Intro
Otitis media, also known as middle ear infection, is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide, particularly children. It occurs when the middle ear, which is the air-filled space behind the eardrum, becomes infected with bacteria or viruses. The infection can cause a range of symptoms, including ear pain, fever, and hearing loss. In severe cases, otitis media can lead to complications such as permanent hearing loss, meningitis, and brain abscess. Therefore, it is essential to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available for otitis media.
The importance of addressing otitis media cannot be overstated. If left untreated, the infection can lead to long-term consequences, including delayed speech development, learning difficulties, and social isolation. Furthermore, otitis media can have a significant impact on a person's quality of life, affecting their ability to communicate, work, and engage in daily activities. Fortunately, there are various treatment options available, ranging from antibiotics and pain relievers to surgical interventions. In this article, we will delve into the world of otitis media, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
Otitis media is a complex condition, and its treatment requires a comprehensive approach. While some cases may resolve on their own, others may require medical attention. It is crucial to seek medical help if symptoms persist or worsen over time. A healthcare professional can diagnose otitis media by performing a physical examination, taking a medical history, and conducting diagnostic tests such as tympanometry and acoustic reflectometry. Once diagnosed, treatment can begin, and the road to recovery can start. In the following sections, we will discuss the different aspects of otitis media, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
Otitis Media Causes and Risk Factors
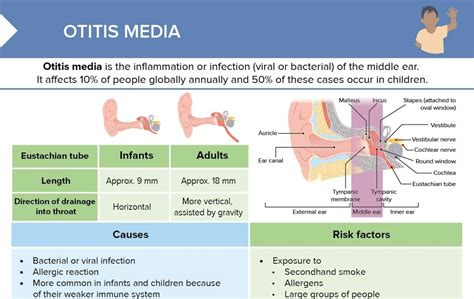
Otitis Media Risk Factors
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing otitis media. These include: * Age: Children under the age of 5 are more susceptible to otitis media due to their underdeveloped Eustachian tube. * Family history: A family history of otitis media can increase the risk of developing the condition. * Allergies: Allergies can increase the risk of developing otitis media by causing Eustachian tube dysfunction. * Cold and sinus infections: Colds and sinus infections can increase the risk of developing otitis media by causing Eustachian tube dysfunction. * Anatomical abnormalities: Anatomical abnormalities, such as a perforated eardrum or a blocked Eustachian tube, can increase the risk of developing otitis media.Otitis Media Symptoms and Diagnosis
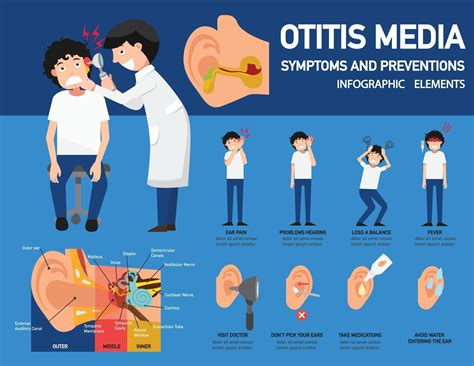
Diagnosing otitis media requires a physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. A healthcare professional will use an otoscope to examine the ear and check for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, and discharge. They will also take a medical history to determine if the patient has any underlying conditions that may be contributing to the infection. Diagnostic tests, such as tympanometry and acoustic reflectometry, may also be used to confirm the diagnosis.
Otitis Media Diagnostic Tests
Several diagnostic tests can be used to confirm the diagnosis of otitis media. These include: * Tympanometry: A test that measures the movement of the eardrum and the reflexes of the middle ear muscles. * Acoustic reflectometry: A test that measures the reflection of sound waves off the eardrum and the middle ear. * Otoscopy: A visual examination of the ear using an otoscope. * Audiometry: A test that measures hearing loss.Otitis Media Treatment Options
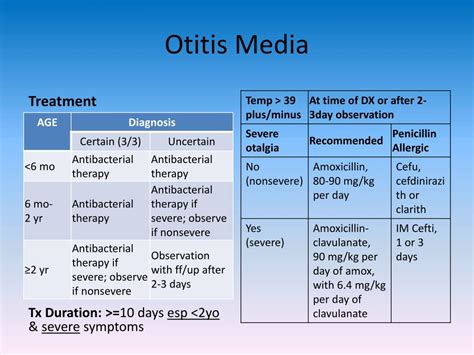
Otitis Media Treatment Options
Several treatment options are available for otitis media, including: * Antibiotics: Amoxicillin, azithromycin, and clarithromycin are commonly used to treat bacterial otitis media. * Pain relievers: Acetaminophen and ibuprofen can be used to manage ear pain and fever. * Surgical interventions: Tympanostomy tubes, adenoidectomy, and mastoidectomy may be necessary in severe cases of otitis media. * Alternative therapies: Alternative therapies, such as ear drops, ear sprays, and herbal remedies, may be used to manage symptoms and promote healing.Otitis Media Prevention Strategies
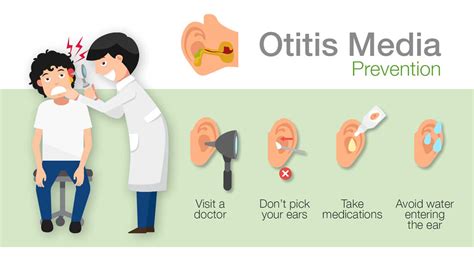
Otitis Media Prevention Tips
Several prevention tips can help reduce the risk of developing otitis media, including: * Practicing good hygiene: Washing hands regularly and avoiding close contact with people who have colds or flu. * Getting regular medical check-ups: Regular medical check-ups can help identify underlying conditions that may be contributing to the risk of otitis media. * Avoiding allergies: Avoiding allergens, such as dust, pollen, and pet dander, can help reduce the risk of developing otitis media. * Getting vaccinated: Getting vaccinated against flu and pneumococcal disease can help reduce the risk of developing otitis media.What is otitis media?
+Otitis media is a common condition that affects the middle ear, causing symptoms such as ear pain, fever, and hearing loss.
What are the causes of otitis media?
+Otitis media is caused by a combination of factors, including bacterial and viral infections, allergies, and anatomical abnormalities.
How is otitis media diagnosed?
+Otitis media is diagnosed through a physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests such as tympanometry and acoustic reflectometry.
What are the treatment options for otitis media?
+The treatment of otitis media depends on the severity of the infection and the patient's overall health, and may include antibiotics, pain relievers, or surgical interventions.
How can otitis media be prevented?
+Otitis media can be prevented by practicing good hygiene, making healthy lifestyle choices, and getting regular medical check-ups.
In conclusion, otitis media is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies is essential for managing the condition and preventing long-term consequences. By practicing good hygiene, making healthy lifestyle choices, and getting regular medical check-ups, individuals can reduce their risk of developing otitis media. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of otitis media, it is essential to seek medical attention to prevent complications and promote healing. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with otitis media in the comments section below, and to share this article with others who may benefit from this information.
