Intro
Discover 5 ways osmolarity affects cells, including isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic solutions, and learn how osmotic balance impacts cellular health, fluid dynamics, and membrane transport, with key insights into osmoregulation and its significance.
The concept of osmolarity plays a crucial role in various fields, including biology, medicine, and chemistry. Osmolarity refers to the measure of the concentration of osmotically active particles in a solution, expressed as the number of osmoles per liter of solution. Understanding osmolarity is essential for maintaining proper cellular functions, regulating fluid balance, and ensuring the overall health of living organisms. In this article, we will delve into the significance of osmolarity and explore five key aspects of this concept.
Osmolarity is vital for maintaining cellular homeostasis, as it helps regulate the balance of fluids and electrolytes within cells. When the osmolarity of a solution is higher than that of the cell, water flows out of the cell, causing it to shrink. Conversely, when the osmolarity of the solution is lower, water flows into the cell, causing it to swell. This delicate balance is crucial for maintaining proper cellular functions, including metabolism, growth, and reproduction. Moreover, osmolarity plays a critical role in various physiological processes, such as nerve impulse transmission, muscle contraction, and blood pressure regulation.
The importance of osmolarity cannot be overstated, as it has far-reaching implications for human health and disease. For instance, abnormalities in osmolarity can lead to conditions such as dehydration, edema, and electrolyte imbalances. Furthermore, osmolarity is a critical factor in the development of various diseases, including diabetes, kidney disease, and certain types of cancer. Therefore, understanding the concept of osmolarity and its applications is essential for developing effective treatments and therapies for these conditions.
Introduction to Osmolarity

Types of Osmolarity
There are several types of osmolarity, including isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic. Isotonic solutions have the same osmolarity as the cell, resulting in no net movement of water into or out of the cell. Hypotonic solutions have a lower osmolarity than the cell, causing water to flow into the cell and potentially leading to cell lysis. Hypertonic solutions have a higher osmolarity than the cell, causing water to flow out of the cell and potentially leading to cell shrinkage.Measuring Osmolarity
Applications of Osmolarity Measurement
Measuring osmolarity has numerous applications in various fields. In medicine, osmolarity measurement is used to diagnose and monitor conditions such as dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and kidney disease. In biology, osmolarity measurement is used to study the behavior of cells and tissues in different environments. In chemistry, osmolarity measurement is used to understand the properties of solutions and to develop new materials and products.Regulation of Osmolarity
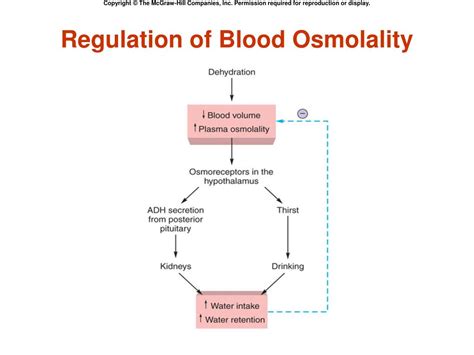
Importance of Osmolarity Regulation
The regulation of osmolarity is essential for maintaining proper cellular functions and overall health. Abnormalities in osmolarity regulation can lead to conditions such as dehydration, edema, and electrolyte imbalances. Furthermore, abnormalities in osmolarity regulation can also lead to more serious conditions such as kidney disease, heart disease, and certain types of cancer.Effects of Osmolarity on Cells
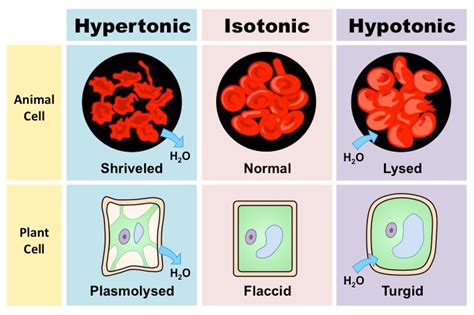
Cellular Responses to Osmolarity Changes
Cells respond to changes in osmolarity by activating various signaling pathways that help to regulate the balance of fluids and electrolytes within the cell. These signaling pathways involve the activation of various proteins, including ion channels, transporters, and enzymes. The activation of these proteins helps to regulate the movement of ions and water into and out of the cell, thereby maintaining proper cellular functions.5 Ways Osmolarity Affects Human Health
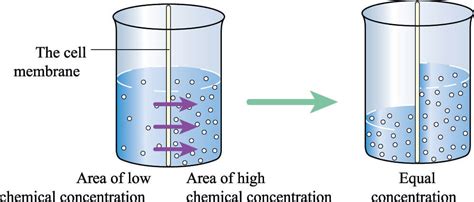
Prevention and Treatment of Osmolarity-Related Disorders
Prevention and treatment of osmolarity-related disorders involve maintaining proper fluid and electrolyte balance, regulating blood pressure, and controlling hormone secretion. This can be achieved through various lifestyle modifications, including drinking plenty of water, eating a balanced diet, and engaging in regular exercise. Furthermore, various medications and therapies can also be used to treat osmolarity-related disorders, including diuretics, electrolyte supplements, and hormone replacement therapy.What is osmolarity and why is it important?
+Osmolarity refers to the measure of the concentration of osmotically active particles in a solution. It is essential for maintaining proper cellular functions, regulating fluid balance, and ensuring overall health.
How is osmolarity measured?
+Osmolarity can be measured using various methods, including freezing point depression, boiling point elevation, and vapor pressure osmometry.
What are the effects of osmolarity on cells?
+Osmolarity affects the balance of fluids and electrolytes within cells, causing changes in cellular shape, size, and function. Changes in osmolarity can also affect cellular behavior, including cell division, differentiation, and response to stimuli.
In conclusion, osmolarity plays a vital role in maintaining proper cellular functions, regulating fluid balance, and ensuring overall health. Understanding the concept of osmolarity and its applications is essential for developing effective treatments and therapies for various diseases and disorders. By recognizing the importance of osmolarity and taking steps to maintain proper fluid and electrolyte balance, individuals can reduce their risk of developing osmolarity-related disorders and promote overall health and well-being. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences related to osmolarity in the comments section below, and to share this article with others who may benefit from this information.
