Intro
Learn about postpartum bleeding after childbirth, including causes, symptoms, and management of excessive uterine bleeding, lochia, and hemorrhage, to ensure a safe recovery.
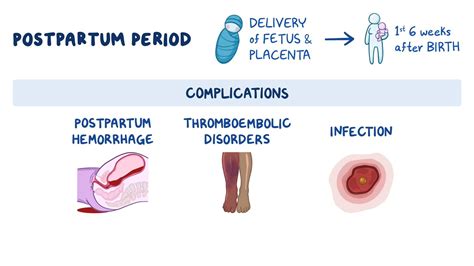
Postpartum bleeding, also known as postpartum hemorrhage (PPH), is a common condition that affects many women after childbirth. It is characterized by excessive bleeding from the uterus, which can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. The importance of understanding postpartum bleeding cannot be overstated, as it is a leading cause of maternal mortality worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 27% of all maternal deaths are attributed to postpartum hemorrhage.
The physical and emotional changes that occur after childbirth can be overwhelming, and postpartum bleeding can add an extra layer of complexity to the recovery process. Women who experience postpartum bleeding may feel anxious, scared, and unsure of what to expect. However, with proper medical attention and support, most women can recover from postpartum bleeding and go on to have a healthy and happy postpartum experience. In this article, we will delve into the world of postpartum bleeding, exploring its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
Postpartum bleeding is a natural process that occurs after childbirth, as the uterus sheds its lining and returns to its pre-pregnancy size. However, in some cases, the bleeding can become excessive, leading to postpartum hemorrhage. The causes of postpartum bleeding are multifaceted and can include factors such as uterine atony, retained placental tissue, and lacerations. Uterine atony, which is the failure of the uterus to contract after childbirth, is the most common cause of postpartum hemorrhage. When the uterus fails to contract, it cannot stop the bleeding, leading to excessive blood loss.
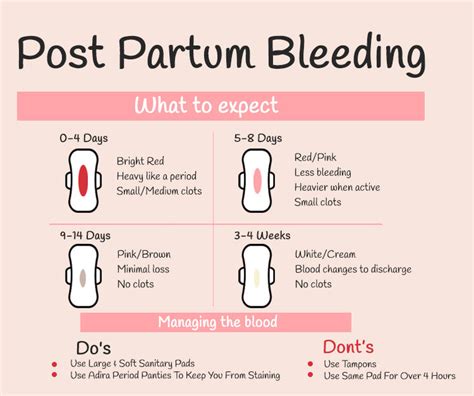
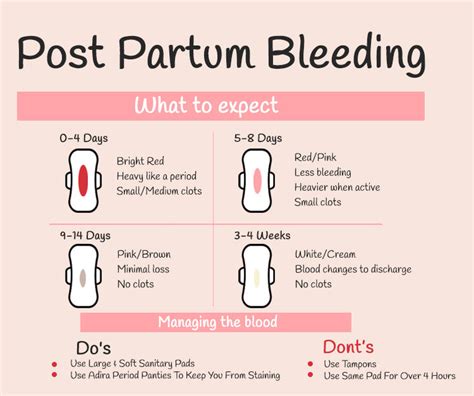
Causes of Postpartum Bleeding
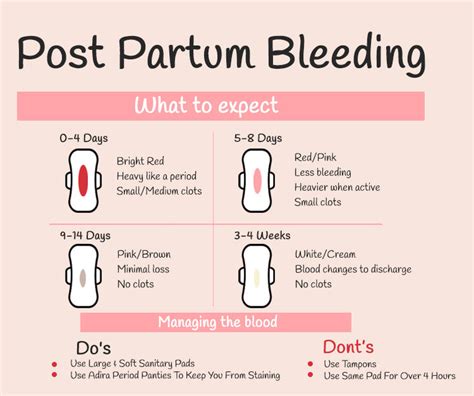
Uterine Atony
Uterine atony is the failure of the uterus to contract after childbirth, leading to excessive bleeding. The uterus is a muscular organ that contracts and relaxes to stop bleeding after childbirth. However, in some cases, the uterus may fail to contract, leading to uterine atony. Uterine atony can be caused by several factors, including overdistension of the uterus, prolonged labor, and uterine fatigue. Overdistension of the uterus can occur when the uterus is stretched too far, leading to a decrease in uterine contractions. Prolonged labor can also lead to uterine fatigue, which can increase the risk of uterine atony.Symptoms of Postpartum Bleeding
Treatment Options for Postpartum Bleeding
The treatment options for postpartum bleeding depend on the severity of the condition. Mild postpartum bleeding may be treated with uterine massage, which involves massaging the uterus to stimulate contractions. Severe postpartum bleeding may require more aggressive treatment, including intravenous fluids, blood transfusions, and surgery. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to stimulate uterine contractions and reduce bleeding. Women who experience postpartum bleeding should seek medical attention immediately, as prompt treatment can help prevent complications and promote a healthy recovery.Prevention Strategies for Postpartum Bleeding
