Intro
Understand A1c, a vital diabetes metric, and its impact on blood sugar control, glucose management, and hemoglobin levels, to better manage your condition and improve overall health outcomes.
The A1c test, also known as the hemoglobin A1c or HbA1c test, is a crucial tool for managing and monitoring diabetes. It provides a snapshot of a person's average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months, helping healthcare professionals diagnose, treat, and prevent complications related to diabetes. Understanding the A1c test and its significance can empower individuals to take control of their health and make informed decisions about their care.
The A1c test measures the percentage of glucose that has bound to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen to different parts of the body. When glucose is present in the blood, it can bind to hemoglobin, forming a molecule called glycated hemoglobin. The higher the blood glucose levels, the more glucose binds to hemoglobin, resulting in a higher A1c reading. This test is essential for people with diabetes, as it helps them understand how well their condition is being managed and whether their treatment plan needs to be adjusted.
For individuals without diabetes, the A1c test can also be a useful tool for assessing their risk of developing the condition. Research has shown that people with an A1c level between 5.7% and 6.4% are at higher risk of developing diabetes and cardiovascular disease. By monitoring A1c levels, healthcare professionals can identify individuals who may benefit from lifestyle changes or preventive measures to reduce their risk of developing diabetes and related complications.
A1c Test Procedure and Results
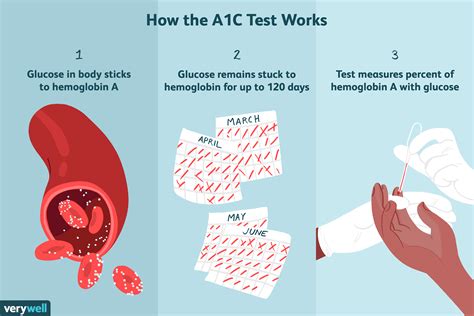
The A1c test is a simple blood test that can be performed in a healthcare setting. A healthcare professional will take a blood sample from a vein in the arm, and the sample will be sent to a laboratory for analysis. The results are usually available within a few days. The A1c test results are reported as a percentage, which indicates the average amount of glucose that has bound to hemoglobin in the blood over the past 2-3 months. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends the following A1c targets for individuals with diabetes: less than 7% for most adults, less than 7.5% for adults with a history of severe hypoglycemia, and less than 8% for adults with a history of cardiovascular disease.
Understanding A1c Results
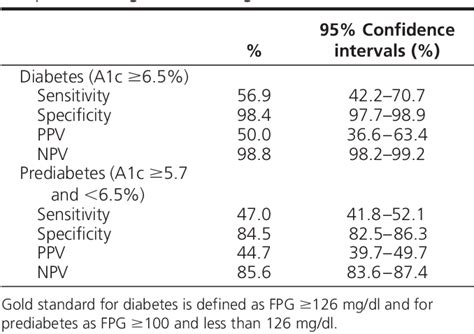
The A1c results can be interpreted in different ways, depending on the individual's health status and medical history. For example, an A1c level of 6% or less is generally considered normal, while an A1c level of 6.5% or higher is indicative of diabetes. An A1c level between 5.7% and 6.4% is considered prediabetes, which means that the individual is at risk of developing diabetes. Healthcare professionals may also use the A1c test to monitor the effectiveness of diabetes treatment and adjust the treatment plan as needed.A1c and Diabetes Management

The A1c test is an essential tool for managing diabetes. By monitoring A1c levels, individuals with diabetes can assess the effectiveness of their treatment plan and make adjustments as needed. The A1c test can also help healthcare professionals identify potential complications related to diabetes, such as kidney disease or nerve damage. For example, an A1c level above 9% can indicate a higher risk of kidney disease, while an A1c level above 10% can indicate a higher risk of nerve damage.
Lifestyle Changes and A1c
Lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, can significantly impact A1c levels. A healthy diet that is low in sugar and refined carbohydrates, and high in fiber and healthy fats, can help lower A1c levels. Regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming, can also help improve insulin sensitivity and lower A1c levels. Additionally, stress management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can help reduce stress and improve overall health.A1c and Cardiovascular Disease
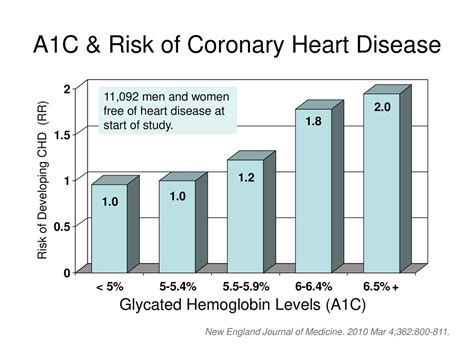
The A1c test can also be used to assess the risk of cardiovascular disease. Research has shown that individuals with an A1c level above 7% are at higher risk of cardiovascular disease, including heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral artery disease. The A1c test can help healthcare professionals identify individuals who may benefit from preventive measures, such as statins or blood pressure medication, to reduce their risk of cardiovascular disease.
