Intro
Discover 5 crucial fecal blood test facts, including occult blood testing, gastrointestinal health, and colon cancer screening, to understand the importance of this diagnostic tool in detecting hidden blood in stool and preventing digestive diseases.
The presence of blood in stool can be a symptom of various health issues, ranging from minor to severe conditions. A fecal blood test, also known as a fecal occult blood test (FOBT), is a diagnostic tool used to detect hidden blood in the stool. This test is crucial for identifying potential health problems early on, allowing for timely interventions and treatments. The importance of fecal blood tests cannot be overstated, as they play a significant role in preventive care, particularly in the screening for colorectal cancer, which is one of the most common types of cancer worldwide.
The process of conducting a fecal blood test is relatively straightforward and non-invasive, making it a widely accepted screening method. Individuals are provided with a test kit that includes materials to collect stool samples, which are then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The test detects the presence of hemoglobin or other blood components in the stool, indicating gastrointestinal bleeding. This early detection is vital for initiating further diagnostic procedures to determine the source and cause of the bleeding.
Understanding the significance of fecal blood tests is essential for maintaining good health and preventing serious diseases. By being aware of the benefits, limitations, and procedures involved in these tests, individuals can take proactive steps towards their health. Moreover, the advancement in medical technology has led to the development of more sensitive and specific tests, enhancing the accuracy of results and patient outcomes. As the medical community continues to emphasize the importance of preventive care, the role of fecal blood tests in early disease detection will become increasingly prominent.
Introduction to Fecal Blood Tests
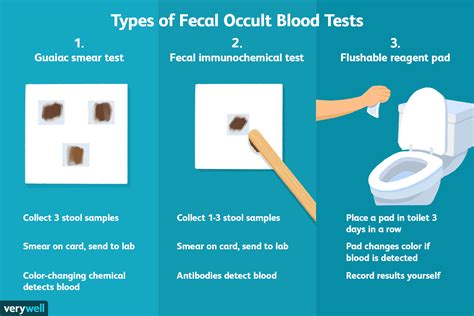
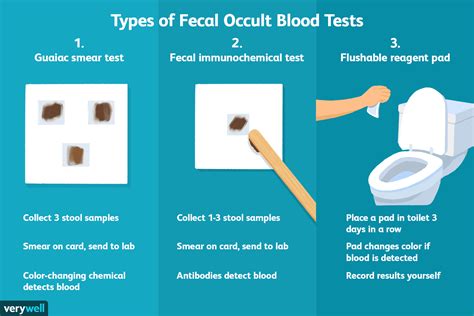
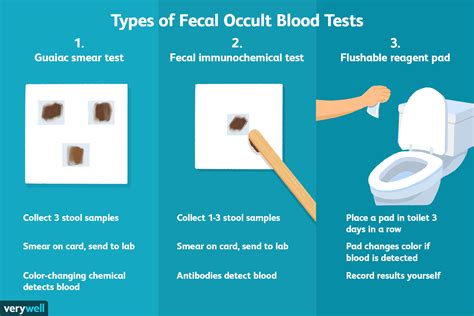
How Fecal Blood Tests Work
The mechanism behind fecal blood tests involves chemical reactions that detect the presence of blood in the stool sample. There are different types of tests, including guaiac-based tests and immunochemical tests, each with its own methodology for detecting blood. Guaiac tests, for example, use a chemical that reacts with the heme part of the hemoglobin molecule in red blood cells, turning the test paper blue if blood is present. Immunochemical tests, on the other hand, use antibodies that specifically bind to human hemoglobin, providing a more specific result.Benefits of Fecal Blood Tests
Preparation and Procedure
Preparing for a fecal blood test involves certain dietary restrictions to avoid false-positive results. Patients are usually advised to avoid foods that can interfere with the test, such as red meat, certain vegetables, and vitamin C supplements, for a specified period before the test. The collection of stool samples is done according to the instructions provided with the test kit, and the samples are then sent to a laboratory for analysis. It is crucial to follow the instructions carefully to ensure accurate results.Interpreting Fecal Blood Test Results
Limitations and False Results
While fecal blood tests are valuable diagnostic tools, they are not without limitations. False-positive results can occur due to dietary factors or certain medications, and false-negative results might miss the presence of blood, especially if the bleeding is intermittent. Understanding these limitations is crucial for healthcare providers to make informed decisions about patient care and for patients to be aware of the potential for false results.Advancements in Fecal Blood Testing
Importance of Regular Screening
Regular screening with fecal blood tests is crucial for the early detection of colorectal cancer and other gastrointestinal issues. Guidelines typically recommend annual screening for individuals of average risk starting at the age of 50, though these recommendations may vary based on individual risk factors and new evidence. The importance of adherence to screening guidelines cannot be overstated, as it significantly impacts the effectiveness of early detection and treatment strategies.Fecal Blood Tests in Preventive Care
Public Health Implications
The public health implications of fecal blood tests are profound, given their potential to reduce morbidity and mortality from colorectal cancer and other gastrointestinal diseases. Widespread adoption of these tests as part of routine screening could lead to a significant decrease in the incidence of advanced colorectal cancer, ultimately saving lives. Moreover, the awareness and education campaigns surrounding these tests contribute to a broader understanding of gastrointestinal health and the importance of preventive care.Future Directions in Fecal Blood Testing
Conclusion and Recommendations
In conclusion, fecal blood tests are a vital component of preventive care, offering a simple yet effective method for the early detection of gastrointestinal issues, including colorectal cancer. As research continues to refine these tests and develop new screening technologies, it is essential for healthcare providers and patients alike to stay informed about the latest recommendations and advancements. By prioritizing regular screening and leveraging the benefits of fecal blood tests, individuals can take a proactive approach to their health, contributing to better outcomes and a reduction in the burden of colorectal cancer.What is the purpose of a fecal blood test?
+A fecal blood test is used to detect hidden blood in the stool, which can be a symptom of various gastrointestinal issues, including colorectal cancer.
How often should I undergo a fecal blood test?
+Screening guidelines typically recommend annual fecal blood tests for individuals of average risk starting at the age of 50, though recommendations may vary based on individual risk factors.
What can cause a false-positive result in a fecal blood test?
+False-positive results can occur due to certain foods, medications, or other factors that may interfere with the test, such as red meat, some vegetables, and vitamin C supplements.
We hope this comprehensive overview of fecal blood tests has provided you with valuable insights into their importance, benefits, and role in preventive care. By staying informed and proactive about your health, you can contribute to the early detection and prevention of gastrointestinal diseases. If you have any questions or concerns about fecal blood tests or would like to share your experiences, please do not hesitate to comment below. Your engagement and feedback are crucial in fostering a community dedicated to health awareness and education.