Risk Factors for Postpartum Bleeding
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of postpartum bleeding, including previous postpartum hemorrhage, multiple pregnancy, and placental abruption. Women who have experienced previous postpartum hemorrhage are at increased risk of postpartum bleeding, as are women who have had multiple pregnancies. Placental abruption, which occurs when the placenta separates from the uterus, can also increase the risk of postpartum bleeding. Other risk factors for postpartum bleeding include uterine fibroids, placenta previa, and coagulopathy.Complications of Postpartum Bleeding
Recovery from Postpartum Bleeding
Recovery from postpartum bleeding can be a long and challenging process. Women who experience postpartum bleeding may need to stay in the hospital for several days or even weeks, depending on the severity of the condition. During this time, women may receive intravenous fluids, blood transfusions, and medication to stimulate uterine contractions and reduce bleeding. Women may also need to rest and avoid strenuous activities, such as heavy lifting and exercise, to promote healing and prevent complications.Support for Women with Postpartum Bleeding
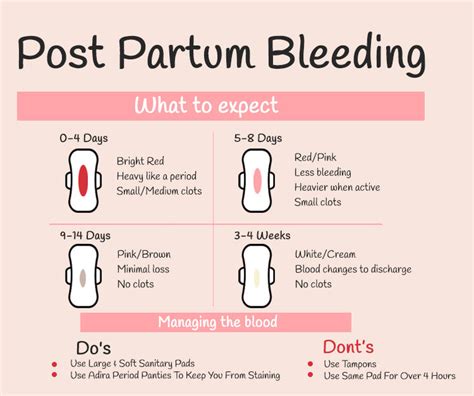
Coping with Postpartum Bleeding
Coping with postpartum bleeding can be a challenging and emotional experience. Women who experience postpartum bleeding may feel anxious, scared, and unsure of what to expect. However, with the right support and care, women can cope with postpartum bleeding and promote a healthy recovery. Women may find it helpful to talk to their healthcare provider, partner, or a therapist about their feelings and concerns. Women may also find it helpful to connect with other women who have experienced postpartum bleeding, either in person or online.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

What is postpartum bleeding?
+Postpartum bleeding, also known as postpartum hemorrhage (PPH), is a common condition that affects many women after childbirth, characterized by excessive bleeding from the uterus.
What are the symptoms of postpartum bleeding?
+The symptoms of postpartum bleeding can vary depending on the severity of the condition, but may include light bleeding or spotting, heavy bleeding, dizziness, and fainting.
How is postpartum bleeding treated?
+The treatment options for postpartum bleeding depend on the severity of the condition, but may include uterine massage, intravenous fluids, blood transfusions, and surgery.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of postpartum bleeding, its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider. Additionally, we invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with postpartum bleeding in the comments section below. Your feedback and insights can help others who may be going through similar challenges. Thank you for reading, and we look forward to hearing from you!
