Intro
Learn about the PPD TB skin test, including its purpose, procedure, and interpretation. Understand tuberculin purified protein derivative, Mantoux testing, and BCG vaccine implications for accurate results and diagnosis of tuberculosis infection.
The PPD TB skin test, also known as the Mantoux test, is a widely used diagnostic tool to detect tuberculosis (TB) infection. TB is a serious and potentially life-threatening disease that affects millions of people worldwide. The PPD TB skin test is an essential tool in the fight against TB, and understanding how it works and what the results mean is crucial for healthcare professionals and individuals alike. In this article, we will delve into the world of PPD TB skin testing, exploring its importance, benefits, and limitations, as well as providing a comprehensive guide on how to administer and interpret the test.
The PPD TB skin test is a simple, yet effective way to detect TB infection. The test involves injecting a small amount of purified protein derivative (PPD) tuberculin into the skin, usually on the forearm. The PPD tuberculin is derived from the TB bacterium and is designed to stimulate an immune response in individuals who have been infected with TB. The test is typically used to diagnose latent TB infection, which is a condition where the TB bacteria are present in the body, but not actively causing symptoms. Latent TB infection can progress to active TB disease if left untreated, making early detection and treatment crucial.
The importance of the PPD TB skin test cannot be overstated. TB is a major public health concern, and the test is a vital tool in identifying individuals who are at risk of developing active TB disease. The test is particularly useful in high-risk populations, such as healthcare workers, individuals with compromised immune systems, and those who have been in close contact with someone with active TB. By detecting TB infection early, healthcare professionals can provide timely treatment and prevent the spread of the disease.
How the PPD TB Skin Test Works
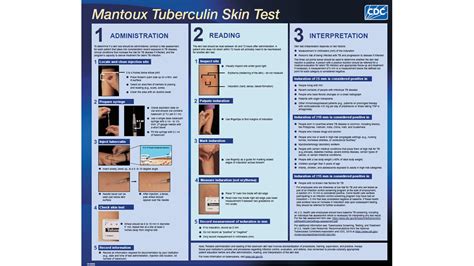
Administering the PPD TB Skin Test
Administering the PPD TB skin test is a relatively simple process that requires some training and expertise. The test should be administered by a healthcare professional who has experience with the procedure. The test involves the following steps: * Prepare the skin: The skin should be cleaned and prepared for the injection. * Inject the PPD tuberculin: A small amount of PPD tuberculin is injected into the skin, usually on the forearm. * Measure the reaction: The reaction is measured in millimeters, usually 48-72 hours after the injection. * Interpret the results: The results are interpreted based on the size of the induration.Interpreting PPD TB Skin Test Results
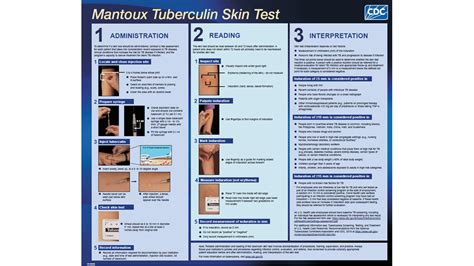
PPD TB Skin Test Results Classification
The PPD TB skin test results can be classified into the following categories: * Positive: 10mm or more of induration * Negative: Less than 5mm of induration * Uncertain: 5-9mm of induration * False negative: A negative result in an individual who has been infected with TB * False positive: A positive result in an individual who has not been infected with TBBenefits and Limitations of the PPD TB Skin Test
Advantages of the PPD TB Skin Test
The PPD TB skin test has several advantages, including: * Simplicity: The test is relatively simple to administer and interpret. * Low cost: The test is low-cost and widely available. * High sensitivity: The test is highly sensitive and can detect TB infection in most individuals. * Wide availability: The test can be administered in a variety of settings, including healthcare clinics and community health centers.Disadvantages of the PPD TB Skin Test
The PPD TB skin test also has some disadvantages, including: * Low specificity: The test can produce false positive results in individuals who have not been infected with TB. * False negative results: The test can produce false negative results in individuals who have been infected with TB. * Requires follow-up visit: The test requires a follow-up visit to measure the reaction, which can be inconvenient for some individuals.PPD TB Skin Test vs. Other Diagnostic Tests
Comparison of Diagnostic Tests for TB Infection
The following table compares the PPD TB skin test with other diagnostic tests for TB infection: | Test | Sensitivity | Specificity | Cost | Availability | | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | | PPD TB skin test | High | Low | Low | Wide | | QuantiFERON Gold In-Tube test | High | High | High | Limited | | T-SPOT.TB test | High | High | High | Limited |Conclusion and Future Directions

What is the PPD TB skin test?
+The PPD TB skin test is a diagnostic test used to detect tuberculosis (TB) infection. The test involves injecting a small amount of purified protein derivative (PPD) tuberculin into the skin, which causes a localized reaction.
How is the PPD TB skin test administered?
+The PPD TB skin test is administered by a healthcare professional who injects a small amount of PPD tuberculin into the skin, usually on the forearm. The reaction is measured in millimeters, usually 48-72 hours after the injection.
What are the benefits and limitations of the PPD TB skin test?
+The PPD TB skin test has several benefits, including its simplicity, low cost, and high sensitivity. However, the test also has some limitations, including low specificity and the potential for false negative and false positive results.
