaceted endeavor that requires attention to diet, exercise, stress management, and, when necessary, medication. By adopting a holistic approach to health and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals with diabetes can lead active, healthy lives. We invite you to share your experiences, ask questions, and seek support from the diabetes community. Together, we can promote greater awareness and understanding of this condition, ultimately improving the lives of those affected by diabetes.