A1c and Kidney Disease
The A1c test can also be used to assess the risk of kidney disease. Research has shown that individuals with an A1c level above 9% are at higher risk of kidney disease, including end-stage renal disease. The A1c test can help healthcare professionals identify individuals who may benefit from preventive measures, such as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), to reduce their risk of kidney disease.A1c and Pregnancy
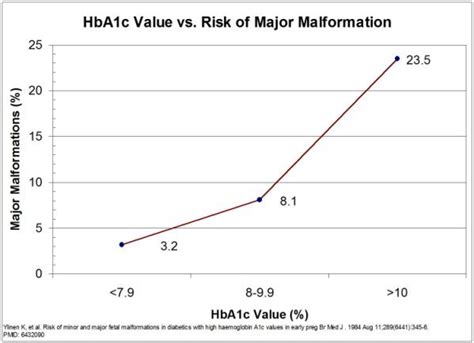
The A1c test is also essential for pregnant women with diabetes. High blood sugar levels during pregnancy can increase the risk of complications, such as birth defects, miscarriage, and stillbirth. The A1c test can help healthcare professionals monitor blood sugar levels and adjust the treatment plan as needed to ensure a healthy pregnancy and birth.
A1c Targets for Pregnant Women
The ADA recommends the following A1c targets for pregnant women with diabetes: less than 6.5% before conception, less than 6% during the first trimester, and less than 6.5% during the second and third trimesters. Pregnant women with diabetes should work closely with their healthcare provider to achieve these targets and minimize the risk of complications.A1c and Children

The A1c test is also essential for children with diabetes. The A1c test can help healthcare professionals monitor blood sugar levels and adjust the treatment plan as needed to ensure optimal growth and development. The ADA recommends the following A1c targets for children with diabetes: less than 7.5% for children under 6 years old, less than 7% for children 6-12 years old, and less than 6.5% for children 13-18 years old.
A1c and Adolescent Diabetes
Adolescents with diabetes may face unique challenges in managing their condition, such as peer pressure, body image issues, and emotional stress. The A1c test can help healthcare professionals identify potential issues and develop strategies to improve blood sugar control and overall health.A1c and Elderly Adults
The A1c test is also essential for elderly adults with diabetes. The A1c test can help healthcare professionals monitor blood sugar levels and adjust the treatment plan as needed to minimize the risk of complications, such as hypoglycemia, falls, and cognitive decline. The ADA recommends the following A1c targets for elderly adults with diabetes: less than 7.5% for adults 65-74 years old, less than 8% for adults 75-84 years old, and less than 8.5% for adults 85 years old or older.
A1c and Geriatric Care
Elderly adults with diabetes may require specialized care to manage their condition. The A1c test can help healthcare professionals develop strategies to improve blood sugar control, manage medications, and prevent complications.What is the A1c test, and why is it important?
+The A1c test is a blood test that measures the average amount of glucose that has bound to hemoglobin in the blood over the past 2-3 months. It is essential for managing and monitoring diabetes, as it provides a snapshot of blood glucose levels and helps healthcare professionals diagnose, treat, and prevent complications related to diabetes.
What are the normal A1c levels, and what do they mean?
+Normal A1c levels are less than 5.7%. An A1c level between 5.7% and 6.4% is considered prediabetes, while an A1c level of 6.5% or higher is indicative of diabetes. The A1c test results can be interpreted in different ways, depending on the individual's health status and medical history.
How can lifestyle changes affect A1c levels?
+Lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, can significantly impact A1c levels. A healthy diet that is low in sugar and refined carbohydrates, and high in fiber and healthy fats, can help lower A1c levels. Regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming, can also help improve insulin sensitivity and lower A1c levels.
In conclusion, the A1c test is a vital tool for managing and monitoring diabetes. By understanding the A1c test and its significance, individuals can take control of their health and make informed decisions about their care. We encourage readers to share their experiences with the A1c test and ask questions in the comments section below. Additionally, we invite readers to explore our website for more information on diabetes management and prevention. By working together, we can improve health outcomes and reduce the risk of complications related to diabetes.
