Intro
The Pap test, also known as the Pap smear, is a vital screening tool for cervical cancer and other cervical abnormalities. It's a simple, yet highly effective procedure that has been instrumental in reducing the incidence and mortality rates of cervical cancer worldwide. The test is named after its developer, Dr. Georgios Papanikolaou, who introduced it in the 1940s. Since then, the Pap test has become a standard component of women's health care, and its importance cannot be overstated. In this article, we'll delve into the world of Pap tests, exploring their meaning, benefits, and significance in maintaining good health.
The Pap test is a preventive measure that aims to detect abnormal cell changes in the cervix, which is the lower part of the uterus. These abnormal cells can potentially develop into cancer if left untreated. The test involves collecting a sample of cells from the cervix using a specialized tool, which is then sent to a laboratory for examination. The results of the Pap test can indicate whether the cells are normal, abnormal, or potentially cancerous. This information is crucial in identifying women who may be at risk of developing cervical cancer, allowing for early intervention and treatment.
The significance of the Pap test lies in its ability to detect cervical abnormalities at an early stage, often before symptoms appear. Cervical cancer is a slow-growing disease, and if caught early, it can be treated effectively. The Pap test has been shown to reduce the incidence of cervical cancer by up to 80%, making it an essential tool in the fight against this disease. Moreover, the test can also detect other cervical abnormalities, such as human papillomavirus (HPV) infections, which are a common cause of cervical cancer. By detecting these abnormalities early, women can take steps to prevent the development of cervical cancer, and healthcare providers can monitor their condition closely.
Pap Test Procedure

Preparation for the Pap Test
To ensure accurate results, it's essential to prepare properly for the Pap test. Women should avoid scheduling the test during their menstrual period, as blood can interfere with the results. Additionally, they should avoid using tampons, vaginal creams, or douching for at least 24 hours before the test, as these can also affect the results. It's also important to inform the healthcare provider about any medications or supplements being taken, as these can impact the test results.Pap Test Results
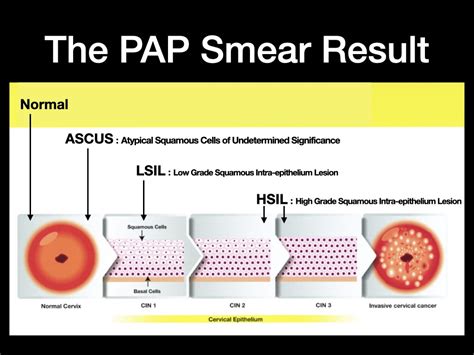
Understanding Abnormal Pap Test Results
Abnormal Pap test results can be concerning, but it's essential to understand that they don't necessarily mean that cervical cancer is present. In many cases, abnormal results can be caused by other factors, such as HPV infections or hormonal changes. If the results are abnormal, the healthcare provider may recommend further testing, such as a colposcopy or biopsy, to determine the cause of the abnormality. In some cases, treatment may be necessary to remove the abnormal cells and prevent the development of cervical cancer.Pap Test Frequency
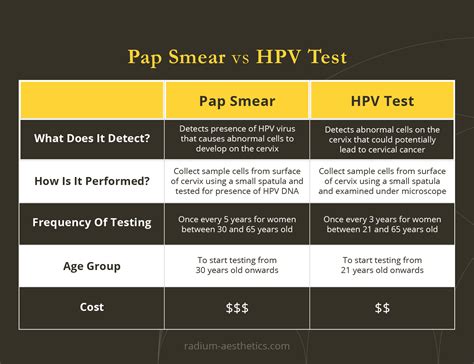
Risk Factors for Cervical Cancer
Certain risk factors can increase a woman's chances of developing cervical cancer, including HPV infections, smoking, and a weakened immune system. Women who have had multiple sexual partners or have a history of cervical cancer are also at higher risk. Additionally, women who have been diagnosed with HIV or have a weakened immune system due to other medical conditions may be more susceptible to cervical cancer. By understanding these risk factors, women can take steps to reduce their risk and stay on top of their cervical health.Pap Test Benefits
Pap Test Limitations
While the Pap test is a highly effective screening tool, it's not perfect. Some of the limitations include: * False-negative results, which can occur if the sample collected is not sufficient or if the abnormal cells are not detected * False-positive results, which can lead to unnecessary further testing and anxiety * Limited ability to detect other types of cervical cancer, such as adenocarcinomaPap Test and HPV Vaccine
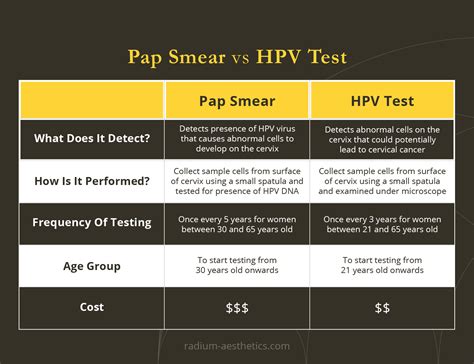
HPV Vaccine Benefits
The HPV vaccine has several benefits, including: * Protection against certain types of HPV that can cause cervical cancer * Reduction in the risk of cervical cancer and other HPV-related diseases * Opportunity for women to take control of their cervical healthPap Test and Pregnancy
Pap Test During Pregnancy
The Pap test during pregnancy is similar to the test performed on non-pregnant women. However, the healthcare provider may use a different type of speculum or take additional precautions to ensure the safety of the mother and the baby. Women who are pregnant should discuss their Pap test results with their healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.Pap Test and Menopause

Pap Test After Menopause
The Pap test after menopause is similar to the test performed on premenopausal women. However, the healthcare provider may use a different type of speculum or take additional precautions to ensure the safety of the patient. Women who are postmenopausal should discuss their Pap test results with their healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.What is the Pap test, and why is it important?
+The Pap test is a screening tool for cervical cancer and other cervical abnormalities. It's essential for detecting abnormal cell changes in the cervix, which can potentially develop into cancer if left untreated.
How often should I have a Pap test?
+The frequency of Pap tests depends on several factors, including age, medical history, and risk factors. Women between the ages of 21 and 29 should have a Pap test every three years, while those between 30 and 65 should have a Pap test and an HPV test every five years.
What do abnormal Pap test results mean?
+Abnormal Pap test results can indicate the presence of abnormal cells, which can be further categorized into different types. In some cases, abnormal results can be caused by other factors, such as HPV infections or hormonal changes. If the results are abnormal, the healthcare provider may recommend further testing or treatment.
Can I still have a Pap test if I'm pregnant or postmenopausal?
+Yes, women who are pregnant or postmenopausal can still have a Pap test. The test is an essential tool for detecting cervical abnormalities, and it's crucial for ensuring the health of the mother and the baby during pregnancy. Women who are postmenopausal should continue to have regular Pap tests, usually every three to five years, depending on their medical history and risk factors.
How can I prepare for a Pap test?
+To prepare for a Pap test, women should avoid scheduling the test during their menstrual period, as blood can interfere with the results. Additionally, they should avoid using tampons, vaginal creams, or douching for at least 24 hours before the test, as these can also affect the results.
In conclusion, the Pap test is a vital screening tool for cervical cancer and other cervical abnormalities. By understanding the importance of the Pap test, women can take control of their cervical health and reduce their risk of developing cervical cancer. If you have any questions or concerns about the Pap test, don't hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider. Share this article with your friends and family to raise awareness about the importance of cervical health, and let's work together to reduce the incidence of cervical cancer.
