Intro
Discover how Prothrombin Time works through 5 key mechanisms, including blood clotting, coagulation, and thrombosis, to diagnose bleeding disorders and monitor anticoagulant therapy effectively.
Prothrombin time, also known as PT, is a crucial blood test that measures the time it takes for blood to clot. This test is essential in evaluating the effectiveness of blood clotting and identifying potential bleeding disorders. The prothrombin time test is widely used in medical settings to assess the risk of bleeding in patients, particularly those undergoing surgery or taking anticoagulant medications. In this article, we will delve into the world of prothrombin time and explore its mechanisms, benefits, and applications.
The prothrombin time test is a vital tool in the diagnosis and management of bleeding disorders. It measures the time it takes for blood to clot, which is essential in preventing excessive bleeding during surgical procedures or injuries. The test is also used to monitor patients taking anticoagulant medications, such as warfarin, to ensure that their blood is not too thin or too thick. By understanding how prothrombin time works, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions about patient care and treatment.
Prothrombin time is a complex process that involves the interaction of various blood components, including clotting factors, platelets, and fibrinogen. The test measures the time it takes for these components to come together and form a blood clot. This process is triggered by the addition of tissue factor, a substance that stimulates the clotting cascade. The resulting clotting time is then measured and compared to a standard reference range. By analyzing the prothrombin time, healthcare professionals can identify potential bleeding disorders, monitor anticoagulant therapy, and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
What is Prothrombin Time?

How is Prothrombin Time Measured?
The prothrombin time test is measured using a blood sample, which is typically collected from a vein in the arm. The blood sample is then mixed with a substance called tissue factor, which stimulates the clotting cascade. The resulting clotting time is then measured and compared to a standard reference range. The prothrombin time is typically reported in seconds, and the normal range is usually between 10-14 seconds. However, the normal range may vary depending on the laboratory and the specific testing method used.Benefits of Prothrombin Time

Applications of Prothrombin Time
The prothrombin time test has several applications in medical settings. Some of the applications include: * Monitoring patients taking anticoagulant medications, such as warfarin * Evaluating the risk of bleeding in patients undergoing surgery * Identifying potential bleeding disorders, such as hemophilia or von Willebrand disease * Assessing the effectiveness of blood clotting and identifying potential clotting disorders * Guiding treatment decisions for patients with bleeding disorders or clotting disordersHow Prothrombin Time Works
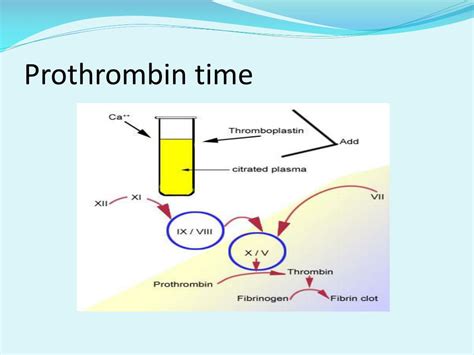
Steps Involved in Prothrombin Time
The prothrombin time test involves several steps, including: 1. Blood sample collection: A blood sample is typically collected from a vein in the arm. 2. Mixing with tissue factor: The blood sample is mixed with tissue factor, which stimulates the clotting cascade. 3. Measuring clotting time: The resulting clotting time is measured and compared to a standard reference range. 4. Reporting results: The prothrombin time is typically reported in seconds, and the normal range is usually between 10-14 seconds.Interpretation of Prothrombin Time Results
Factors that Affect Prothrombin Time
Several factors can affect the prothrombin time results, including: * Anticoagulant medications, such as warfarin * Bleeding disorders, such as hemophilia or von Willebrand disease * Clotting disorders, such as thrombophilia * Liver disease or kidney disease * Vitamin K deficiencyProthrombin Time and Anticoagulant Therapy

Monitoring Anticoagulant Therapy
The prothrombin time test is typically used to monitor anticoagulant therapy in patients taking medications such as warfarin. The test measures the time it takes for blood to clot, which is essential in preventing excessive bleeding during surgical procedures or injuries. By monitoring the prothrombin time, healthcare professionals can adjust the anticoagulant dosage to ensure that the patient's blood is not too thin or too thick.Prothrombin Time and Bleeding Disorders

Diagnosing Bleeding Disorders
The prothrombin time test is typically used to diagnose bleeding disorders, such as hemophilia or von Willebrand disease. The test measures the time it takes for blood to clot, which is essential in preventing excessive bleeding during surgical procedures or injuries. By understanding the prothrombin time, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions about patient care and treatment.What is prothrombin time?
+Prothrombin time is a blood test that measures the time it takes for blood to clot.
What is the normal range for prothrombin time?
+The normal range for prothrombin time is usually between 10-14 seconds.
What factors can affect prothrombin time results?
+Several factors can affect prothrombin time results, including anticoagulant medications, bleeding disorders, clotting disorders, liver disease or kidney disease, and vitamin K deficiency.
In conclusion, prothrombin time is a vital tool in the diagnosis and management of bleeding disorders and clotting disorders. By understanding how prothrombin time works, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions about patient care and treatment. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with prothrombin time in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns about prothrombin time, please do not hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider. Additionally, we invite readers to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about prothrombin time and its applications in medical settings.
