Intro
Discover 5 crucial facts about the Papanicolaou test, a cervical screening procedure, including its importance in cervical cancer detection, Pap smear results, and abnormal cell identification, ensuring womens health and wellness through early diagnosis and prevention.
The Papanicolaou test, commonly referred to as the Pap test or Pap smear, is a crucial screening procedure for cervical cancer and other cervical abnormalities. It's a simple, yet highly effective method that has significantly reduced the incidence and mortality rates of cervical cancer over the years. Understanding the importance and the specifics of the Pap test can empower individuals, especially women, to take charge of their reproductive health.
The Pap test is not just a tool for detecting cancer; it's also a way to identify pre-cancerous changes in the cervix, allowing for early intervention and treatment. This can prevent the development of cancer altogether. The test involves collecting cells from the cervix, which are then examined under a microscope for any abnormalities. Given its significance, it's essential to delve into the specifics of the Pap test, including its history, how it's performed, its benefits, and the follow-up actions based on the test results.
The history of the Pap test is rooted in the pioneering work of Dr. Georgios Papanikolaou, who first described the procedure in the early 20th century. Since then, the Pap test has undergone several improvements, making it more accurate and less invasive. Today, it remains a cornerstone of women's health care, recommended for women between the ages of 21 and 65. The frequency of the test can vary based on factors such as age, previous test results, and other risk factors for cervical cancer.
Introduction to the Papanicolaou Test

Benefits of the Papanicolaou Test
How the Papanicolaou Test Works
The Pap test works by collecting cells from the cervix, which are then examined for any abnormalities. The procedure is relatively simple and can be performed in a healthcare provider's office. It involves inserting a speculum into the vagina to hold it open, allowing the healthcare provider to see the cervix. A spatula and a brush are then used to collect cell samples from the cervix, which are sent to a laboratory for analysis. The results of the Pap test can indicate whether any abnormal cell changes are present, and if so, what type of changes they are.Preparation for the Papanicolaou Test

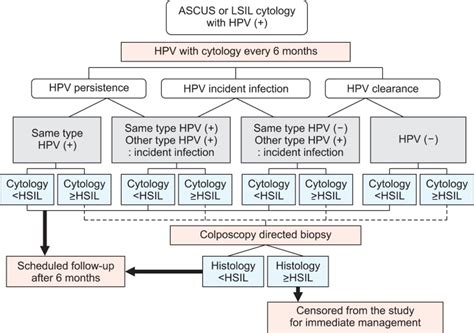
Understanding Papanicolaou Test Results
Understanding the results of a Pap test is crucial for determining the next steps in care. A normal result indicates that no abnormal cell changes were found. However, an abnormal result can mean several things, including the presence of pre-cancerous or cancerous cells. In such cases, further testing, such as a colposcopy or biopsy, may be necessary to determine the extent of the abnormality. It's essential to follow up with a healthcare provider to discuss the results and any recommended follow-up actions.Follow-Up Actions After the Papanicolaou Test
Importance of Regular Papanicolaou Tests
Regular Pap tests are crucial for maintaining cervical health and preventing cervical cancer. The frequency of Pap tests can depend on age and previous test results. For most women, a Pap test every three to five years is recommended, but this can vary based on individual risk factors and healthcare provider recommendations. Adhering to the recommended screening schedule is vital for early detection and prevention of cervical abnormalities.Common Questions About the Papanicolaou Test

Papanicolaou Test and HPV Vaccination
The relationship between the Pap test and HPV vaccination is also a topic of interest. While the HPV vaccine protects against certain types of HPV that can cause cervical cancer, it does not replace the need for regular Pap tests. The vaccine is most effective when administered before exposure to HPV, typically recommended for preteens and teens. However, even vaccinated individuals should follow the recommended Pap test schedule, as the vaccine does not protect against all types of HPV.Future of the Papanicolaou Test
Global Impact of the Papanicolaou Test
The global impact of the Pap test has been significant, particularly in countries where cervical cancer screening programs are well-established. However, disparities in access to screening and follow-up care exist, both within and between countries. Efforts to increase access to the Pap test and other cervical cancer screening methods are crucial for reducing the global burden of cervical cancer.What is the purpose of the Papanicolaou test?
+The Papanicolaou test, or Pap test, is used to screen for cervical cancer and pre-cancerous changes in the cervix. It involves collecting cells from the cervix and examining them under a microscope for any abnormalities.
How often should I get a Papanicolaou test?
+The frequency of Pap tests depends on age and previous test results. Generally, women between 21 and 65 years old should get a Pap test every three to five years, but this may vary based on individual risk factors and healthcare provider recommendations.
Does the HPV vaccine replace the need for Papanicolaou tests?
+No, the HPV vaccine does not replace the need for regular Pap tests. While the vaccine protects against certain types of HPV that can cause cervical cancer, it does not protect against all types, and regular screening is still necessary for early detection and prevention of cervical abnormalities.
What do abnormal Papanicolaou test results mean?
+Abnormal Pap test results can indicate the presence of pre-cancerous or cancerous cells in the cervix. In such cases, further testing, such as a colposcopy or biopsy, may be necessary to determine the extent of the abnormality and guide treatment decisions.
Can the Papanicolaou test detect other health issues?
+The Pap test is specifically designed to detect cervical abnormalities, including cervical cancer and pre-cancerous changes. While it may incidentally detect other conditions, such as infections, its primary purpose is cervical cancer screening.
In summary, the Papanicolaou test is a vital tool in the early detection and prevention of cervical cancer. Understanding its importance, how it works, and what the results mean can empower individuals to take control of their cervical health. By addressing common questions and misconceptions, and by continuing to advance screening technologies, we can work towards reducing the global burden of cervical cancer. We invite readers to share their experiences, ask questions, and engage in discussions about the Papanicolaou test and cervical health, promoting awareness and education on this critical topic.
