Intro
Phencyclidine medical condition: Learn about PCP effects, symptoms, and treatment. Discover related disorders like schizophrenia and psychosis, and understand the importance of medical intervention for PCP addiction and abuse.
The medical condition associated with phencyclidine, commonly referred to as PCP, is a complex and multifaceted issue that affects individuals who use this substance. PCP is a mind-altering drug that may lead to hallucinations, changes in perception, and a range of other psychological and physiological effects. It's essential to understand the medical implications of PCP use to provide effective treatment and support for those affected.
PCP has been linked to various medical conditions, including addiction, psychosis, and cognitive impairment. The drug's effects on the brain and body can be severe and long-lasting, making it crucial for medical professionals to be aware of the potential risks and complications associated with its use. Moreover, the increasing availability and accessibility of PCP have raised concerns about its impact on public health, highlighting the need for comprehensive education and prevention strategies.
The use of PCP can lead to a range of medical emergencies, including seizures, coma, and respiratory depression. In severe cases, PCP use can result in life-threatening conditions, such as hyperthermia, cardiac arrest, and stroke. Furthermore, long-term PCP use has been linked to cognitive decline, memory loss, and increased risk of psychiatric disorders, including schizophrenia and depression. Understanding the medical condition associated with PCP use is vital for developing effective treatment plans and providing support for individuals struggling with addiction and related health issues.
Introduction to Phencyclidine

History of Phencyclidine
The history of phencyclidine dates back to the 1950s, when it was first synthesized as an anesthetic. Initially, PCP was used in medical settings due to its ability to induce dissociation, a state characterized by feelings of detachment from one's body and environment. However, its use was soon discontinued due to reports of hallucinations, delirium, and other adverse effects. In the 1960s and 1970s, PCP gained popularity as a recreational substance, particularly among young people. Its use was often associated with the counterculture movement, and it was frequently used in combination with other substances, such as LSD and marijuana.Phencyclidine Medical Condition

- Hallucinations and altered perception
- Changes in mood and emotional state
- Increased heart rate and blood pressure
- Numbness or tingling in the extremities
- Confusion and disorientation
- Aggressive behavior and violent outbursts
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing PCP use can be challenging due to the drug's complex effects on the brain and body. Medical professionals may use a combination of physical examination, laboratory tests, and psychological evaluation to diagnose PCP use. Treatment for PCP addiction typically involves a multidisciplinary approach, including medication, counseling, and behavioral therapy. Medications such as benzodiazepines and antipsychotics may be used to manage symptoms of withdrawal and psychosis, while counseling and behavioral therapy can help individuals address underlying issues and develop coping strategies.Phencyclidine Addiction

- Intense cravings and urges to use PCP
- Withdrawal symptoms such as anxiety, insomnia, and tremors
- Tolerance and increased use over time
- Loss of control and inability to quit using PCP
- Continued use despite negative consequences
Causes and Risk Factors
The causes and risk factors associated with PCP addiction are complex and multifaceted. Genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and mental health issues can all contribute to the development of PCP addiction. Individuals who use PCP may be more likely to experience addiction due to the drug's potent effects on the brain and body. Risk factors for PCP addiction include:- Family history of substance abuse
- Mental health issues such as depression and anxiety
- Trauma and stress
- Peer pressure and social influence
- Easy access to PCP and other substances
Phencyclidine Overdose
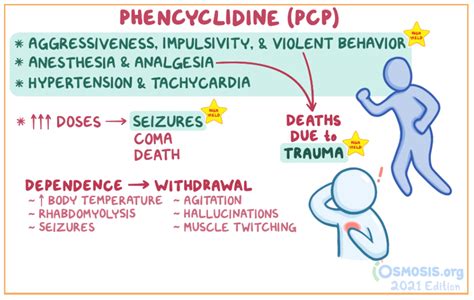
- Respiratory depression and slowed breathing
- Cardiac arrest and irregular heartbeat
- Seizures and convulsions
- Hyperthermia and elevated body temperature
- Coma and loss of consciousness
Emergency Response
In the event of a PCP overdose, it's essential to respond quickly and effectively to prevent long-term damage and death. Emergency responders should follow these steps:- Call 911 or emergency services immediately
- Provide basic life support, including CPR and oxygen therapy
- Administer naloxone or other opioid antagonists to reverse overdose effects
- Transport the individual to a medical facility for further treatment
Phencyclidine Withdrawal

- Intense cravings and urges to use PCP
- Anxiety, insomnia, and restlessness
- Depression, irritability, and mood swings
- Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
- Headaches, tremors, and muscle pain
Management and Treatment
Managing PCP withdrawal requires a comprehensive approach, including medication, counseling, and behavioral therapy. Medical professionals may use medications such as benzodiazepines and antipsychotics to manage symptoms of withdrawal and psychosis. Counseling and behavioral therapy can help individuals address underlying issues and develop coping strategies.Phencyclidine Abuse Prevention

- Educating themselves and others about the risks and dangers of PCP
- Promoting healthy coping mechanisms and stress management techniques
- Encouraging open and honest communication about substance use
- Supporting community-based initiatives and prevention programs
- Seeking medical attention and support for individuals struggling with PCP addiction
Community-Based Initiatives
Community-based initiatives play a critical role in preventing PCP abuse and supporting individuals struggling with addiction. These initiatives may include:- Public awareness campaigns and education programs
- Community-based treatment and support services
- Peer support groups and counseling services
- Family-based interventions and therapy
- Law enforcement and public health collaboration
What is phencyclidine, and how does it affect the brain and body?
+Phencyclidine, also known as PCP, is a synthetic substance that affects the brain and body by altering perception, mood, and cognitive function. It can cause users to experience hallucinations, changes in mood, and altered states of consciousness.
What are the symptoms of phencyclidine overdose, and how can it be treated?
+Phencyclidine overdose can cause users to experience respiratory depression, cardiac arrest, and seizures. Treatment typically involves emergency response, including basic life support, naloxone administration, and transportation to a medical facility.
How can individuals prevent phencyclidine abuse, and what community-based initiatives are available?
+Individuals can prevent phencyclidine abuse by educating themselves and others about the risks and dangers of PCP, promoting healthy coping mechanisms, and seeking medical attention and support. Community-based initiatives, such as public awareness campaigns, community-based treatment, and peer support groups, can also play a critical role in preventing PCP abuse.
In conclusion, the medical condition associated with phencyclidine use is complex and multifaceted, requiring a comprehensive approach to treatment and prevention. By understanding the risks and dangers of PCP, individuals, families, and communities can work together to prevent abuse and support those struggling with addiction. If you or someone you know is struggling with PCP addiction, it's essential to seek medical attention and support. Comment below with your thoughts and experiences, and share this article with others to raise awareness about the importance of phencyclidine abuse prevention.
