Intro
Discover NSAID side effects, risks, and warnings. Learn about gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, and renal complications, as well as interactions and allergic reactions associated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
The use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, commonly referred to as NSAIDs, has become widespread due to their effectiveness in managing pain, reducing inflammation, and lowering fever. However, like all medications, NSAIDs come with their own set of side effects, some of which can be severe and even life-threatening. Understanding these side effects is crucial for individuals who rely on NSAIDs for pain management, as it allows them to make informed decisions about their health and to recognize when they might need to seek medical attention.
NSAIDs work by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, which are substances in the body that mediate inflammation, pain, and fever. While this action is beneficial for relieving symptoms, it can also lead to unwanted effects, particularly on the gastrointestinal system, kidneys, and cardiovascular system. The severity and likelihood of these side effects can vary depending on the specific type of NSAID, the dosage, and the duration of use, as well as individual factors such as age, health status, and other medications being taken.
For many people, the benefits of NSAIDs in managing pain and inflammation outweigh the risks, but it's essential to be aware of the potential side effects to minimize harm. This includes knowing how to take NSAIDs safely, recognizing early signs of problems, and discussing concerns with healthcare providers. Moreover, with the advancement of medical research, alternative treatments and management strategies are being explored and developed, offering hopes for reducing reliance on NSAIDs or mitigating their adverse effects.
Common Side Effects of NSAIDs
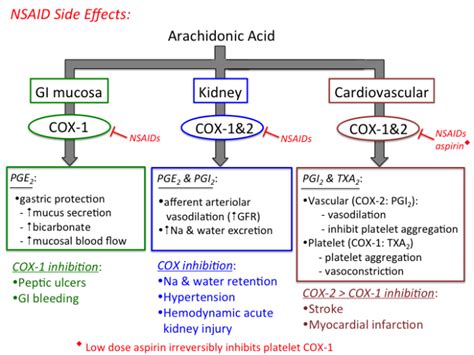
The most common side effects of NSAIDs are related to the gastrointestinal system. These can range from mild stomach upset and nausea to more severe conditions like ulcers and bleeding. The risk of gastrointestinal complications is higher in individuals who are over 60 years old, have a history of stomach ulcers, take other medications that can irritate the stomach, or consume alcohol while taking NSAIDs. Other common side effects include dizziness, headache, and rash, though these are generally less severe and may resolve on their own.
Gastrointestinal Side Effects
The gastrointestinal side effects of NSAIDs are among the most concerning because they can lead to serious health issues. The use of NSAIDs can cause stomach ulcers and increase the risk of bleeding in the stomach and intestines. Symptoms of gastrointestinal problems may include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and black, tarry stools, which indicate bleeding. To mitigate these risks, healthcare providers may prescribe medications that protect the stomach lining or recommend over-the-counter antacids.Less Common but Serious Side Effects

While less common, some side effects of NSAIDs can be severe and potentially life-threatening. These include an increased risk of heart attack and stroke, particularly in individuals with pre-existing heart disease or risk factors for cardiovascular disease. NSAIDs can also affect kidney function, leading to kidney failure in rare cases, especially in people who already have kidney disease or are taking other medications that can harm the kidneys. Additionally, there is a risk of allergic reactions, which can range from mild to anaphylaxis, a severe and potentially fatal condition.
Cardiovascular Risks
The cardiovascular risks associated with NSAIDs have been a subject of extensive study. It is known that long-term use of NSAIDs, especially at high doses, can increase blood pressure and affect the kidneys' ability to regulate fluid balance, leading to an increased risk of heart failure. Furthermore, NSAIDs can interfere with the effects of certain medications used to treat heart failure and high blood pressure, complicating the management of these conditions.Managing and Preventing Side Effects

To manage and prevent the side effects of NSAIDs, it's crucial to use these medications judiciously. This includes taking the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration necessary, avoiding the use of multiple NSAIDs at the same time, and being cautious when combining NSAIDs with other medications that can increase the risk of side effects. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding alcohol and tobacco, can help minimize the risks associated with NSAID use.
Alternative Pain Management Strategies
For individuals concerned about the side effects of NSAIDs or who experience significant adverse effects, there are alternative pain management strategies available. These can include physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, and other types of medications that may have fewer side effects. Acetaminophen, for example, can be effective for pain relief without the same level of gastrointestinal risk as NSAIDs, though it does come with its own set of potential side effects, particularly liver damage at high doses.Special Considerations

Certain groups of people need to be particularly cautious when using NSAIDs. These include older adults, individuals with a history of ulcers or gastrointestinal bleeding, those with kidney or liver disease, and people with heart disease or risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Pregnant women should also use NSAIDs with caution, especially during the third trimester, as they can affect fetal development and increase the risk of pregnancy complications.
Pregnancy and NSAID Use
The use of NSAIDs during pregnancy is a topic of concern due to the potential effects on the fetus and the pregnancy itself. While NSAIDs are sometimes necessary for managing pain during pregnancy, their use should be carefully monitored and limited to the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration possible. This is particularly important during the third trimester, when NSAIDs can cause the fetal ductus arteriosus to close prematurely, leading to complications.Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, while NSAIDs are valuable for their anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic properties, their use is not without risks. Being informed about the potential side effects and taking steps to minimize them can help individuals use NSAIDs more safely. As medical research continues to advance, there is hope for the development of new pain management therapies that are both effective and have fewer side effects than traditional NSAIDs. This could include novel medications, alternative therapies, and personalized treatment approaches tailored to an individual's specific needs and health status.
Looking Ahead
Looking ahead, the future of pain management is likely to involve a more holistic and personalized approach, incorporating not just medications but also lifestyle changes, physical therapies, and psychological interventions. By understanding the complexities of pain and the individual factors that influence its perception and experience, healthcare providers can offer more effective and safer treatment options. This shift towards a more comprehensive and patient-centered care model holds promise for reducing the reliance on NSAIDs and improving the overall quality of life for individuals living with chronic pain.What are the most common side effects of NSAIDs?
+The most common side effects of NSAIDs are gastrointestinal, including stomach upset, nausea, and an increased risk of ulcers and bleeding. Other common side effects include dizziness, headache, and rash.
Can NSAIDs increase the risk of heart attack and stroke?
+Yes, long-term use of NSAIDs, especially at high doses, can increase the risk of heart attack and stroke, particularly in individuals with pre-existing heart disease or risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
How can I minimize the risks associated with NSAID use?
+To minimize the risks, take the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration necessary, avoid using multiple NSAIDs at the same time, and be cautious when combining NSAIDs with other medications. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can also help.
We hope this comprehensive overview of NSAID side effects has been informative and helpful. If you have any further questions or concerns about NSAIDs or pain management, we encourage you to discuss them with your healthcare provider. Additionally, sharing this article with others who may benefit from this information can help spread awareness and promote safer use of NSAIDs. Your health and well-being are paramount, and being an active participant in your care is the first step towards achieving the best possible outcomes.
